

Chinese General Practice ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (02): 236-242.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.402
Special Issue: 中医最新文章合集; 心力衰竭最新文章合集; 心血管最新文章合集
• Evidence-based Medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy and Safety Combined with Conventional and Western Medicine Treatments on Coronary Heart Disease Complicated with Heart Failure:a Systematic Review
1.Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Capital Medical University,Beijing 100010,China
2.Beijing Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Beijing 100010,China
3.Beijing Evidence-based Chinese Medicine Center,Beijing 100010,China
4.Beijing General Hospital of the Chinese People's Armed Police Force,Beijing 100027,China
*Corresponding author:LI Bo,Associate chief physician;E-mail:libo@bjzhongyi.com
WANG Tianyuan and WANG Yanbo are co-first authors
Received:2021-08-05
Revised:2021-09-08
Published:2022-01-15
Online:2021-12-29
通讯作者:
李博
基金资助:CLC Number:
WANG Tianyuan, WANG Yanbo, FENG Shuo, HU Jing, ZHANG Huina, WANG Hong, LI Bo.
Efficacy and Safety Combined with Conventional and Western Medicine Treatments on Coronary Heart Disease Complicated with Heart Failure:a Systematic Review [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2022, 25(02): 236-242.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.402
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 样本量(例)试验组/对照组 | 平均年龄(岁) | 干预措施 | 疗程 | 结局指标 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | |||||
| 胡威[ | 2018 | 50/50 | 63.6±5.2 | 63.2±5.5 | 常规治疗+酒石酸美托洛尔片+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+酒石酸美托洛尔片 | 30 d | ③⑧⑨⑩⑪⑫ |
| 华翠娥[ | 2017 | 42/41 | 63.1±14.3 | 62.7±14.2 | 常规治疗+盐酸曲美他嗪片+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+盐酸曲美他嗪片 | 4周 | ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧ |
| 金慧[ | 2016 | 52/52 | 58.8±3.7 | 58.5 ± 4.2 | 常规治疗+前列地尔+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+前列地尔 | 10 d | ①②③⑥⑧⑩⑬⑭⑮ |
| 赖晓菁[ | 2019 | 35/35 | 55.4±5.1 | 56.5±4.9 | 常规治疗+前列地尔+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+前列地尔 | 28 d | ①②③⑥⑬⑭⑯ |
| 王冬松[ | 2018 | 63/63 | 68.2±10.0 | 68.8±10.2 | 常规治疗+左卡尼汀+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+左卡尼汀 | 10 d | ①②⑤⑪⑭⑮ |
| 许文元[ | 2019 | 40/40 | 58.2±6.5 | 57.47±6.3 | 常规治疗+盐酸曲美他嗪片+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+盐酸曲美他嗪片 | 4周 | ①②③④⑤⑧ |
| 张妍[ | 2018 | 204/204 | 63.4±5.7 | 70.2±10.8 | 常规治疗+盐酸曲美他嗪片+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+盐酸曲美他嗪片 | 1个月 | ①②③④⑧ |
| 张志亮[ | 2020 | 52/52 | 55.3±8.4 | 57.0±9.0 | 常规治疗+前列地尔+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+前列地尔 | 20 d | ①②③⑤⑥⑩⑬⑭ |
Table 1 Basic characteristics of the included RCTs
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 样本量(例)试验组/对照组 | 平均年龄(岁) | 干预措施 | 疗程 | 结局指标 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | |||||
