

Chinese General Practice ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (12): 1465-1472.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0484
• Original Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2024-03-27
Revised:2024-08-18
Published:2025-04-20
Online:2025-02-06
Contact:
FU Chun
通讯作者:
符淳
作者简介:作者贡献:
袁晓瑞负责撰写论文、影像特征提取、数据分析;谭延林负责PET-CT影像评估及肿瘤分割;符淳负责文章的质量控制,对文章整体负责。
基金资助:CLC Number:
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0484
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄[M(QR),岁] | 血型[例(%)] | FIGO分期[例(%)] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A型 | B型 | O型 | AB型 | Ⅰ期 | Ⅱ期 | Ⅲ期 | Ⅳ期 | |||
| 淋巴结转移组 | 65 | 55.2(8.8) | 18(27.7) | 15(23.1) | 26(40.0) | 6(9.2) | 1(1.5) | 3(4.6) | 45(69.2) | 16(24.6) |
| 非淋巴结转移组 | 33 | 54.9(8.9) | 10(30.3) | 9(27.3) | 7(21.2) | 7(21.2) | 3(9.1) | 5(15.2) | 20(60.6) | 5(15.2) |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.150a | 4.870b | — | |||||||
| P值 | 0.884 | 0.181 | 0.071 | |||||||
| 组别 | CA125[例(%)] | HE4[例(%)] | 病理类型[例(%)] | |||||||
| <743 U/mL | ≥743 U/mL | <343 pmol/L | ≥343 pmol/L | 浆液性囊腺癌 | 子宫内膜样癌 | 黏液性囊腺癌 | 透明细胞癌 | |||
| 淋巴结转移组 | 27(41.5) | 38(58.5) | 6(9.2) | 59(90.8) | 61(93.8) | 2(3.1) | 1(1.5) | 1(1.5) | ||
| 非淋巴结转移组 | 18(54.5) | 15(45.5) | 11(33.3) | 22(66.7) | 28(84.8) | 3(9.1) | 1(3.0) | 1(3.0) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | 1.490b | — | — | |||||||
| P值 | 0.222 | 0.003 | 0.372 | |||||||
| 组别 | 病理分级[例(%)] | 原发灶位置[例(%)] | 腹腔积液细胞学检查结果[例(%)] | 淋巴细胞计数[M(QR),×109/L] | 淋巴细胞分数[M(QR),%] | SUVmax[M(QR)] | ||||
| 中分化 | 低分化 | 高分化 | 单侧 | 双侧 | 阴性 | 阳性 | ||||
