中国全科医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (15): 1847-1854.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0432
所属专题: 内分泌代谢性疾病最新文章合辑
聂媛媛1, 方达2, 徐浩1, 杨东辉2, 毕艳2, 顾天伟1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-25
修回日期:2024-11-27
出版日期:2025-05-20
发布日期:2025-03-21
通讯作者:
顾天伟
作者贡献:
聂媛媛负责临床数据收集、整理、分析,并撰写论文初稿;方达负责绘制图表并协助统计分析;徐浩协助参与论文内容及格式修改;杨东辉负责FibroTouch检查的检测;毕艳完善论文的审校;顾天伟提出研究思路,设计研究方案,完善论文最终内容及审校,并对论文负责。
基金资助:
NIE Yuanyuan1, FANG Da2, XU Hao1, YANG Donghui2, BI Yan2, GU Tianwei1,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-25
Revised:2024-11-27
Published:2025-05-20
Online:2025-03-21
Contact:
GU Tianwei
摘要: 背景 2型糖尿病(T2DM)和代谢相关脂肪性肝病(MAFLD)之间相互影响,两者并存会进一步增加心血管疾病(CVD)及肝纤维化等不良结局风险。因此有必要对T2DM患者,特别是伴有多种心脏代谢风险的患者,进行MAFLD筛查和肝纤维化风险分层。 目的 探讨不同肝纤维化风险的T2DM患者的临床特征及CVD风险。 方法 回顾性纳入2020年7月—2023年6月在南京鼓楼医院内分泌科住院的T2DM患者1 425例为研究对象,患者均接受肝脏瞬时弹性扫描仪检查。参考2023年美国糖尿病协会(ADA)《糖尿病诊疗标准》建议,根据肝纤维化4指数(FIB4)与肝脏硬度值(LSM)将患者分为3组:肝纤维化低风险组(1 235例)、肝纤维化中风险组(110例)和肝纤维化高风险组(80例)。比较各组之间临床特征,利用Framingham风险评分(FRS)评估10年心血管疾病发生风险。进一步将不同肝纤维化风险患者根据CVD风险分层进一步分为4组:心肝低危组(214例)、心高肝低危组(1 021例)、心肝高危组(178例)和心低肝高危组(12例),比较前3组T2DM患者的临床特征。 结果 纳入1 425例T2DM患者中有5.6%属于肝纤维化高风险患者。肝纤维化高风险组患者年龄、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)、直胆红素(DBIL)、糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)、脂肪衰减参数(UAP)、LSM、FIB4、肌肉质量减少、糖尿病周围神经病变、降脂治疗高于肝纤维化低风险组,血小板计数(PLT)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、总胆固醇(TC)、骨骼肌质量指数(SMI)低于肝纤维化低风险组,天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)、糖尿病视网膜病变高于肝纤维化低风险组和肝纤维化中风险组(P<0.05)。分层分析结果显示,年龄>60岁、HbA1c>9%、肝酶异常以及合并肌肉质量减少的T2DM患者肝纤维化风险更高(P<0.05)。不同肝纤维化风险患者CVD风险发生率比较结果显示,随着肝纤维化风险的增加,CVD高风险的发生率逐渐增加(χ2趋势=35.900,P<0.001)。心肝高危组患者的年龄、AST、DBIL、UAP、LSM、FIB4、FRS、糖尿病周围神经病变、降脂治疗高于心肝低危组和心高肝低危组,PLT低于心肝低危组和心高肝低危组(P<0.05)。 结论 T2DM患者是发生肝纤维化及CVD的高风险人群,其中高龄、血糖控制不佳、合并多种糖尿病并发症、肝酶异常、肝脏脂质沉积增加或肌肉质量减少会增加CVD和肝纤维化风险,应加强对这部分患者的早期监测与预防管理。
中图分类号:
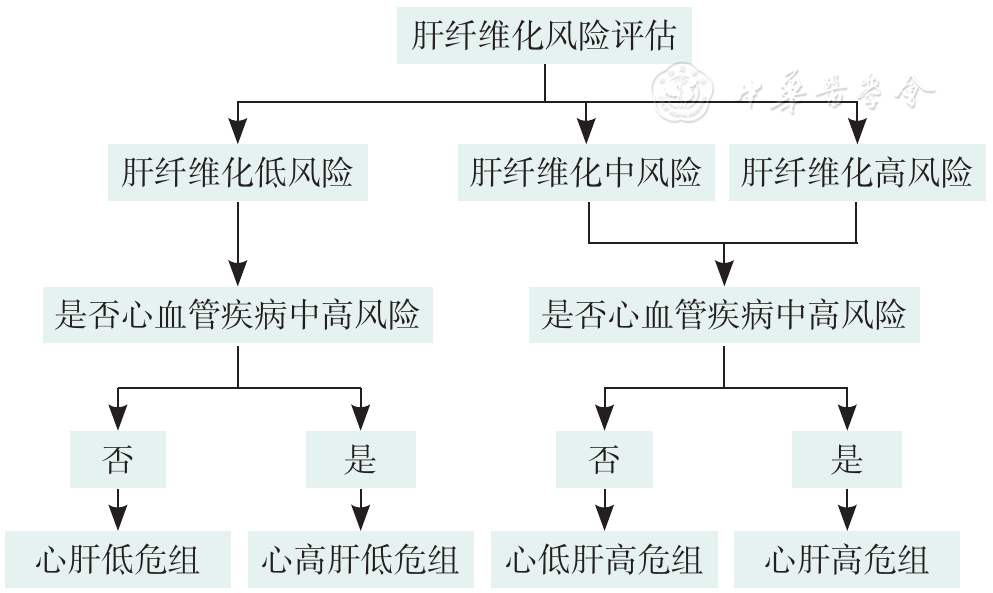
图1 不同肝纤维化风险分组及CVD风险分层流程图注:该流程图肝纤维化风险评估参考2023年美国糖尿病协会及2022年美国肝病学会针对糖尿病人群肝纤维化风险分层标准,将T2DM患者分为肝纤维化低、中、高三个风险等级;由于分组后肝纤维化高风险的人数较少,因此将肝纤维化风险中高风人群进行合并,再将不同肝纤维化风险人群根据心血管疾病风险进一步分为心肝低危组、心肝高危组、心低肝高危组、心高肝低危组。
Figure 1 Flowchart of different liver fibrosis risk groups and stratification of cardiovascular disease risk