| 胡威[ | 2018 | 50/50 | 63.6±5.2 | 63.2±5.5 | 常规治疗+酒石酸美托洛尔片+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+酒石酸美托洛尔片 | 30 d | ③⑧⑨⑩⑪⑫ |
| 华翠娥[ | 2017 | 42/41 | 63.1±14.3 | 62.7±14.2 | 常规治疗+盐酸曲美他嗪片+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+盐酸曲美他嗪片 | 4周 | ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧ |
| 金慧[ | 2016 | 52/52 | 58.8±3.7 | 58.5 ± 4.2 | 常规治疗+前列地尔+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+前列地尔 | 10 d | ①②③⑥⑧⑩⑬⑭⑮ |
| 赖晓菁[ | 2019 | 35/35 | 55.4±5.1 | 56.5±4.9 | 常规治疗+前列地尔+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+前列地尔 | 28 d | ①②③⑥⑬⑭⑯ |
| 王冬松[ | 2018 | 63/63 | 68.2±10.0 | 68.8±10.2 | 常规治疗+左卡尼汀+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+左卡尼汀 | 10 d | ①②⑤⑪⑭⑮ |
| 许文元[ | 2019 | 40/40 | 58.2±6.5 | 57.47±6.3 | 常规治疗+盐酸曲美他嗪片+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+盐酸曲美他嗪片 | 4周 | ①②③④⑤⑧ |
| 张妍[ | 2018 | 204/204 | 63.4±5.7 | 70.2±10.8 | 常规治疗+盐酸曲美他嗪片+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+盐酸曲美他嗪片 | 1个月 | ①②③④⑧ |
| 张志亮[ | 2020 | 52/52 | 55.3±8.4 | 57.0±9.0 | 常规治疗+前列地尔+大株红景天注射液 | 常规治疗+前列地尔 | 20 d | ①②③⑤⑥⑩⑬⑭ |
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 随机方法 | 分配隐藏 | 对研究者和受试者施盲 | 研究结局盲法评价 | 结局数据的完整性 | 选择性报告研究结果 | 其他偏倚 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 胡威[ | 2018 | 随机数字表法 | 未分配隐藏 | 未对研究者和受试者施盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
| 华翠娥[ | 2017 | 未提及 | 未分配隐藏 | 未对研究者和受试者施盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
| 金慧[ | 2016 | 随机数字表法 | 未分配隐藏 | 未对研究者和受试者施盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
| 赖晓菁[ | 2019 | 随机数字表法 | 未分配隐藏 | 未对研究者和受试者施盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
| 王冬松[ | 2018 | 随机数字表法 | 未分配隐藏 | 未对研究者和受试者施盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
| 许文元[ | 2019 | 未提及 | 未分配隐藏 | 未对研究者和受试者施盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
| 张妍[ | 2018 | 随机数字表法 | 未分配隐藏 | 双盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
| 张志亮[ | 2020 | 未提及 | 未分配隐藏 | 未对研究者和受试者施盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
Table 2 The methodological quality of of the included RCTs
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 随机方法 | 分配隐藏 | 对研究者和受试者施盲 | 研究结局盲法评价 | 结局数据的完整性 | 选择性报告研究结果 | 其他偏倚 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 胡威[ | 2018 | 随机数字表法 | 未分配隐藏 | 未对研究者和受试者施盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
| 华翠娥[ | 2017 | 未提及 | 未分配隐藏 | 未对研究者和受试者施盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
| 金慧[ | 2016 | 随机数字表法 | 未分配隐藏 | 未对研究者和受试者施盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
| 赖晓菁[ | 2019 | 随机数字表法 | 未分配隐藏 | 未对研究者和受试者施盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
| 王冬松[ | 2018 | 随机数字表法 | 未分配隐藏 | 未对研究者和受试者施盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