| 淋巴结转移组 | 4(6.2) | 59(90.8) | 2(3.1) | 16(24.6) | 49(75.4) | 12(41.4) | 17(58.6) | 1.1(0.6) | 19.8(7.1) | 15.0(8.0) |
| 非淋巴结转移组 | 2(6.1) | 27(81.8) | 4(12.1) | 16(48.5) | 17(51.5) | 5(33.3) | 10(66.7) | 1.3(0.5) | 21.3(7.4) | 12.7(7.9) |
| 检验统计量值 | — | 5.670b | 0.270b | 1 263.000a | 0.910a | 886.500a | ||||
| P值 | 0.319 | 0.017 | 0.603 | 0.153 | 0.363 | 0.163 | ||||
Table 1 Comparison of clinical features between epithelial ovarian cancer patients with or without lymph node metastasis
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄[M(QR),岁] | 血型[例(%)] | FIGO分期[例(%)] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A型 | B型 | O型 | AB型 | Ⅰ期 | Ⅱ期 | Ⅲ期 | Ⅳ期 | |||
| 淋巴结转移组 | 65 | 55.2(8.8) | 18(27.7) | 15(23.1) | 26(40.0) | 6(9.2) | 1(1.5) | 3(4.6) | 45(69.2) | 16(24.6) |
| 非淋巴结转移组 | 33 | 54.9(8.9) | 10(30.3) | 9(27.3) | 7(21.2) | 7(21.2) | 3(9.1) | 5(15.2) | 20(60.6) | 5(15.2) |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.150a | 4.870b | — | |||||||
| P值 | 0.884 | 0.181 | 0.071 | |||||||
| 组别 | CA125[例(%)] | HE4[例(%)] | 病理类型[例(%)] | |||||||
| <743 U/mL | ≥743 U/mL | <343 pmol/L | ≥343 pmol/L | 浆液性囊腺癌 | 子宫内膜样癌 | 黏液性囊腺癌 | 透明细胞癌 | |||
| 淋巴结转移组 | 27(41.5) | 38(58.5) | 6(9.2) | 59(90.8) | 61(93.8) | 2(3.1) | 1(1.5) | 1(1.5) | ||
| 非淋巴结转移组 | 18(54.5) | 15(45.5) | 11(33.3) | 22(66.7) | 28(84.8) | 3(9.1) | 1(3.0) | 1(3.0) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | 1.490b | — | — | |||||||
| P值 | 0.222 | 0.003 | 0.372 | |||||||
| 组别 | 病理分级[例(%)] | 原发灶位置[例(%)] | 腹腔积液细胞学检查结果[例(%)] | 淋巴细胞计数[M(QR),×109/L] | 淋巴细胞分数[M(QR),%] | SUVmax[M(QR)] | ||||
