

Chinese General Practice ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (15): 1811-1816.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0821
• Monographic Research of Inpatient Glucose Menitoring • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2022-09-12
Revised:2022-12-21
Published:2023-05-20
Online:2022-12-30
Contact:
CHEN Xiangjun
通讯作者:
陈相军
作者简介:基金资助:
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0821
| 目的 | 负责部门 | 工作内容 |
|---|---|---|
| 建立管理制度 | 医务部、护理部 | 1.医务部牵头开展血糖管理项目,协调工作推进 |
| 2.制订管理制度,开展监测、评估和考核 | ||
| 制订诊疗规范 | 内分泌科 | 1.内分泌科制订血糖管理诊疗方案,对院内高血糖患者进行主动管理,评估患者病情,持续监测疗效 |
| 开发血糖管理系统 | 信息中心、内分泌科、医务部 | 1.信息中心依据临床科室需求开发血糖管理系统 |
| 2.在系统运行后台持续优化改进 | ||
| 3.建立血糖管理工作监测数据报表 | ||
| 血糖监测数据信息化 | 信息中心、实验医学科、护理部、医务部 | 1.设备部、护理部更新血糖监测设备统一为蓝牙血糖监测仪,并对各科室进行操作使用培训 |
| 2.内分泌科与实验医学科共同开展血糖监测仪准确度验证试验,并定期进行监测数据质控 | ||
| 3.信息中心建立住院患者血糖监测数据平台,建立血糖管理系统、医院信息系统连接 | ||
| 开展血糖管理宣传培训 | 医务部、护理部、内分泌科、临床科室(非内分泌科) | 1.医务部、内分泌科组织血糖管理宣传周活动 |
| 2.对临床科室医护人员(非内分泌科)进行院内血糖管理培训 | ||
| 提供绩效保障 | 运管部、医务部、内分泌科 | 1.设立血糖管理专职岗,由内分泌科安排高级职称医师参与血糖管理工作 |
| 2.医务部监测统计内分泌科医师管理工作数量与质量 | ||
| 3.运管部门依据医师工作开展情况进行考核绩效 |
Table 1 The blood glucose management services undertaken by various departments
| 目的 | 负责部门 | 工作内容 |
|---|---|---|
| 建立管理制度 | 医务部、护理部 | 1.医务部牵头开展血糖管理项目,协调工作推进 |
| 2.制订管理制度,开展监测、评估和考核 | ||
| 制订诊疗规范 | 内分泌科 | 1.内分泌科制订血糖管理诊疗方案,对院内高血糖患者进行主动管理,评估患者病情,持续监测疗效 |
| 开发血糖管理系统 | 信息中心、内分泌科、医务部 | 1.信息中心依据临床科室需求开发血糖管理系统 |
| 2.在系统运行后台持续优化改进 | ||
| 3.建立血糖管理工作监测数据报表 | ||
| 血糖监测数据信息化 | 信息中心、实验医学科、护理部、医务部 | 1.设备部、护理部更新血糖监测设备统一为蓝牙血糖监测仪,并对各科室进行操作使用培训 |
| 2.内分泌科与实验医学科共同开展血糖监测仪准确度验证试验,并定期进行监测数据质控 | ||
| 3.信息中心建立住院患者血糖监测数据平台,建立血糖管理系统、医院信息系统连接 | ||
| 开展血糖管理宣传培训 | 医务部、护理部、内分泌科、临床科室(非内分泌科) | 1.医务部、内分泌科组织血糖管理宣传周活动 |
| 2.对临床科室医护人员(非内分泌科)进行院内血糖管理培训 | ||
| 提供绩效保障 | 运管部、医务部、内分泌科 | 1.设立血糖管理专职岗,由内分泌科安排高级职称医师参与血糖管理工作 |
| 2.医务部监测统计内分泌科医师管理工作数量与质量 | ||
| 3.运管部门依据医师工作开展情况进行考核绩效 |
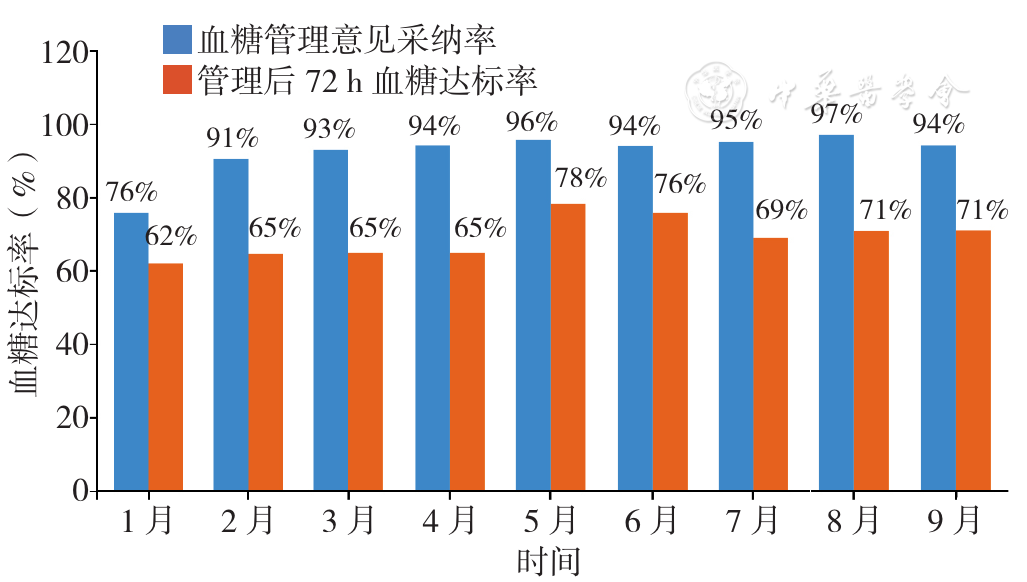
Figure 4 The rate of accepting the glycemic management opinion using the PDCA cycle and rate of achieving the target blood glucose level after 72-hour administration in clinical departments of West China Hospital,Sichuan University from January to September 2022
| [1] |
The International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas 2021 [EB/OL].(2021-12-06) [2021-12-19].
|
| [2] |
陈平,杨国庆,窦京涛,等. 住院患者2型糖尿病患病率、病死率及风险分析[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2013,5(6):332-337. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-5809.2013.06.004.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
