

Chinese General Practice ›› 2021, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (36): 4618-4622.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.051
Special Issue: 神经系统疾病最新文章合辑; 脑健康最新研究合辑
• Monographic Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Published:2021-12-20
Online:2021-12-20
LI Jianhong,SU Qingjie,ZHANG Yuhui. Predictive Value of Thromboelastography for Hemorrhagic Transformation in Acute Ischemic Stroke [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2021, 24(36): 4618-4622.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.chinagp.net/EN/10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.02.051
| 变量 | 卒中有出血转化(n=280) | 卒中无出血转化(n=1 760) | 检验统计量值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
年龄(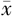 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 69±14 | 67±13 | 4.329a | <0.001 | |
| 性别(男/女) | 180/100 | 1 170/590 | 0.518 | 0.472 | |
| 既往合并疾病〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 高血压 | 210(75.00) | 1 060(60.23) | 22.435 | <0.001 | |
| 糖尿病 | 70(25.00) | 390(22.16) | 1.116 | 0.291 | |
| 缺血性卒中 | 70(25.00) | 430(24.43) | 0.042 | 0.837 | |
| 颅内出血 | 20(7.14) | 70(3.98) | 5.740 | 0.017 | |
| 冠状动脉疾病 | 10(3.57) | 190(10.80) | 14.256 | <0.001 | |
| 慢性阻塞性肺疾病 | 12(4.29) | 98(5.57) | 0.779 | 0.377 | |
| 肝硬化 | 10(3.57) | 10(0.57) | 2.444 | <0.001 | |
| 慢性肾病 | 20(7.14) | 110(6.25) | 0.323 | 0.570 | |
| 恶性肿瘤 | 50(17.86) | 260(14.77) | 1.783 | 0.182 | |
| 卒中特点及干预情况 | |||||
| 出现症状到就诊时间〔M(P25,P75),h〕 | 5.0(0.9,8.8) | 2.5(1.0,6.0) | -3.218b | 0.001 | |
| 单一抗血小板药〔n(%)〕 | 40(14.28) | 210(11.93) | 1.245 | 0.265 | |
| 变量 | 卒中有出血转化(n=280) | 卒中无出血转化(n=1 760) | 检验统计量值 | P值 | |
| 使用双重抗血小板药〔n(%)〕 | 120(42.86) | 1 100(62.50) | 38.774 | <0.001 | |
| 使用抗凝剂〔n(%)〕 | 30(10.71) | 30(1.70) | 68.692 | <0.001 | |
| 使用rt-PA〔n(%)〕 | 60(21.43) | 370(21.02) | 0.024 | 0.877 | |
| 血栓动脉内膜切除术〔n(%)〕 | 80(28.57) | 210(11.93) | 54.847 | <0.001 | |
| 基线实验室检查结果 | |||||
| 白细胞计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/L〕 | 8.1(5.9,10.2) | 7.3(6.0,8.9) | -0.696b | 0.486 | |
血红蛋白(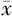 ±s,g/dl) ±s,g/dl) | 13.4±1.5 | 13.5±2.0 | -1.033a | 0.302 | |
| 血小板计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/μl〕 | 208(162,260) | 225(185,261) | -8.025b | <0.001 | |
| INR〔M(P25,P75)〕 | 1.03(0.99,1.06) | 0.98(0.95,1.04) | -4.985b | 0.025 | |
| APTT〔M(P25,P75),s〕 | 24.8(23.7,26.8) | 25.9(24.2,27.6) | -9.248b | <0.001 | |
| 血肌酐〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 86.6(71.6,107.0) | 83.1(69.8,98.1) | -0.214b | 0.852 | |
| 血尿素氮〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 2.98(4.71,8.88) | 5.80(4.71,7.25) | -0.554b | 0.580 | |
| 白蛋白〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 39.2(36.4,40.2) | 38.6(35.4,40.7) | -0.809b | 0.419 | |
| 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | 26.0(19.3,30.0) | 24.0(19.0,31.0) | -5.308b | <0.001 | |