| 中分化 | 低分化 | 高分化 | 单侧 | 双侧 | 阴性 | 阳性 | ||||
| 淋巴结转移组 | 4(6.2) | 59(90.8) | 2(3.1) | 16(24.6) | 49(75.4) | 12(41.4) | 17(58.6) | 1.1(0.6) | 19.8(7.1) | 15.0(8.0) |
| 非淋巴结转移组 | 2(6.1) | 27(81.8) | 4(12.1) | 16(48.5) | 17(51.5) | 5(33.3) | 10(66.7) | 1.3(0.5) | 21.3(7.4) | 12.7(7.9) |
| 检验统计量值 | — | 5.670b | 0.270b | 1 263.000a | 0.910a | 886.500a | ||||
| P值 | 0.319 | 0.017 | 0.603 | 0.153 | 0.363 | 0.163 | ||||
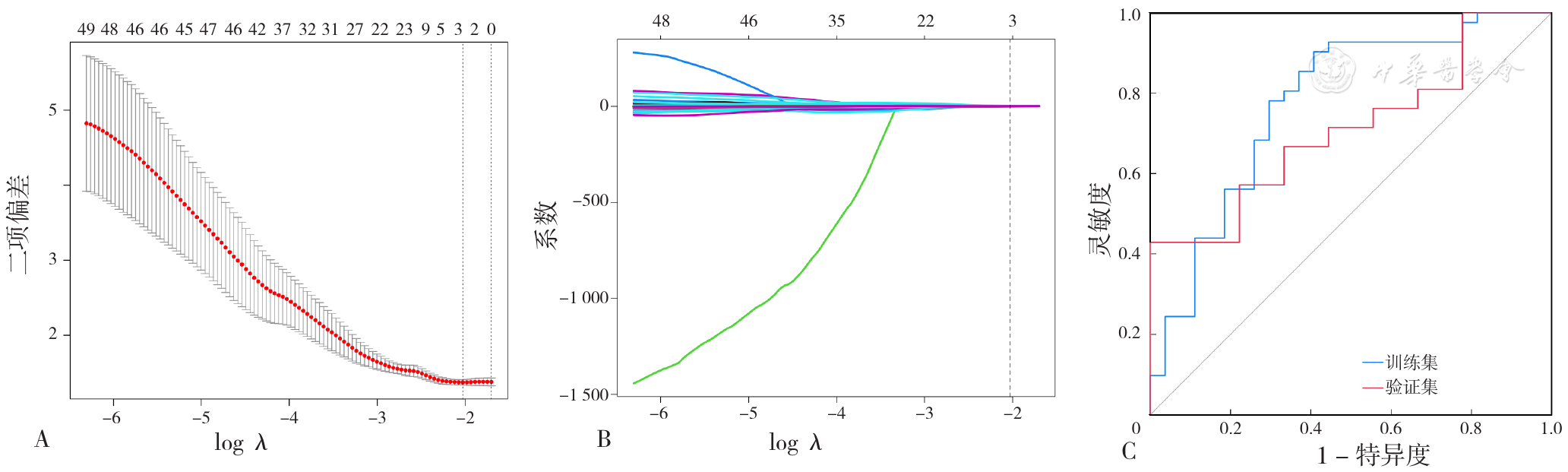
Figure 3 The selection of radiomics features and their ROC curve for predicting lymph node metastasis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer in the training set and validation set
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE4 | 1.528 | 0.608 | 2.513 | 0.012 | 4.61(1.40~15.18) |
| 原发灶位置 | 1.651 | 0.489 | 3.376 | <0.001 | 5.21(2.00~13.60) |
Table 2 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis for influencing factors of lymph node metastasis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer(clinical predictive model)
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE4 | 1.528 | 0.608 | 2.513 | 0.012 | 4.61(1.40~15.18) |
| 原发灶位置 | 1.651 | 0.489 | 3.376 | <0.001 | 5.21(2.00~13.60) |
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE4 | 1.905 | 0.698 | 2.728 | 0.006 | 6.72(1.71~26.40) |
| 原发灶位置 | 0.772 | 0.518 | 1.491 | 0.019 | 2.88(1.19~6.99) |
| Radscore | 3.400 | 1.088 | 3.125 | 0.002 | 12.12(1.21~121.69) |
Table 3 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis for influencing factors of lymph node metastasis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer(combined predictive model)