伍羿,王德宇,赵祥庚. 急诊多发伤患者血糖变化与院内死亡率的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2019,22(29):3623-3626. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.081.
|
| [6] |
宋比佳,常媛媛,李诗怡,等. 围术期血糖变化与术后病死率关系的研究进展[J]. 中国实验诊断学,2018,22(1):167-170. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2018.01.063.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
王铭,奚志,孟启哲,等. 血糖变异性和葡萄糖目标范围内时间与急性缺血性脑卒中合并糖尿病患者早期神经功能恶化的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2022,25(12):1418-1423. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.133.
|
| [9] | |
| [10] |
蒋薇,肖倩蓉,沈洁,等. 信息整合化院内血糖管理模式的临床应用现状[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志,2016,24(12):1123-1125. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6187.2016.12.015.
|
| [11] |
中国医师协会内分泌代谢科医师分会,中国住院患者血糖管理专家组. 中国住院患者血糖管理专家共识[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志,2017,33(1):1-10. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.2017.01.001.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
李小红,刘敏. PDCA循环护理干预在2型糖尿病患者中的研究[J]. 中国继续医学教育,2020,12(9):193-195. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-9308.2020.09.081.
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
董璐,王煜非. 智慧转型升级下的医院内血糖管理实践与思考[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2022,14(2):115-119. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn115791-20211225-00691.
|
| [17] |
朱颖,杨淼,周卉,等. 团队模式院内血糖管理联合网络血糖监测系统对胃肠外科高血糖患者血糖控制状况的影响[J]. 实用医院临床杂志,2020,17(2):130-133. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6170.2020.02.039.
|
| [18] |
熊真真,袁丽,贺莉,等. 大型综合医院血糖管理团队对非内分泌科血糖异常住院患者血糖控制的效果研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2015,18(4):443-445. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2015.04.022.
|
| [19] |
李蓓,赵雪,王丽萍,等. 非内分泌专科住院2型糖尿病患者血糖管理现状调查[J]. 护理学杂志,2016,31(21):43-44,47. DOI:10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2016.21.043.
|
| [20] |
周卉,朱颖,杨淼,等. 团队模式信息化院内血糖联网监测和标准化血糖管理对外科重症监护室患者血糖控制情况的影响[J]. 实用医院临床杂志,2020,17(4):5-8. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6170.2020.04.002.
|
| [21] |
王莉,付阿丹,易兰,等. "互联网+"糖尿病健康管理站在2型糖尿病患者管理中的应用[J]. 中国全科医学,2019,22(15):1836-1841. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.004.
|
| [22] |
《关于推动公立医院高质量发展的意见》政策解读[EB/OL].(2021-06-04)[2022-05-19].
|
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||