| 丙氨酸氨基转移酶〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | 19.0(13.8,28.3) | 19.0(15.0,29.0) | -0.116b | 0.667 | |
| 血钠〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 140(138,142) | 140(138,142) | -0.210b | 0.833 | |
| 血钾〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 4.1(3.9,4.5) | 4.2(3.9,4.6) | -1.621b | 0.105 | |
| C反应蛋白〔M(P25,P75),mg/dl〕 | 0.1(0.1,0.4) | 0.1(0.1,0.3) | -1.247b | 0.221 | |
| 纤维蛋白原〔M(P25,P75),mg/dl〕 | 276(225,314) | 286(233,354) | -28.397b | <0.001 | |
| D-二聚体〔M(P25,P75),μg/ml〕 | 1.1(0.5,1.7) | 0.6(0.3,1.1) | -2.702b | 0.029 | |
| TOAST分型〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 大动脉粥样硬化 | 210(75.00) | 1160(65.91) | 9.051 | 0.003 | |
| 心脏栓塞 | 30(10.71) | 250(14.20) | 2.485 | 0.115 | |
| 小血管病 | 40(14.28) | 140(7.95) | 12.036 | 0.001 | |
| 其他原因 | 0 | 210(11.93) | 37.243 | <0.001 | |
| 卒中部位〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 额叶 | 50(17.86) | 470(26.70) | 9.956 | 0.002 | |
| 颞叶 | 100(35.71) | 500(28.41) | 6.209 | 0.013 | |
| 顶叶 | 20(7.14) | 360(20.45) | 28.241 | <0.001 | |
| 枕叶 | 40(14.29) | 230(13.07) | 0.312 | 0.577 | |
| 丘脑 | 20(7.14) | 130(7.39) | 0.021 | 0.885 | |
| 基底节 | 60(21.43) | 390(22.16) | 0.075 | 0.784 | |
| 脑干 | 40(14.29) | 130(7.39) | 15.053 | <0.001 | |
Table 1 Demographic characteristics,previous comorbidities,stroke characteristics,interventions,baseline laboratory results,TOAST classification,and stroke location in acute ischemic stroke patients with and without hemorrhagic transformation
| 变量 | 卒中有出血转化(n=280) | 卒中无出血转化(n=1 760) | 检验统计量值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
年龄(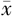 ±s,岁) ±s,岁) | 69±14 | 67±13 | 4.329a | <0.001 | |
| 性别(男/女) | 180/100 | 1 170/590 | 0.518 | 0.472 | |
| 既往合并疾病〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 高血压 | 210(75.00) | 1 060(60.23) | 22.435 | <0.001 | |
| 糖尿病 | 70(25.00) | 390(22.16) | 1.116 | 0.291 | |
| 缺血性卒中 | 70(25.00) | 430(24.43) | 0.042 | 0.837 | |
| 颅内出血 | 20(7.14) | 70(3.98) | 5.740 | 0.017 | |
| 冠状动脉疾病 | 10(3.57) | 190(10.80) | 14.256 | <0.001 | |
| 慢性阻塞性肺疾病 | 12(4.29) | 98(5.57) | 0.779 | 0.377 | |
| 肝硬化 | 10(3.57) | 10(0.57) | 2.444 | <0.001 | |
| 慢性肾病 | 20(7.14) | 110(6.25) | 0.323 | 0.570 | |
| 恶性肿瘤 | 50(17.86) | 260(14.77) | 1.783 | 0.182 | |
| 卒中特点及干预情况 | |||||
| 出现症状到就诊时间〔M(P25,P75),h〕 | 5.0(0.9,8.8) | 2.5(1.0,6.0) | -3.218b | 0.001 | |
| 单一抗血小板药〔n(%)〕 | 40(14.28) | 210(11.93) | 1.245 | 0.265 | |
| 变量 | 卒中有出血转化(n=280) | 卒中无出血转化(n=1 760) | 检验统计量值 | P值 | |
| 使用双重抗血小板药〔n(%)〕 | 120(42.86) | 1 100(62.50) | 38.774 | <0.001 | |
| 使用抗凝剂〔n(%)〕 | 30(10.71) | 30(1.70) | 68.692 | <0.001 | |
| 使用rt-PA〔n(%)〕 | 60(21.43) | 370(21.02) | 0.024 | 0.877 | |
| 血栓动脉内膜切除术〔n(%)〕 | 80(28.57) | 210(11.93) | 54.847 | <0.001 | |
| 基线实验室检查结果 | |||||
| 白细胞计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/L〕 | 8.1(5.9,10.2) | 7.3(6.0,8.9) | -0.696b | 0.486 | |
血红蛋白(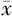 ±s,g/dl) ±s,g/dl) | 13.4±1.5 | 13.5±2.0 | -1.033a | 0.302 | |
