

Chinese General Practice ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (12): 1506-1512.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0134
• Original Research·Research Trends of Traditional Chinese Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2023-10-25
Revised:2024-02-20
Published:2025-04-20
Online:2025-02-06
Contact:
LIU Jian
通讯作者:
刘健
作者简介:作者贡献:
陈晓露、刘健参与了研究设计;陈晓露参与数据分析,撰写初稿并修订稿件;刘健负责监督管理项目,并负责手稿的修订。所有作者对最终稿件进行了审核并确认。
基金资助:
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0134
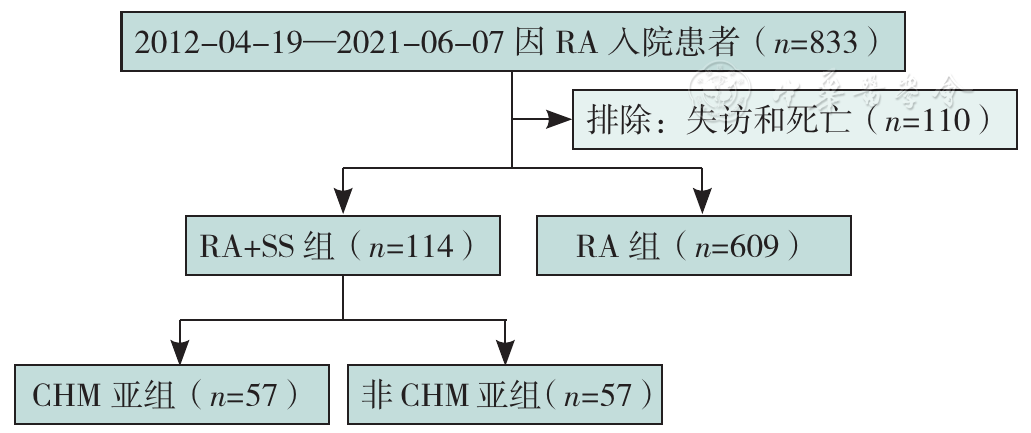
Figure 1 Flow chart of participant selection in the hospitol information system of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine (HIS System) database,2012-2021
| 特征 | RA组(n=609) | RA+SS组(n=114) | Z(χ2)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[例(%)] | 5.32a | 0.22 | ||
| 女 | 78(12.80) | 6(5.26) | ||
| 男 | 531(87.20) | 108(94.74) | ||
| 年龄[例(%)] | ||||
| 18~<45岁 | 42(6.90) | 6(56.26) | 0.67a | 0.46 |
| 45~60岁 | 244(40.07) | 50(43.86) | ||
| >60岁 | 323(53.03) | 58(50.88) | ||
| 合并疾病[例(%)] | ||||
| 糖尿病 | 134(22.00) | 21(6.30) | 1.89a | 0.17 |
| 高血压 | 168(27.58) | 32(25.20) | 0.30a | 0.58 |
| 骨关节炎 | 448(73.56) | 94(74.01) | 0.01a | 0.92 |
| 间质性肺炎 | 113(18.55) | 22(17.32) | 0.11a | 0.74 |
| 虹膜睫状体炎 | 1(0.16) | 0 | 0.21a | 0.65 |
| 肝功能不全 | 28(4.60) | 31(24.41) | 0.65a | <0.01 |
| 慢性肾功能不全 | 20(3.28) | 20(15.75) | 4.29a | <0.01 |
| 自身免疫性肝炎 | 3(0.49) | 7(5.51) | 28.49a | <0.01 |
| 基础用药[例(%)] | 462(75.86) | 100(78.74) | 0.48a | 0.49 |
| RFM[M(P25,P75),U/mL] | 73.00(18.45,196.05) | 111.60(31.60,259.00) | -2.69 | 0.01 |
| anti-CCP[M(P25,P75),U/mL] | 122.55(25.00,331.96) | 139.00(25.15,401.14) | -0.63 | 0.52 |
| SSA[例(%)] | 5(0.82) | 7(5.51) | 0.35a | <0.01 |
| SSB[例(%)] | 3(0.49) | 5(3.94) | 0.23a | 0.01 |
| 治疗天数[M(P25,P75),d] | 13(10,18) | 13(9,17) | -0.09 | 0.42 |
| 随访期[M(P25,P75),月] | 70(43,95) | 69(50,93) | -0.80 | 0.93 |
| 再发入院人数[例(%)] | 379(62.23) | 95(74.80) | 7.24a | <0.01 |
Table 1 Demographic characteristics of RA+SS and RA.
