Page 96 - 2022-22-中国全科医学
P. 96
http://www.chinagp.net E-mail:zgqkyx@chinagp.net.cn ·2781·
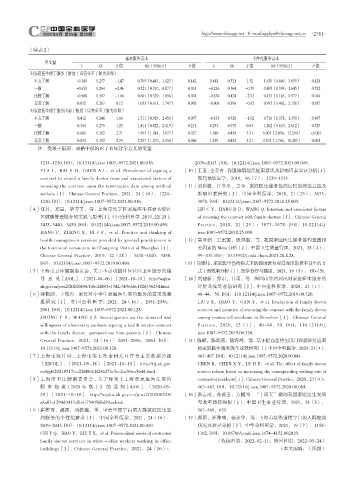
(续表 2)
基本服务需求 个性化服务需求
自变量
b SE Z 值 OR(95%CI) P 值 b SE Z 值 OR(95%CI) P 值
对家庭医生楼宇服务了解度(以完全不了解为参照)
不太了解 -0.349 0.237 -1.47 0.705(0.443,1.123) 0.142 0.488 0.321 1.52 1.630(0.869,3.059) 0.128
一般 -0.650 0.264 -2.46 0.521(0.310,0.877) 0.014 -0.216 0.364 -0.59 0.805(0.394,1.645) 0.552
比较了解 -0.508 0.307 -1.66 0.601(0.329,1.098) 0.098 -0.854 0.424 -2.02 0.425(0.185,0.977) 0.044
非常了解 0.032 0.267 0.12 1.033(0.611,1.747) 0.902 -0.006 0.390 -0.02 0.993(0.462,2.138) 0.987
对家庭医生楼宇服务内容了解度(以完全不了解为参照)
不太了解 0.412 0.248 1.66 1.511(0.929,2.459) 0.097 -0.333 0.326 -1.02 0.716(0.378,1.359) 0.307
一般 0.344 0.275 1.25 1.411(0.822,2.419) 0.211 0.233 0.370 0.63 1.262(0.610,2.612) 0.529
比较了解 0.689 0.312 2.21 1.993(1.081,3.677) 0.027 1.610 0.458 3.51 5.003(2.036,12.294) <0.001
非常了解 0.831 0.302 2.75 2.297(1.270,4.154) 0.006 1.459 0.454 3.21 4.302(1.766,10.483) 0.001
注:受限于版面,表格中仅给出了有统计学意义的变量
1224-1230. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.016. 2039-2043. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.049.
YI F L,BAI Y H,CHEN A L,et al. Prevalence of signing a [10]王玉,仝春冉 . 我国城镇居民健康意识及影响因素实证分析[J].
contract to attend a family doctor team and associated factors of 现代预防医学,2019,46(7):1229-1233.
renewing the contract upon the termination date among medical [11]刘彩茵,江冬冬,王全 . 家庭医生服务签约居民的续签意愿及
workers[J]. Chinese General Practice,2021,24(10):1224- 影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2018,21(25):3073-
1230. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.016. 3078. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2018.25.009.
[4]江萍,郑星,毕芳芳,等 . 上海市长宁区家庭医生探索功能社 LIU C Y,JIANG D D,WANG Q. Intention and associated factors
区健康管理服务的实践与思考[J]. 中国全科医学,2019,22(28): of renewing the contract with family doctors[J]. Chinese General
3438-3440,3450. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.490. Practice,2018,21(25):3073-3078. DOI:10.12114/j.
JIANG P,ZHENG X,BI F F,et al. Practice and thinking of issn.1007-9572.2018.25.009.
health management services provided by general practitioners in [12]高亚娟,王蜜源,张凤銮,等 . 我国家庭医生服务签约意愿相
the functional community in Changning District of Shanghai[J]. 关因素的 Meta 分析[J]. 中国卫生质量管理,2021,28(4):
Chinese General Practice,2019,22(28):3438-3440,3450. 99-103. DOI:10.13912/j.cnki.chqm.2021.28.4.28.
DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.490. [13]尚建伟 . 家庭医生签约模式下的健康教育对高血压患者不良生活方
[5]上海市卫生健康委员会 . 关于本市功能社区社区卫生服务的指 式干预效果分析[J]. 医学食疗与健康,2021,19(5):150-151.
导 意 见[A/OL]. (2021-04-06)[2021-10-10]. http://wsjkw. [14]刘建新,乔岩,甘勇,等 . 深圳市签约居民对家庭医生服务的
sh.gov.cn/jcws2/20210406/146c24803e1342c3b96b6b1824356234.html. 评价及续签意愿研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2020,23(1):
[6]钟艳熙,王俊舟 . 家长对小学生家庭医生签约服务的需求及意 40-44,50. DOI:110.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.320.
愿研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2021,24(16):2051-2056, LIU J X,QIAO Y,GAN Y,et al. Evaluation of family doctor
2061. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.128. services and intention of renewing the contract with the family doctor
ZHONG Y X,WANG J Z. Investigation on the demand and among contracted residents in Shenzhen[J]. Chinese General
willingness of elementary students signing a health service contract Practice,2020,23(1):40-44,50. DOI:110.12114/j.
with the family doctor:perspectives from parents[J]. Chinese issn.1007-9572.2019.00.320.
General Practice,2021,24(16):2051-2056,2061. DOI: [15]陈斌,陈晓燕,陆海峰,等 . 基于提高签约居民门诊就诊对应率
10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.128. 的家庭医生服务改革成效研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2020,23(4):
[7]上海市统计局 . 上海市第七次全国人口普查主要数据公报 463-467. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2020.00.084.
[EB/OL]. (2021-05-18)[2021-10-10]. http://tjj.sh.gov. CHEN B,CHEN X Y,LU H F,et al. The effect of family doctor
cn/tjgb/20210517/cc22f48611f24627bc5ee2ae96ca56d4.html. service reform based on increasing the corresponding visiting rate of
[8]上海市卫生健康委员会 . 关于印发《上海市家庭医生签约 contracted residents[J]. Chinese General Practice,2020,23(4):
服 务 规 范(2020 年 版 )》 的 通 知[A/OL]. (2020-05- 463-467. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2020.00.084.
29)[2021-10-10]. http://wsjkw.sh.gov.cn/jcws2/20200529/ [16]张志霞,孙骏玉,方鹏骞 . “十四五”期间我国家庭医生发展
a8a87c1294d9413a8b41754056bd59aa.html. 与改革路径探析[J]. 中国卫生事业管理,2021,38(8):
[9]崔雅琦,郝雨,刘铁鑫,等 . 中青年楼宇白领人群家庭医生签 567-569,635.
约服务的个性化需求[J]. 中国全科医学,2021,24(16): [17]郝雨,崔雅琦,杨永华,等 . 上海市某街道楼宇白领人群健康
2039-2043. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.049. 状况及差异分析[J]. 中华全科医学,2021,19(7):1158-
CUI Y Q,HAO Y,LIU T X,et al. Personalized needs of contracted 1162. DOI:10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.002010.
family doctor services in white-collar workers working in office (收稿日期:2022-02-11;修回日期:2022-05-24)
buildings[J]. Chinese General Practice,2021,24(16): (本文编辑:王凤微)