| 血小板计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/μl〕 | 208(162,260) | 225(185,261) | -8.025b | <0.001 | |
| INR〔M(P25,P75)〕 | 1.03(0.99,1.06) | 0.98(0.95,1.04) | -4.985b | 0.025 | |
| APTT〔M(P25,P75),s〕 | 24.8(23.7,26.8) | 25.9(24.2,27.6) | -9.248b | <0.001 | |
| 血肌酐〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 86.6(71.6,107.0) | 83.1(69.8,98.1) | -0.214b | 0.852 | |
| 血尿素氮〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 2.98(4.71,8.88) | 5.80(4.71,7.25) | -0.554b | 0.580 | |
| 白蛋白〔M(P25,P75),g/L〕 | 39.2(36.4,40.2) | 38.6(35.4,40.7) | -0.809b | 0.419 | |
| 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | 26.0(19.3,30.0) | 24.0(19.0,31.0) | -5.308b | <0.001 | |
| 丙氨酸氨基转移酶〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | 19.0(13.8,28.3) | 19.0(15.0,29.0) | -0.116b | 0.667 | |
| 血钠〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 140(138,142) | 140(138,142) | -0.210b | 0.833 | |
| 血钾〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 4.1(3.9,4.5) | 4.2(3.9,4.6) | -1.621b | 0.105 | |
| C反应蛋白〔M(P25,P75),mg/dl〕 | 0.1(0.1,0.4) | 0.1(0.1,0.3) | -1.247b | 0.221 | |
| 纤维蛋白原〔M(P25,P75),mg/dl〕 | 276(225,314) | 286(233,354) | -28.397b | <0.001 | |
| D-二聚体〔M(P25,P75),μg/ml〕 | 1.1(0.5,1.7) | 0.6(0.3,1.1) | -2.702b | 0.029 | |
| TOAST分型〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 大动脉粥样硬化 | 210(75.00) | 1160(65.91) | 9.051 | 0.003 | |
| 心脏栓塞 | 30(10.71) | 250(14.20) | 2.485 | 0.115 | |
| 小血管病 | 40(14.28) | 140(7.95) | 12.036 | 0.001 | |
| 其他原因 | 0 | 210(11.93) | 37.243 | <0.001 | |
| 卒中部位〔n(%)〕 | |||||
| 额叶 | 50(17.86) | 470(26.70) | 9.956 | 0.002 | |
| 颞叶 | 100(35.71) | 500(28.41) | 6.209 | 0.013 | |
| 顶叶 | 20(7.14) | 360(20.45) | 28.241 | <0.001 | |
| 枕叶 | 40(14.29) | 230(13.07) | 0.312 | 0.577 | |
| 丘脑 | 20(7.14) | 130(7.39) | 0.021 | 0.885 | |
| 基底节 | 60(21.43) | 390(22.16) | 0.075 | 0.784 | |
| 脑干 | 40(14.29) | 130(7.39) | 15.053 | <0.001 | |
| 人群 | 例数 | R值(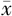 ±s,min) ±s,min) | K值(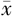 ±s,min) ±s,min) | α角〔M(P25,P75)〕 | MA值(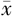 ±s,mm) ±s,mm) | LY30 〔M(P25,P75),%〕 | R值<5.0 min 〔n(%)〕 | K值<1.0 min 〔n(%)〕 | MA值≥69 mm 〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 卒中有出血转化 | 280 | 4.3±0.8 | 1.5(1.2,1.8) | 68.4°(62.9°,72.5°) | 61.1±7.1 | 2.6(0.1,6.5) | 230(82.14) | 2(0.7) | 30(10.71) |
| 卒中无出血转化 | 1 760 | 4.7±1.1 | 1.4(1.2,1.7) | 69.6°(65.3°,72.9°) | 62.2±8.7 | 1.8(0.4,5.4) | 1 070(60.45) | 160(9.04) | 380(21.47) |
| 检验统计量值 | -2.378a | -0.191b | -1.224b | -0.605a | -0.988b | 49.027 | 27.453 | 17.476 | |
| P值 | 0.019 | 0.848 | 0.258 | 0.546 | 0.430 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Table 2 Comparison of main thromboelastography parameters in acute ischemic stroke patients with and without hemorrhage transformation after stroke