| 许文元[ | 2019 | 未提及 | 未分配隐藏 | 未对研究者和受试者施盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
| 张妍[ | 2018 | 随机数字表法 | 未分配隐藏 | 双盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
| 张志亮[ | 2020 | 未提及 | 未分配隐藏 | 未对研究者和受试者施盲 | 没有进行结局盲法评价 | 结局数据完整 | 未选择性报告研究结果 | 未提及 |
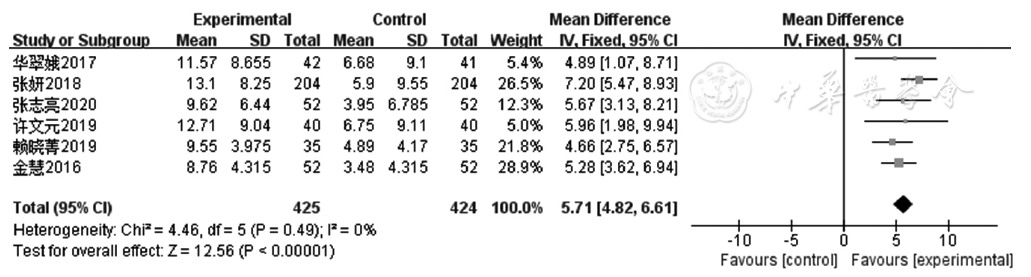
Figure 5 Forest plot of the experimental group versus the control group for improving LVEDD in patients with coronary heart disease with heart failure
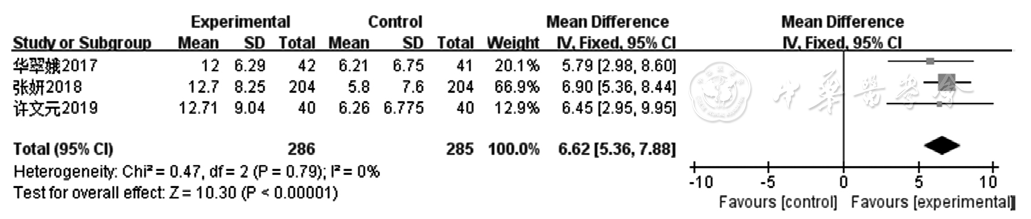
Figure 6 Forest plot of the experimental group versus the control groupt for improving LAEDD in patients with coronary heart disease with heart failure
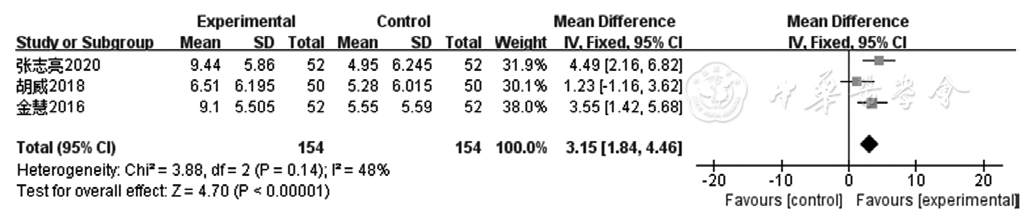
Figure 7 Forest plot of the experimental group versus the control group for improving LVESD in patients with coronary heart disease with heart failure
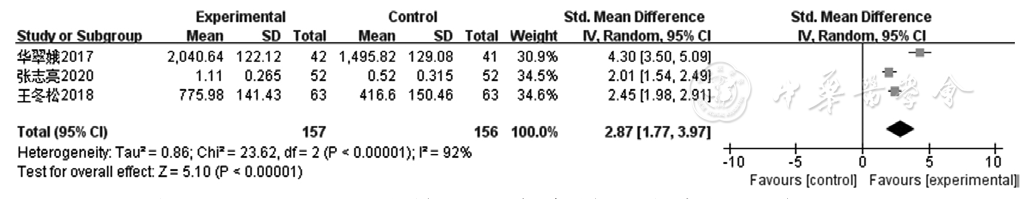
Figure 9 Forest plot of the experimental group versus the control group for improving NT-proBNP in patients with coronary heart disease with heart failure
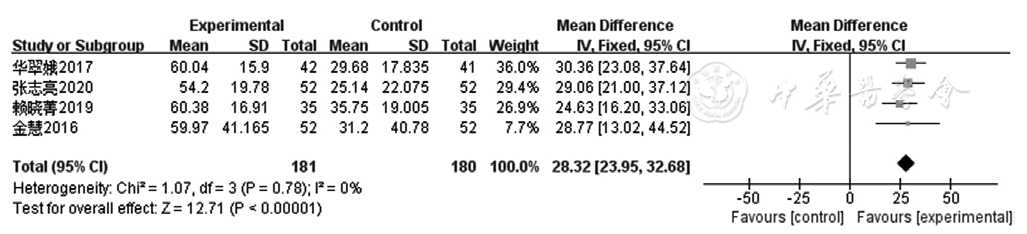
Figure 10 Forest plot of the experimental group versus the control group for improving ET-1 in patients with coronary heart disease with heart failure
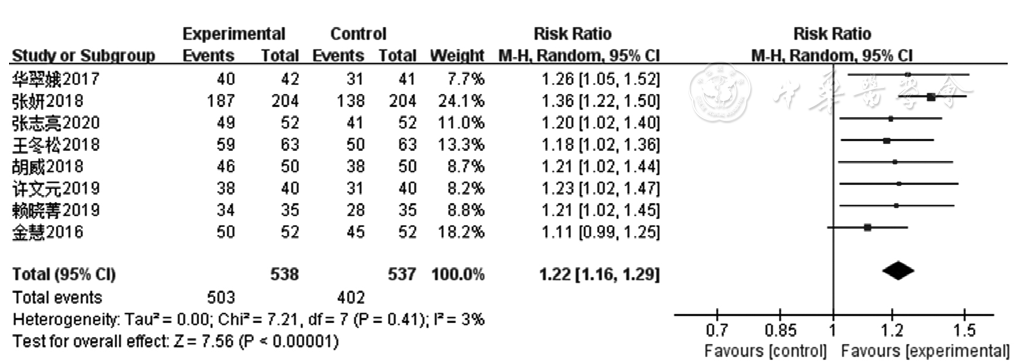
Figure 12 Forest plot of overall clinical response rate in patients with coronary heart disease with heart failure achieved by the experimental group versus the control group
| 结局指标 | 影响证据质量的因素 | 样本量 | 结果RR (95%CI) | 质量 | 重要性 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 研究数量 | 研究类型 | 偏倚风险 | 不一致性 | 间接性 | 精确性 | 其他 | 试验组 | 对照组 | ||||
| 临床总有效率 | 8 | RCT | 严重a | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 发表偏移c | 503/538(93.5%) | 402/537(74.9%) | 1.25(1.18,1.32) | 极低级 | 很重要 |
| LVEF | 8 | RCT | 严重d | 严重e | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 538 | 537 | - | 极低级 | 很重要 |
| LVEDD | 6 | RCT | 严重a | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 425 | 424 | - | 低级 | 很重要 |
| LAEDD | 3 | RCT | 严重f | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 286 | 285 | - | 低级 | 很重要 |
| LVESD | 3 | RCT | 严重g | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 154 | 154 | - | 低级 | 很重要 |
| CO | 3 | RCT | 严重g | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 139 | 139 | - | 低级 | 重要 |
| ET-1 | 4 | RCT | 严重d | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 发表偏倚c | 181 | 180 | - | 极低级 | 重要 |
| NO | 3 | RCT | 严重g | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 139 | 139 | - | 低级 | 重要 |
| NT-proBNP | 3 | RCT | 严重f | 严重h | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 157 | 156 | - | 极低级 | 重要 |
| 不良反应发生率 | 2 | RCT | 非常严重f | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 13/92(14.1%) | 11/91(12.1%) | 1.17(0.55,2.48) | 极低级 | 重要 |
Table 3 Quality of research indicators about Sofren Injection combined with usual and western treatment in treatment of coronary heart disease complicated with heart failure rated by GRADE approach