| 特征 | RA组(n=609) | RA+SS组(n=114) | Z(χ2)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[例(%)] | 5.32a | 0.22 | ||
| 女 | 78(12.80) | 6(5.26) | ||
| 男 | 531(87.20) | 108(94.74) | ||
| 年龄[例(%)] | ||||
| 18~<45岁 | 42(6.90) | 6(56.26) | 0.67a | 0.46 |
| 45~60岁 | 244(40.07) | 50(43.86) | ||
| >60岁 | 323(53.03) | 58(50.88) | ||
| 合并疾病[例(%)] | ||||
| 糖尿病 | 134(22.00) | 21(6.30) | 1.89a | 0.17 |
| 高血压 | 168(27.58) | 32(25.20) | 0.30a | 0.58 |
| 骨关节炎 | 448(73.56) | 94(74.01) | 0.01a | 0.92 |
| 间质性肺炎 | 113(18.55) | 22(17.32) | 0.11a | 0.74 |
| 虹膜睫状体炎 | 1(0.16) | 0 | 0.21a | 0.65 |
| 肝功能不全 | 28(4.60) | 31(24.41) | 0.65a | <0.01 |
| 慢性肾功能不全 | 20(3.28) | 20(15.75) | 4.29a | <0.01 |
| 自身免疫性肝炎 | 3(0.49) | 7(5.51) | 28.49a | <0.01 |
| 基础用药[例(%)] | 462(75.86) | 100(78.74) | 0.48a | 0.49 |
| RFM[M(P25,P75),U/mL] | 73.00(18.45,196.05) | 111.60(31.60,259.00) | -2.69 | 0.01 |
| anti-CCP[M(P25,P75),U/mL] | 122.55(25.00,331.96) | 139.00(25.15,401.14) | -0.63 | 0.52 |
| SSA[例(%)] | 5(0.82) | 7(5.51) | 0.35a | <0.01 |
| SSB[例(%)] | 3(0.49) | 5(3.94) | 0.23a | 0.01 |
| 治疗天数[M(P25,P75),d] | 13(10,18) | 13(9,17) | -0.09 | 0.42 |
| 随访期[M(P25,P75),月] | 70(43,95) | 69(50,93) | -0.80 | 0.93 |
| 再发入院人数[例(%)] | 379(62.23) | 95(74.80) | 7.24a | <0.01 |
| 变量 | CHM亚组(n=57) | 非CHM亚组(n=57) | χ2(Z)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(男/女) | 4/53 | 7/50 | 0.906 | 0.341 |
| 年龄[例(%)] | ||||
| 18~<45岁 | 3(5.26) | 3(5.26) | 0 | 1.00 |
| 45~60岁 | 28(49.12) | 22(39.28) | 1.283 | 0.257 |
| >60~91岁 | 26(45.61) | 31(55.35) | 0.877 | 0.339 |
| 合并疾病[例(%)] | ||||
| 糖尿病 | 9(15.79) | 10(17.85) | 0.063 | 0.802 |
| 高血压 | 16(28.07) | 16(28.07) | 0 | 1.000 |
| 间质性肺炎 | 8(14.03) | 10(17.50) | 0.264 | 0.607 |
| 骨关节炎 | 45(78.94) | 46(80.7) | 0.054 | 0.815 |
| 肝功能不全 | 3(5.26) | 4(7.01) | 0.152 | 0.696 |
| 自身免疫性肝炎 | 4(7.01) | 4(7.01) | 0 | 1.000 |
| 基础用药[例(%)] | 47(82.45) | 44(78.57) | 0.490 | 0.484 |
| RF[M(P25,P75),U/mL] | 122.20(30.50,241.60) | 93.10(29.17,305.65) | -0.320a | 0.850 |
| anti-CCP[M(P25,P75),U/mL] | 217.41(31.18,480.99) | 102.19(25.00,345.48) | -0.450a | 0.180 |
| SSA[例(%)] | 2(3.51) | 4(7.01) | 0.704 | 0.402 |
| SSB[例(%)] | 2(3.51) | 2(3.51) | 0 | 1.000 |