| 人群 | 例数 | R值(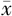 ±s,min) ±s,min) | K值(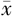 ±s,min) ±s,min) | α角〔M(P25,P75)〕 | MA值(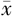 ±s,mm) ±s,mm) | LY30 〔M(P25,P75),%〕 | R值<5.0 min 〔n(%)〕 | K值<1.0 min 〔n(%)〕 | MA值≥69 mm 〔n(%)〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 卒中有出血转化 | 280 | 4.3±0.8 | 1.5(1.2,1.8) | 68.4°(62.9°,72.5°) | 61.1±7.1 | 2.6(0.1,6.5) | 230(82.14) | 2(0.7) | 30(10.71) |
| 卒中无出血转化 | 1 760 | 4.7±1.1 | 1.4(1.2,1.7) | 69.6°(65.3°,72.9°) | 62.2±8.7 | 1.8(0.4,5.4) | 1 070(60.45) | 160(9.04) | 380(21.47) |
| 检验统计量值 | -2.378a | -0.191b | -1.224b | -0.605a | -0.988b | 49.027 | 27.453 | 17.476 | |
| P值 | 0.019 | 0.848 | 0.258 | 0.546 | 0.430 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 变量 | 赋值 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 实测值 | 0.381 | 0.148 | 6.627 | 0.010 | 1.464 | (1.095,1.956) |
| 高血压 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.284 | 0.112 | 3.891 | 0.049 | 1.328 | (1.067,1.655) |
| 颅内出血 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.301 | 0.087 | 11.970 | 0.001 | 1.351 | (1.602,3.460) |
| 冠状动脉疾病 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.512 | 0.265 | 1.369 | 0.242 | 1.669 | (0.993,2.805) |
| 肝硬化 | 是=1,否=0 | -0.472 | 0.368 | 1.645 | 0.200 | 0.624 | (0.303,1.283) |
| 出现症状到就诊时间 | 实测值 | 0.529 | 0.399 | 1.758 | 0.185 | 1.697 | (0.776,3.710) |
| 使用双重抗血小板药 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.324 | 0.148 | 4.793 | 0.029 | 1.383 | (1.848,2.189) |
| 使用抗凝剂 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.553 | 0.482 | 1.316 | 0.251 | 1.738 | (0.676,4.471) |
| 血栓动脉内膜切除术 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.537 | 0.264 | 4.138 | 0.042 | 1.711 | (1.020,2.870) |
| 血小板计数 | 实测值 | -0.287 | 0.057 | 25.352 | <0.001 | 0.751 | (0.671,0.839) |
| INR | 实测值 | 0.333 | 0.254 | 1.721 | 0.190 | 1.395 | (0.848,2.295) |
| APTT | 实测值 | -0.102 | 0.087 | 1.375 | 0.241 | 0.903 | (0.761,1.071) |
| 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶 | 实测值 | 0.209 | 0.841 | 0.062 | 0.804 | 1.232 | (0.237,6.407) |
| 纤维蛋白原 | 实测值 | 0.346 | 0.258 | 1.799 | 0.180 | 1.413 | (0.852,2.344) |
| D-二聚体 | 实测值 | 0.234 | 0.089 | 5.472 | 0.009 | 1.264 | (1.061,1.504) |
| TOAST分型为大动脉粥样硬化 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.416 | 0.257 | 2.620 | 0.106 | 1.516 | (0.916,2.509) |
| TOAST分型为小血管 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.169 | 0.093 | 3.302 | 0.069 | 1.184 | (0.987,1.421) |
| TOAST分型为其他原因 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.287 | 0.221 | 1.686 | 0.194 | 1.332 | (0.864,2.055) |
| 卒中部位为额叶 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.194 | 0.254 | 0.583 | 0.445 | 1.214 | (0.738,1.997) |
| 卒中部位为颞叶 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.246 | 0.172 | 2.046 | 0.153 | 1.279 | (0.913,1.792) |
| 卒中部位为顶叶 | 是=1,否=0 | -0.047 | 0.106 | 0.197 | 0.657 | 0.954 | (0.775,1.174) |
| 卒中部位为脑干 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.649 | 0.487 | 1.776 | 0.183 | 1.914 | (0.737,4.970) |
| R值 | 实测值 | 0.092 | 0.032 | 8.266 | 0.004 | 1.096 | (1.030,1.167) |