| 结局指标 | 影响证据质量的因素 | 样本量 | 结果RR (95%CI) | 质量 | 重要性 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 研究数量 | 研究类型 | 偏倚风险 | 不一致性 | 间接性 | 精确性 | 其他 | 试验组 | 对照组 | ||||
| 临床总有效率 | 8 | RCT | 严重a | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 发表偏移c | 503/538(93.5%) | 402/537(74.9%) | 1.25(1.18,1.32) | 极低级 | 很重要 |
| LVEF | 8 | RCT | 严重d | 严重e | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 538 | 537 | - | 极低级 | 很重要 |
| LVEDD | 6 | RCT | 严重a | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 425 | 424 | - | 低级 | 很重要 |
| LAEDD | 3 | RCT | 严重f | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 286 | 285 | - | 低级 | 很重要 |
| LVESD | 3 | RCT | 严重g | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 154 | 154 | - | 低级 | 很重要 |
| CO | 3 | RCT | 严重g | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 139 | 139 | - | 低级 | 重要 |
| ET-1 | 4 | RCT | 严重d | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 发表偏倚c | 181 | 180 | - | 极低级 | 重要 |
| NO | 3 | RCT | 严重g | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 139 | 139 | - | 低级 | 重要 |
| NT-proBNP | 3 | RCT | 严重f | 严重h | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 157 | 156 | - | 极低级 | 重要 |
| 不良反应发生率 | 2 | RCT | 非常严重f | 无明显不一致性 | 无明显间接性 | 严重b | 无 | 13/92(14.1%) | 11/91(12.1%) | 1.17(0.55,2.48) | 极低级 | 重要 |
| [1] | 吴迪,张庆军. 中国冠心病诊疗现状和进展[J]. 中国研究型医院,2020,7(1):71-75,192-197. DOI:10.19450/jcnki.jcrh.2020.01.015. |
| [2] | KLEIN L,GHEORGHIADE M. Coronary artery disease and prevention of heart failure[J]. Med Clin N Am,2004,88(5):1209-1235. DOI:10.1016/j.mcna.2004.03.002. |
| [3] | 张敏,孟照辉. 心力衰竭发病机制及药物治疗进展[J]. 临床医学,2015,35(5):118-121. |
| [4] | LAVIE C J,MILANI R V,VENTURA H O. Disparate effects of metabolically healthy obesity in coronary heart disease and heart failure[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol,2014,63(11):1079-1081. DOI:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.10.080. |
| [5] | 陈文生,杨立明,纪征. 大株红景天注射液联合前列地尔治疗冠心病心力衰竭的疗效分析[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2016,43(10):2131-2133. DOI:10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2016.10.038. |
| [6] | 王华,梁延春. 中国心力衰竭诊断和治疗指南2018[J]. 中华心血管病杂志,2018,46(10):760-789. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2018.10.004. |
| [7] | GUYATT G H,OXMAN A D,VIST G E,等. GRADE:证据质量和推荐强度分级的共识[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2009,9(1):8-11. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-2531.2009.01.005. |
| [8] | 胡威,易日霞,李朋,等. 美托洛尔联合大株红景天注射液治疗冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病心力衰竭临床研究[J]. 中国药业,2018,27(23):59-61. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2018.23.019. |
| [9] | 华翠娥,王达理,王经,等. 大株红景天注射液联合曲美他嗪治疗冠心病心力衰竭的临床研究[J]. 现代药物与临床,2017,32(9):1643-1646. DOI:10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2017.09.009. |