| 治疗天数[M(P25,P75),d] | 13.00(9.00,17.00) | 14.00(9.25,17.75) | -0.120a | 0.840 |
| 随访期[M(P25,P75),m] | 66.00(50.00,90.50) | 70.00(51.00,92.25) | -0.960a | 0.990 |
Table 2 Comparison of baseline data between CHM and non-CHM
| 变量 | CHM亚组(n=57) | 非CHM亚组(n=57) | χ2(Z)值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(男/女) | 4/53 | 7/50 | 0.906 | 0.341 |
| 年龄[例(%)] | ||||
| 18~<45岁 | 3(5.26) | 3(5.26) | 0 | 1.00 |
| 45~60岁 | 28(49.12) | 22(39.28) | 1.283 | 0.257 |
| >60~91岁 | 26(45.61) | 31(55.35) | 0.877 | 0.339 |
| 合并疾病[例(%)] | ||||
| 糖尿病 | 9(15.79) | 10(17.85) | 0.063 | 0.802 |
| 高血压 | 16(28.07) | 16(28.07) | 0 | 1.000 |
| 间质性肺炎 | 8(14.03) | 10(17.50) | 0.264 | 0.607 |
| 骨关节炎 | 45(78.94) | 46(80.7) | 0.054 | 0.815 |
| 肝功能不全 | 3(5.26) | 4(7.01) | 0.152 | 0.696 |
| 自身免疫性肝炎 | 4(7.01) | 4(7.01) | 0 | 1.000 |
| 基础用药[例(%)] | 47(82.45) | 44(78.57) | 0.490 | 0.484 |
| RF[M(P25,P75),U/mL] | 122.20(30.50,241.60) | 93.10(29.17,305.65) | -0.320a | 0.850 |
| anti-CCP[M(P25,P75),U/mL] | 217.41(31.18,480.99) | 102.19(25.00,345.48) | -0.450a | 0.180 |
| SSA[例(%)] | 2(3.51) | 4(7.01) | 0.704 | 0.402 |
| SSB[例(%)] | 2(3.51) | 2(3.51) | 0 | 1.000 |
| 治疗天数[M(P25,P75),d] | 13.00(9.00,17.00) | 14.00(9.25,17.75) | -0.120a | 0.840 |
| 随访期[M(P25,P75),m] | 66.00(50.00,90.50) | 70.00(51.00,92.25) | -0.960a | 0.990 |
| 变量 | B | SE | Waldχ2值 | P值 | HR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHM | -0.80 | 0.24 | 11.61 | 0.001* | 0.45(0.28~0.71) |
| 性别(女) | -0.65 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 0.36 | 0.52(0.13~2.11) |
| 年龄(>60岁) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.81 | 0.28 | 1.02(0.98~1.05) |
| 合并疾病 | |||||
| 糖尿病 | -0.22 | 0.57 | 0.15 | 0.69 | 0.80(0.26~2.46) |
| 高血压 | 0.48 | 0.28 | 2.95 | 0.08 | 1.62(0.93~2.81) |
| 骨关节炎 | -0.68 | 0.37 | 3.48 | 0.06 | 0.50(0.24~1.03) |
| 间质性肺炎 | 0.36 | 0.56 | 0.41 | 0.52 | 1.43(0.47~4.35) |
| 肝功能不全 | -0.73 | 0.73 | 1.02 | 0.31 | 0.48(0.11~2.00) |
| 自身免疫性肝炎 | 0.67 | 0.84 | 0.64 | 0.42 | 1.96(0.37~10.23) |
| 基础用药 | 0.19 | 0.35 | 0.31 | 0.57 | 1.21(0.61~2.40) |
| RF>20 U/mL | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.69 | 0.40 | 1.00(0.99~1.00) |
| anti-CCP | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 0.56 | 1.00(0.99~1.00) |