| R值<5.0 min | 是=1,否=0 | 0.612 | 0.230 | 9.554 | 0.002 | 1.844 | (1.251,2.718) |
| K值<1.0 min | 是=1,否=0 | 0.574 | 0.288 | 3.972 | 0.046 | 1.775 | (1.010,3.122) |
| MA值≥69 mm | 是=1,否=0 | 1.001 | 0.698 | 4.040 | 0.152 | 2.057 | (0.693,10.688) |
Table 3 Univariate Logistic regression analysis of factors possibly associated with hemorrhage transformation in patients with acute ischemic stroke
| 变量 | 赋值 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 实测值 | 0.381 | 0.148 | 6.627 | 0.010 | 1.464 | (1.095,1.956) |
| 高血压 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.284 | 0.112 | 3.891 | 0.049 | 1.328 | (1.067,1.655) |
| 颅内出血 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.301 | 0.087 | 11.970 | 0.001 | 1.351 | (1.602,3.460) |
| 冠状动脉疾病 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.512 | 0.265 | 1.369 | 0.242 | 1.669 | (0.993,2.805) |
| 肝硬化 | 是=1,否=0 | -0.472 | 0.368 | 1.645 | 0.200 | 0.624 | (0.303,1.283) |
| 出现症状到就诊时间 | 实测值 | 0.529 | 0.399 | 1.758 | 0.185 | 1.697 | (0.776,3.710) |
| 使用双重抗血小板药 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.324 | 0.148 | 4.793 | 0.029 | 1.383 | (1.848,2.189) |
| 使用抗凝剂 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.553 | 0.482 | 1.316 | 0.251 | 1.738 | (0.676,4.471) |
| 血栓动脉内膜切除术 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.537 | 0.264 | 4.138 | 0.042 | 1.711 | (1.020,2.870) |
| 血小板计数 | 实测值 | -0.287 | 0.057 | 25.352 | <0.001 | 0.751 | (0.671,0.839) |
| INR | 实测值 | 0.333 | 0.254 | 1.721 | 0.190 | 1.395 | (0.848,2.295) |
| APTT | 实测值 | -0.102 | 0.087 | 1.375 | 0.241 | 0.903 | (0.761,1.071) |
| 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶 | 实测值 | 0.209 | 0.841 | 0.062 | 0.804 | 1.232 | (0.237,6.407) |
| 纤维蛋白原 | 实测值 | 0.346 | 0.258 | 1.799 | 0.180 | 1.413 | (0.852,2.344) |
| D-二聚体 | 实测值 | 0.234 | 0.089 | 5.472 | 0.009 | 1.264 | (1.061,1.504) |
| TOAST分型为大动脉粥样硬化 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.416 | 0.257 | 2.620 | 0.106 | 1.516 | (0.916,2.509) |
| TOAST分型为小血管 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.169 | 0.093 | 3.302 | 0.069 | 1.184 | (0.987,1.421) |
| TOAST分型为其他原因 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.287 | 0.221 | 1.686 | 0.194 | 1.332 | (0.864,2.055) |
| 卒中部位为额叶 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.194 | 0.254 | 0.583 | 0.445 | 1.214 | (0.738,1.997) |
| 卒中部位为颞叶 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.246 | 0.172 | 2.046 | 0.153 | 1.279 | (0.913,1.792) |
| 卒中部位为顶叶 | 是=1,否=0 | -0.047 | 0.106 | 0.197 | 0.657 | 0.954 | (0.775,1.174) |
| 卒中部位为脑干 | 是=1,否=0 | 0.649 | 0.487 | 1.776 | 0.183 | 1.914 | (0.737,4.970) |
| R值 | 实测值 | 0.092 | 0.032 | 8.266 | 0.004 | 1.096 | (1.030,1.167) |
| R值<5.0 min | 是=1,否=0 | 0.612 | 0.230 | 9.554 | 0.002 | 1.844 | (1.251,2.718) |
| K值<1.0 min | 是=1,否=0 | 0.574 | 0.288 | 3.972 | 0.046 | 1.775 | (1.010,3.122) |
| MA值≥69 mm | 是=1,否=0 | 1.001 | 0.698 | 4.040 | 0.152 | 2.057 | (0.693,10.688) |