| [10] | 金慧,李猛. 前列地尔联合大株红景天注射液治疗冠心病心力衰竭疗效观察[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2016,25(31):3518-3519,3531. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2016.31.038. |
| [11] | 赖晓菁,康峰,张秀菊,等. 大株红景天联合前列地尔治疗冠心病心力衰竭的临床研究[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2019,17(9):1308-1311. |
| [12] | 王冬松,沈洁,牛孝辉,等. 大株红景天注射液联合左卡尼汀治疗冠心病心力衰竭患者对其血清NTproBNP及胱抑素C水平的影响[J]. 中外医疗,2018,37(30):8-10,25. DOI:10.16662/j.cnki.1674-0742.2018.30.008. |
| [13] | 许文元. 大株红景天注射液联合曲美他嗪片治疗冠心病心力衰竭的疗效观察[J]. 中国实用医药,2019,14(14):112-114. DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2019.14.061. |
| [14] | 张妍. 大株红景天注射液联合曲美他嗪治疗冠心病心力衰竭的临床研究[J]. 中国保健营养,2018,28(23):8. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-7484.2018.23.008. |
| [15] | 张志亮,张鑫,高卫芳,等. 大株红景天注射液治疗冠心病合并心力衰竭疗效及对患者血清HCY、Gal-3、NT-proBNP水平的影响[J]. 分子诊断与治疗杂志,2020,12(5):611-615. |
| [16] | 陈可冀,吴宗贵,朱明军,等. 慢性心力衰竭中西医结合诊疗专家共识[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志,2016,36(2):133-141. |
| [17] | 毛静远. 中医药在心力衰竭治疗中的应用研究述评[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2015,13(1):3-5,38. |
| [18] | KHANNA K,MISHRA K P,GANJU L,et al. Golden root:a wholesome treat of immunity[J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2017,87:496-502. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.132. |
| [19] | TAO H,WUX,CAO J,et al. Rhodiola species:a comprehensive review of traditional use,phytochemistry,pharmacology,toxicity,and clinical study[J]. Med Res Rev,2019,39(5):1779-1850. DOI:10.1002/med.21564. |
| [20] | 曹磊,平芬,韩书芝,等. 大株红景天在不同系统疾病中的应用进展[J]. 河北医药,2020,42(4):608-612. |
| [21] | 李佳,何俊. 大株红景天注射液对心肌缺血-再灌注损伤的保护作用及机制的临床研究[J]. 中药药理与临床,2016,32(1):175-178. DOI:10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2016.01.050. |
| [1] | WANG Zhe, DONG Zhihao, ZHENG Hao, KONG Wencheng, ZHANG Yukuan, ZHANG Qiuyue, HAN Jing. Construction of Optimized Treatment Plan of Acupuncture for Migraine Based on Entropy Weight-TOPSIS Method [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(34): 4336-4342. |
| [2] | WANG Yue, CHEN Qing, LIU Lurong. Detection Rate of Depression and Its Influencing Factors in Chinese Elderly: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(34): 4329-4335. |
| [3] | ZHANG Jin, DING Zhiguo, QI Shuo, LI Ying, LI Weiqiang, ZHANG Yuanyuan, ZHOU Tong. Relationship between Serum Thyroid Hormone Levels and Prognosis during Hospitalization in Heart Failure Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(33): 4125-4129. |
| [4] | JIAN Qiufeng, XU Ronghua, YAO Qian, ZHOU Yuanyuan. A Meta-analysis of the Prevalence and Influencing Factors of Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment in Chinese Elderly Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(32): 4070-4079. |