| SSA阳性 | 0.87 | 0.82 | 1.13 | 0.28 | 2.39(0.48~11.93) |
| SSB阳性 | -1.10 | 1.30 | 0.72 | 0.39 | 0.33(0.02~4.22) |
Table 3 Cox proportional risk model analysis of readmission factors in patients with RA+SS
| 变量 | B | SE | Waldχ2值 | P值 | HR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHM | -0.80 | 0.24 | 11.61 | 0.001* | 0.45(0.28~0.71) |
| 性别(女) | -0.65 | 0.71 | 0.83 | 0.36 | 0.52(0.13~2.11) |
| 年龄(>60岁) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.81 | 0.28 | 1.02(0.98~1.05) |
| 合并疾病 | |||||
| 糖尿病 | -0.22 | 0.57 | 0.15 | 0.69 | 0.80(0.26~2.46) |
| 高血压 | 0.48 | 0.28 | 2.95 | 0.08 | 1.62(0.93~2.81) |
| 骨关节炎 | -0.68 | 0.37 | 3.48 | 0.06 | 0.50(0.24~1.03) |
| 间质性肺炎 | 0.36 | 0.56 | 0.41 | 0.52 | 1.43(0.47~4.35) |
| 肝功能不全 | -0.73 | 0.73 | 1.02 | 0.31 | 0.48(0.11~2.00) |
| 自身免疫性肝炎 | 0.67 | 0.84 | 0.64 | 0.42 | 1.96(0.37~10.23) |
| 基础用药 | 0.19 | 0.35 | 0.31 | 0.57 | 1.21(0.61~2.40) |
| RF>20 U/mL | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.69 | 0.40 | 1.00(0.99~1.00) |
| anti-CCP | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 0.56 | 1.00(0.99~1.00) |
| SSA阳性 | 0.87 | 0.82 | 1.13 | 0.28 | 2.39(0.48~11.93) |
| SSB阳性 | -1.10 | 1.30 | 0.72 | 0.39 | 0.33(0.02~4.22) |
| 分类 | 中药名称 | 频次 | 频率(%) | 性味 | 归经 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 活血通经药 | 红花 | 30 | 56.60 | 辛、温 | 心、肝 |
| 桃仁 | 27 | 50.94 | 苦、甘、平 | 心、肝、大肠 | |
| 郁金 | 23 | 43.39 | 辛、苦、寒 | 肝、胆、心 | |
| 丹参 | 39 | 73.58 | 苦、寒 | 心、肝 | |
| 祛湿通络止痛药 | 鸡血藤 | 17 | 32.07 | 苦、温 | 肝、肾 |
| 威灵仙 | 23 | 43.39 | 辛、咸、温 | 膀、胱 | |
| 豨签草 | 26 | 49.06 | 辛、苦、寒 | 肝、肾 | |
| 杜仲 | 16 | 30.19 | 甘、苦、温 | 脾、肾 | |
| 益气健脾药 | 茯苓 | 36 | 67.92 | 甘、淡、平 | 心、脾、肾 |
| 陈皮 | 40 | 75.47 | 辛、苦、温 | 脾、肺 | |
| 山药 | 37 | 69.81 | 甘、平 | 脾、肺、肾 | |
| 姜半夏 | 19 | 35.85 | 辛、温 | 脾、胃、肺 | |
| 薏苡仁 | 38 | 71.70 | 甘、淡、凉 | 脾、胃、肺 | |
| 甘草 | 37 | 69.81 | 甘、平 | 心、脾、肺、胃 | |
| 黄芪 | 16 | 30.19 | 甘、温 | 脾、肺 | |
| 谷芽 | 18 | 33.96 | 甘、平 | 脾、胃 | |
| 麦芽 | 21 | 39.62 | 甘、平 | 脾、胃 | |
| 清热解毒利湿药 | 蒲公英 | 33 | 62.26 | 苦、甘、寒 | 肝、胃 |
| 白花蛇舌草 | 18 | 33.96 | 甘、淡、凉 | 胃、大肠、小肠 | |
| 泽泻 | 18 | 33.96 | 甘、淡、寒 | 肾、膀胱 |
Table 4 The top 20 frequency of using CHM in the successfully matched patients with RA+SS