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.496 | 0.304 | 2.662 | 0.103 | 1.642 | (0.905,2.980) |
| 高血压 | 0.351 | 0.200 | 3.080 | 0.079 | 1.420 | (0.960,2.102) |
| 颅内出血 | 0.523 | 0.413 | 1.604 | 0.205 | 1.687 | (0.751,3.790) |
| 血小板计数 | -0.341 | 0.258 | 1.747 | 0.186 | 0.711 | (0.429,1.179) |
| D-二聚体 | 0.294 | 0.167 | 4.287 | 0.078 | 1.342 | (0.967,1.861) |
| 使用双重抗血小板药 | 0.289 | 0.099 | 8.522 | 0.004 | 1.335 | (1.100,1.621) |
| R值 | 0.127 | 0.091 | 1.948 | 0.163 | 1.135 | (0.950,1.357) |
| R值<5.0 min | 0.524 | 0.124 | 17.857 | <0.001 | 1.689 | (1.324,2.153) |
| K值<1.0 min | 0.438 | 0.245 | 3.196 | 0.074 | 1.550 | (0.959,2.505) |
Table 4 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of factors possibly associated with hemorrhage transformation in patients with acute ischemic stroke
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.496 | 0.304 | 2.662 | 0.103 | 1.642 | (0.905,2.980) |
| 高血压 | 0.351 | 0.200 | 3.080 | 0.079 | 1.420 | (0.960,2.102) |
| 颅内出血 | 0.523 | 0.413 | 1.604 | 0.205 | 1.687 | (0.751,3.790) |
| 血小板计数 | -0.341 | 0.258 | 1.747 | 0.186 | 0.711 | (0.429,1.179) |
| D-二聚体 | 0.294 | 0.167 | 4.287 | 0.078 | 1.342 | (0.967,1.861) |
| 使用双重抗血小板药 | 0.289 | 0.099 | 8.522 | 0.004 | 1.335 | (1.100,1.621) |
| R值 | 0.127 | 0.091 | 1.948 | 0.163 | 1.135 | (0.950,1.357) |
| R值<5.0 min | 0.524 | 0.124 | 17.857 | <0.001 | 1.689 | (1.324,2.153) |
| K值<1.0 min | 0.438 | 0.245 | 3.196 | 0.074 | 1.550 | (0.959,2.505) |
| [1] | ZWANK M D. Fast protocol for treating acute ischemic stroke by emergency physicians[J]. Ann Emerg Med,2019,74(2):313-314. DOI:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2019.03.027. |
| [2] | 中华医学会神经病学分会,中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018[J]. 中华神经科杂志,2018,51(9):666-682. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2018.09.004. |
| [3] | ZI W J, QIU Z M, LI F L,et al. Effect of endovascular treatment alone vs intravenous alteplase plus endovascular treatment on functional independence in patients with acute ischemic stroke:the DEVT randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA,2021,325(3):234-243. DOI:10.1001/jama.2020.23523. |
| [4] | ZHU Z, YU Y, KE Y F,et al. Thromboelastography maximum amplitude predicts short-term mortality in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Exp Ther Med,2020,20(3):2657-2664. DOI:10.3892/etm.2020.8990. |
| [5] | ZHOU Q F, MAO M J, MENG J,et al. The thromboelastography G parameter as a potential biomarker of acute coronary syndrome[J]. Scand J Clin Lab Invest,2020,80(3):196-201. DOI:10.1080/00365513.2019.1709986. |
| [6] | ZAKY A. Thromboelastometry versus rotational thromboelastography in cardiac surgery[J]. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth,2017,21(3):206-211. DOI:10.1177/1089253217697146. |
| [7] | XU R, CHENG C J, WU Y,et al. Microbleeds after stent-assisted coil embolization of unruptured intracranial aneurysms:incidence,risk factors and the role of thromboelastography[J]. Curr Neurovasc Res,2020,17(4):502-509. DOI:10.2174/1567202617999200819161033. |