| [5] | JIA Yu, ZHOU Zitong, CAO Xuehua, HU Wanqin, XIANG Feng, XIONG Langyu, WANG Xiaoxia. Incidence of Perimenopausal Syndrome in Chinese Women Aged 40 to 65 Years: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(32): 4080-4088. |
| [6] | LI Jixin, QIU Linjie, REN Yan, WANG Wenru, LI Meijie, ZHANG Jin. The Correlation of Dietary Inflammatory Index with Overweight, Obesity and Abdominal Obesity: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(32): 4089-4097. |
| [7] | LI Fangjian, JI Zequan, YE Huiling, YAN Ping, CHEN Dexiong, ZHANG Kouxing, LIANG Xiang, WANG Jiaji, HU Bingjie. The Development History and Current Situation of General Practice Education in Guangdong Province in the Past 30 Years [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(31): 3915-3921. |
| [8] | HE Jingyi, WANG Fang, SHUI Xiaoling, LI Ling, LIANG Qian. Efficacy of Non-pharmacological Interventions to Improve Perimenopausal Insomnia Symptoms: a Network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(31): 3963-3974. |
| [9] | HUANG Taishuai, CHI Yan, HE Ping, HUANG Guolan, ZUO Yanli. Cost-effectiveness Analysis of GnRH Antagonist Protocol and Short-acting GnRH Agonist Long Protocol in Fresh Embryo Transfer Based on Propensity Score Matching [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(30): 3809-3814. |
| [10] | MA Yanyan, REN Fuxian, WANG Yu, GAO Dengfeng. The Prediction Value of (Neutrophil+Monocyte) /Lymphocyte Ratio on In-hospital Mortality of Heart Failure Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(30): 3791-3796. |
| [11] | ZHU Lin, GUO Yankui, GAO Chen, CHEN Xuezhi, WANG Fashuai. Efficacy of Western Medicine, Chinese Patent Medicine and Their Combination on Post-stroke Insomnia: a Network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(30): 3823-3832. |
| [12] | ZHANG Dongli, SHEN Chong, ZHANG Weichuan, CHEN Haibin, ZHAO Jianjun. Efficacy and Safety of Programmed Death-1/Programmed Death-1 Ligand Inhibitors in the Treatment of Renal Cell Cancer: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(30): 3815-3822. |
| [13] | ZHANG Zhendong, CAI Bin, WANG Hongwei, QIAO Zengyong. Study on the Changes of Intestinal Flora and Its Metabolite Phenylacetylglutamine in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(29): 3665-3673. |
| [14] | HE Li, ZHANG Yifan, SHEN Xuechun, SUN Yan, ZHAO Yang. Prevalence Trends of Multimorbidity among Residents in Mainland China: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(29): 3599-3607. |
| [15] | LIU Minghao, WANG Pan, GAO Lijian, XU Shuqing, WANG Huanhuan, ZHAO Guangxian, CHEN Jue, QIAO Shubin, XU Bo, YUAN Jinqing. Feasibility, Safety and Timing of Secondary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention via Distal Transradial Artery Approach [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2023, 26(27): 3366-3372. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||