| 分类 | 中药名称 | 频次 | 频率(%) | 性味 | 归经 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 活血通经药 | 红花 | 30 | 56.60 | 辛、温 | 心、肝 |
| 桃仁 | 27 | 50.94 | 苦、甘、平 | 心、肝、大肠 | |
| 郁金 | 23 | 43.39 | 辛、苦、寒 | 肝、胆、心 | |
| 丹参 | 39 | 73.58 | 苦、寒 | 心、肝 | |
| 祛湿通络止痛药 | 鸡血藤 | 17 | 32.07 | 苦、温 | 肝、肾 |
| 威灵仙 | 23 | 43.39 | 辛、咸、温 | 膀、胱 | |
| 豨签草 | 26 | 49.06 | 辛、苦、寒 | 肝、肾 | |
| 杜仲 | 16 | 30.19 | 甘、苦、温 | 脾、肾 | |
| 益气健脾药 | 茯苓 | 36 | 67.92 | 甘、淡、平 | 心、脾、肾 |
| 陈皮 | 40 | 75.47 | 辛、苦、温 | 脾、肺 | |
| 山药 | 37 | 69.81 | 甘、平 | 脾、肺、肾 | |
| 姜半夏 | 19 | 35.85 | 辛、温 | 脾、胃、肺 | |
| 薏苡仁 | 38 | 71.70 | 甘、淡、凉 | 脾、胃、肺 | |
| 甘草 | 37 | 69.81 | 甘、平 | 心、脾、肺、胃 | |
| 黄芪 | 16 | 30.19 | 甘、温 | 脾、肺 | |
| 谷芽 | 18 | 33.96 | 甘、平 | 脾、胃 | |
| 麦芽 | 21 | 39.62 | 甘、平 | 脾、胃 | |
| 清热解毒利湿药 | 蒲公英 | 33 | 62.26 | 苦、甘、寒 | 肝、胃 |
| 白花蛇舌草 | 18 | 33.96 | 甘、淡、凉 | 胃、大肠、小肠 | |
| 泽泻 | 18 | 33.96 | 甘、淡、寒 | 肾、膀胱 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
张博纶,高明利. 高明利益气养阴通络法治疗类风湿关节炎继发干燥综合征经验[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2020,47(12):51-54. DOI:10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2020.12.013.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] | |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
干敏芝,俞金金,邓媛. 雷公藤多苷联合白芍总苷治疗干燥综合征的临床效果观察及对血清ACL、RF的影响[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2022,40(2):94-96. DOI:10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2022.02.021.
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
邱杰慧,张伦. 老年消化性溃疡的中医证素与危险因素的相关性分析[J]. 广州中医药大学学报,2022,39(10):2238-2243. DOI:10.13359/j.cnki.gzxbtcm.2022.10.004.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
傅天啸,李天一,吴方平,等. 基于NF-κB P65/IκBα信号通路探讨养阴益气活血方治疗干燥综合征作用机制[J/OL]. (2022-08-24)[2023-02-10].中国中西医结合杂志,2022:1-6.
|
| [39] |
常岑,张润润,时一鸣,等. 中医疗法治疗类风湿性关节炎的研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志,2023,48(2):329-335. DOI:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220922.502.
|
| [1] | YANG Sen, ZHAO Huaxin, GE Xuhua, MA Le, JIN Hua, XIE Mujin, PU Zhen, BAI Zhaohui, YU Dehua. Impact of an Integrated Hospital-community-patient Chronic Disease Management Pathway on Postoperative Colorectal Cancer Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(22): 2724-2730. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||