| [8] | WU Z H, LIU A F, ZHOU J,et al. The safety of triple antiplatelet therapy under thromboelastography guidance in patients undergoing stenting for ischemic cerebrovascular disease[J]. J Neurointerv Surg,2019,11(4):352-356. DOI:10.1136/neurintsurg-2018-013987. |
| [9] | ROSAFIO F, VANDELLI L, BIGLIARDI G,et al. Usefulness of thromboelastography in the detection and management of tissue plasminogen activator-associated hyperfibrinolysis[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis,2017,26(2):e29-31. DOI:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2016.10.039. |
| [10] | ROH D, TORRES G L, CAI C Y,et al. Coagulation differences detectable in deep and lobar primary intracerebral hemorrhage using thromboelastography[J]. Neurosurgery,2020,87(5):918-924. DOI:10.1093/neuros/nyaa056. |
| [11] | SHI Z, ZHENG W C, FU X L,et al. Hypercoagulation on thromboelastography predicts early neurological deterioration in patients with acute ischemic stroke[J]. Cerebrovasc Dis,2018,46(3/4):125-131. DOI:10.1159/000492729. |
| [12] | MA L, CHEN W Q, PAN Y S,et al. Comparison of VerifyNow,thromboelastography,and PL-12 in patients with minor ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack[J]. Aging,2021,13(6):8396-8407. DOI:10.18632/aging.202650. |
| [13] | ZHU J, MA M, FANG J,et al. Prestroke statin use enhances collateralization in acute ischemic stroke patients[J]. Restor Neurol Neurosci,2020,38(4):311-321. DOI:10.3233/RNN-201012. |
| [14] | ZHOU Z E, YOSHIMURA S, DELCOURT C,et al. Thrombolysis outcomes in acute ischemic stroke by fluid-attenuated inversion recovery hyperintense arteries[J]. Stroke,2020,51(7):2240-2243. DOI:10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.028550. |
| [1] | HU Jieman, TAN Feixiang, YUAN Anxin, CHEN Shiyu, TANG Chulei, YIN Yueheng, BA Lei, XU Qin. Analysis of the Trajectory of Postoperative Frailty and Influencing Factors in Patients with Colorectal Cancer [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3276-3282. |
| [2] | CHOU Xintong, PENG Hanyu, MA Hui, ZHANG Zhen, SU Xian, QIU Hongyan. Maternal Preferences in Contraceptive Decision-making: an Analysis of Influencing Factors [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3294-3299. |
| [3] | WEI Jiaohua, PENG Huiru, PENG Jianye, TAN Wenting, HUANG Jine, FANG Li. Expression of the Serum MOTS-c and Its Correlation with Atrial Remodeling in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(26): 3271-3276. |
| [4] | YU Zizi, LIU Duli, LI Ximin, RUAN Chunyi, YIN Xiangyang, CAI Le. Analysis of the Prevalence and Self-management of Hypertension and Its Influencing Factors in Rural [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3137-3143. |
| [5] | FAN Boyang, ZHANG Yu, SUN Wenning, ZHANG Huifang, WANG Yingjie, ZHANG Ao, ZHAO Yang, WANG Haipeng. Study of Behavioral Intention and Influencing Factors of Integrated Medical and Preventive Care Provided by Grassroots Doctors for Patients with Chronic Diseases [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(25): 3144-3150. |