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HE4 | 1.905 | 0.698 | 2.728 | 0.006 | 6.72(1.71~26.40) |
| 原发灶位置 | 0.772 | 0.518 | 1.491 | 0.019 | 2.88(1.19~6.99) |
| Radscore | 3.400 | 1.088 | 3.125 | 0.002 | 12.12(1.21~121.69) |
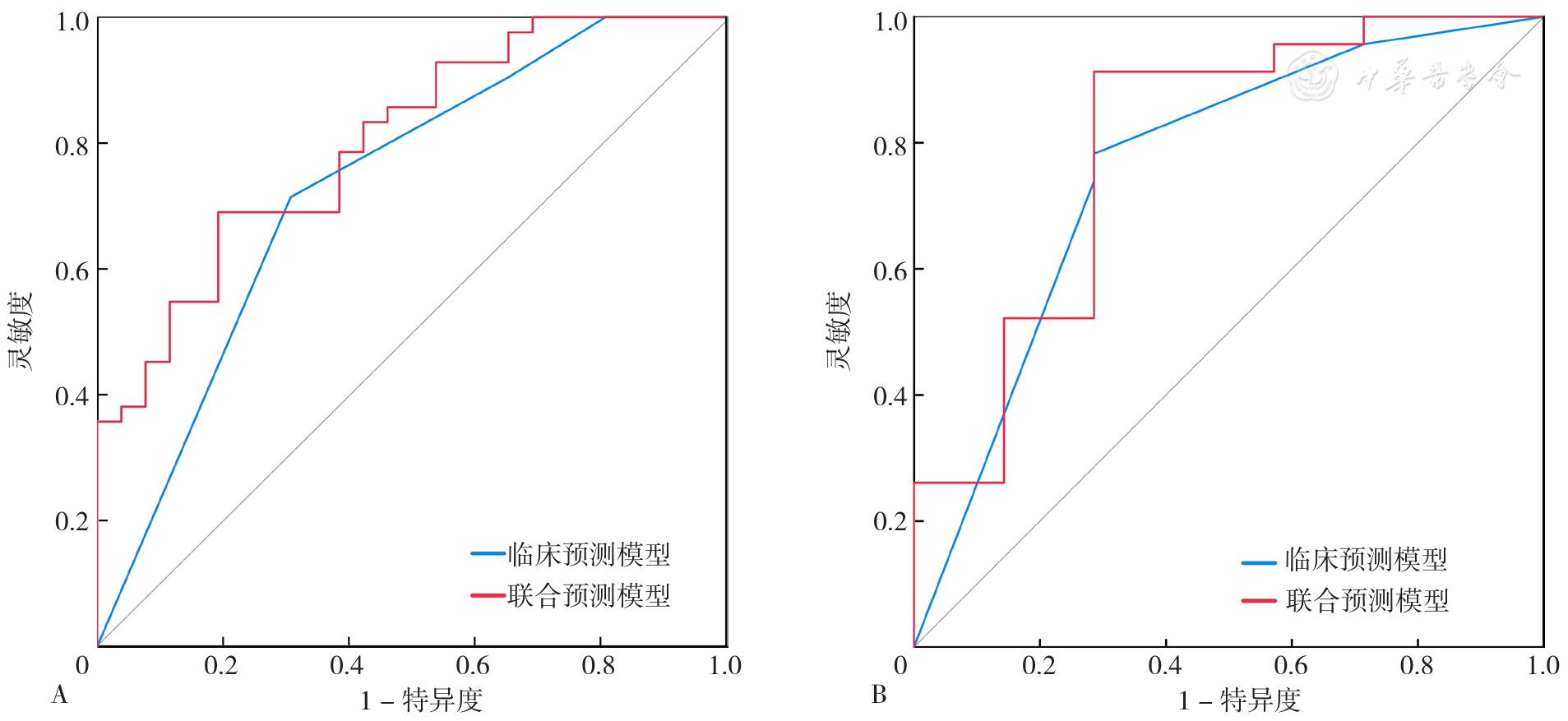
Figure 5 ROC curves of clinical and combined predictive model for predicting lymph node metastasis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer in the training set and validation set
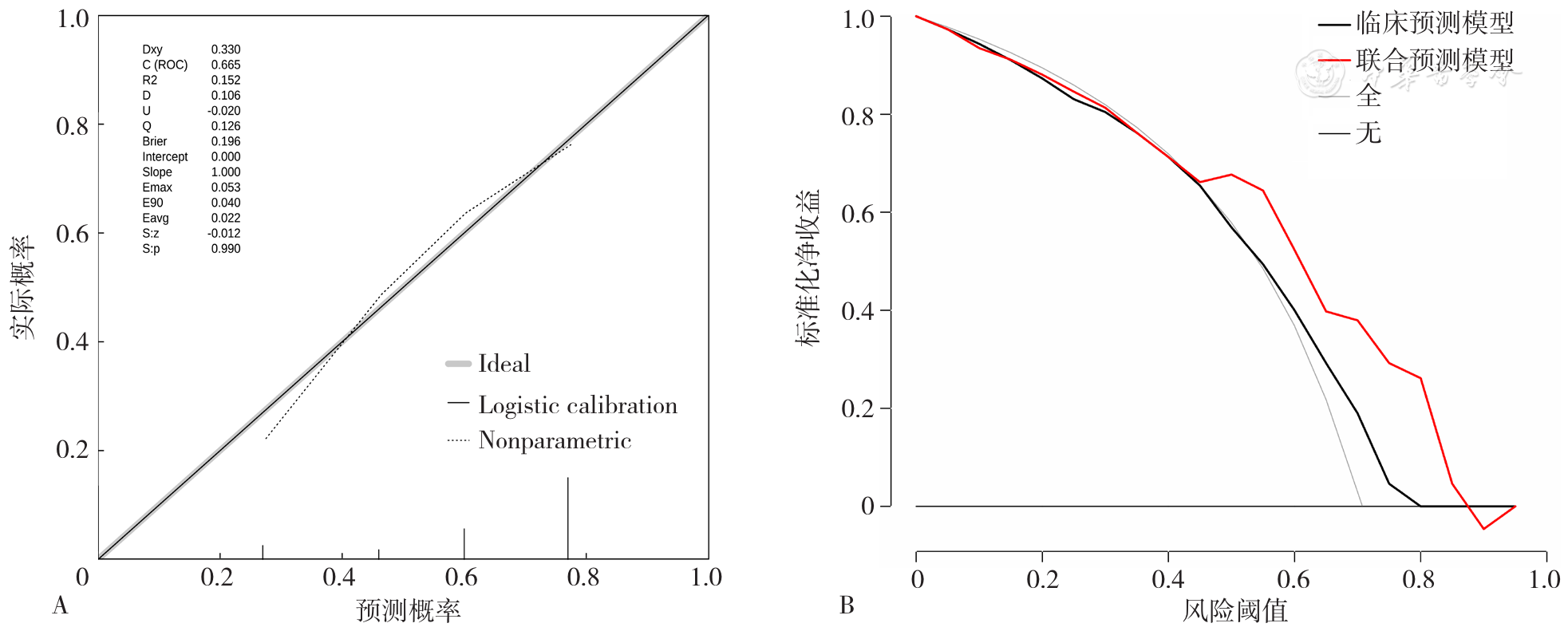
Figure 6 Calibration curve and DCA of clinical and combined predictive model for predicting lymph node metastasis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
姜秋红,程能能,高惠君. ER、PR、CA125、Ki67及P53的表达对上皮性卵巢癌化疗敏感性的预测作用[J]. 中国临床药学杂志,2012,21(6):354-358. DOI:10.19577/j.cnki.issn10074406.2012.06.006.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
赵晓娟,魏珂. 术前血清CA125和HE4水平预测卵巢上皮性癌患者淋巴结转移的应用价值[J]. 解放军医药杂志,2018,30(6):25-28. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-140X.2018.06.007.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [1] | Gynecological Oncology Group of the Oncology Department of Capital Medical University. Expert Consensus on Management of Common Gynecological Malignancies Combining General Practice and Specialist [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(08): 911-922. |
| [2] | ZHAO Li, YANG Chunyan, ZUO Manyun, YANG Hongmei. Short-term Effects of Opportunistic Salpingectomy on Ovarian Reserve: a Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Based on GRADE Evidence Grading System [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(09): 1142-1148. |