| [6] | WANG Rupeng, NAN Jing, HU Yiran, YANG Shenghua, JIN Zening. Predictive Value of the Triglyceride-Glucose Body Mass Index for Slow Flow/No-reflow Phenomenon in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Acute Myocardial Infarction Undergoing Emergency Percutaneous Coronary Intervention [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(24): 2985-2992. |
| [7] | WU Yue, WANG Xuetong, KE Bilian. Evaluation of Vision-related Quality of Life in Myopic Macular Degeneration Patients with Low Vision and Associated Factors [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(23): 2908-2914. |
| [8] | DING Zijun, ZHOU Nannan, LUO Xing, LUO Jieyu, HAO Wenjuan, ZHANG Chunjiang, JIN Xin, ZHAO Dan. Cognitive Impairment in Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis and Its Influencing Factors: a Multicenter Cross-sectional Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(23): 2885-2893. |
| [9] | YANG Ji, ZHANG Yao, ZHAO Yingqiang, ZHANG Qiuyue. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of TCM Three-level Prevention and Control Model in the Management of Patients with Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke: a Single-center, Prospective Cohort Study [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2750-2761. |
| [10] | WEI Xiaoxia, CHEN Nuo, WANG Juanjuan, ZHU Jingfen. The Effects of Depression and Anxiety on Smoking Behavior among Vocational School Students [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2826-2832. |
| [11] | ZHAO Xiaoqing, GUO Tongtong, ZHANG Xinyi, LI Linhong, ZHANG Ya, JI Lihong, DONG Zhiwei, GAO Qianqian, CAI Weiqing, ZHENG Wengui, JING Qi. Construction and Validation of a Risk Prediction Model for Cognitive Impairment in Community-dwelling Older Adults [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(22): 2776-2783. |
| [12] | TAN Yi, ZHU Lihong, YIN Zengwei, HOU Shunan, YU Houming. A Real-world Study of MRI-guided Intravenous Thrombolytic Therapy in Acute Ischemic Stroke [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(20): 2508-2515. |
| [13] | HAO Aihua, ZENG Ziying, JIN Aiqiong, TANG Lingling, ZHENG Zique, MA Jingtai, ZHAO Jianguo, ZENG Weilin, XIAO Jianpeng, NIE Hui, YANG Ying. Analysis of Factors Influencing Avoidable Hospitalization for Elderly Hypertensive Patients [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(19): 2370-2375. |
| [14] | CHU Tianyu, GU Yan. Carotid Artery Calcification Features in Plaque Stability and Clinical Events [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(18): 2247-2252. |
| [15] | TAN Wenbin, LI Jia, LIU Mingyu, LU Yongxin, CHENG Yaxin. Research Progress on the Influence of Nervous System Diseases and Related Therapeutic Drugs on Osteoporosis [J]. Chinese General Practice, 2025, 28(17): 2092-2100. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||