| [3] | JI Mengying, LI Yujing, CHEN Xing, DAI Huihua, SUN Ying. Prediction Value of B-ultrasound with Tumor Markers for Malignant Transformation of Mucinous Ovarian Tumors [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(24): 3022-3027. |
| [4] |
HUANG Haitao, CHEN Shuyu, GENG Xu, WAN Xiao, JIA Ruiying, LIANG Dandan, CHEN Chaoran.
Ovarian Cancer in China:Trends in Incidence and Mortality,2005—2016 [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(08): 990-994. |
| [5] |
ZHANG Xiaomei, KANG Yanfei, SANG Tian, CHENG Jing, LI Qiaoli, CAO Yuwen, MA Jinmei, SHI Linan, LI Wenxiao, LI Jun.
Predictive Value of Combined Use of Ultrasonographic Indicators for Central Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(03): 305-311. |
| [6] | FU Yang,XIA Ji,HAN Fengjuan. Effects of Active Components of Lichong Shengsuiyin on Regulating Genes of Ovarian Cancer Stem Cells and Cisplatin Resistance and Its Mechanism [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2019, 22(9): 1078-1083. |
| [7] | MENG Xin,GUO Hong,WANG Li,ZHOU Jian,ZHAO Wenjing,SUI Xuefeng,CUI Hongsheng,XU Jinzhi. Metabolic Parameters Measured by 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging Predict the Prognosis of Small Cell Lung Cancer [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2019, 22(2): 173-179. |
| [8] | . Clinical Analysis of Androgen-secreting Tumors in Women [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2018, 21(35): 4383-4387. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||