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别(男/女) | 年龄(岁) | BMI[M(Q1,Q3),kg/m2] | DBP[M(Q1,Q3),mmHg] | SBP[M(Q1,Q3),mmHg] | ALT[M(Q1,Q3),U/L] | AST[M(Q1,Q3),U/L] | PLT[M(Q1,Q3),×109/L] | TBIL[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肝纤维化低风险组 | 1 235 | 837/398 | 49±11 | 26.0 (23.5,27.8) | 85.00 (78.00,92.00) | 134.38 (123.00,145.00) | 29.00 (18.00,32.00) | 22.00 (16.00,24.70) | 225.00 (191.25,265.00) | 13.06 (9.82,14.60) |
| 肝纤维化中风险组 | 110 | 72/38 | 58±7d | 25.8 (22.7,26.8) | 83.00 (75.00,90.00)d | 132.00 (122.00,139.00) | 28.00 (19.00,31.40) | 24.00 (19.00,27.00)d | 164.00 (146.00,191.00)d | 12.80 (10.30,14.04) |
| 肝纤维化高风险组 | 80 | 41/39 | 59±6d | 26.0 (23.7,27.1) | 82.29 (77.00,89.25) | 135.00 (126.00,148.75) | 31.40 (19.00,53.50)d | 26.50 (24.00,46.50)de | 151.00 (115.00,185.75)d | 13.09 (10.55,16.05) |
| 检验统计量值 | 9.310a | 49.405b | 3.854c | 6.725c | 5.800c | 6.670c | 57.165c | 219.495c | 2.701c | |
| P值 | 0.010 | <0.001 | 0.156 | 0.035 | 0.055 | 0.032 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.259 | |
| 组别 | DBIL[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | HDL-C[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | LDL-C[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | TC[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | TG[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | HbA1c[M(Q1,Q3),%] | 空腹C肽[M(Q1,Q3),pmol/L] | FBG[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | ||
| 肝纤维化低风险组 | 2.70 (2.00,3.00) | 1.10 (0.95,1.20) | 2.87 (2.50,3.25) | 4.93 (4.40,5.41) | 1.90 (1.23,2.41) | 8.40 (7.10,10.00) | 645.00 (461.25,870.90) | 8.07 (6.6,10.79) | ||
| 肝纤维化中风险组 | 2.80 (2.40,3.40)d | 1.10 (0.94,1.26) | 2.78 (2.45,3.07) | 4.77 (4.22,5.25) | 1.71 (1.12,2.30) | 9.00 (7.37,10.10) | 621.80 (456.00,875.00) | 8.06 (6.09,9.78) | ||
| 肝纤维化高风险组 | 2.83 (2.47,3.62)d | 1.13 (0.97,1.27) | 2.59 (1.92,2.95)d | 4.53 (3.81,5.05)d | 1.64 (1.05,2.14) | 9.50 (8.70,10.40)d | 646.00 (471.00,853.50) | 7.43 (6.17,10.40) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | 16.154c | 1.538c | 16.614c | 15.364c | 5.407c | 10.741c | 0.391c | 2.943c | ||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.463 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.067 | 0.005 | 0.822 | 0.230 | ||
| 组别 | HOMA2-IR [M(Q1,Q3)] | UAP [M(Q1,Q3),dB/m] | LSM[M(Q1,Q3),kPa] | FIB4 [M(Q1,Q3)] | FRS[M(Q1,Q3),分] | SMI[M(Q1,Q3),kg/m2] | VFA[M(Q1,Q3),cm2] | 病程[M(Q1,Q3),年] | ||
| 肝纤维化低风险组 | 1.70 (1.20,2.40) | 263.55 (232.27,294.08) | 7.12 (5.68,8.78) | 0.94 (0.70,1.20) | 16.49 (9.88,26.43) | 7.50 (6.80,8.10) | 90.70 (67.72,113.00) | 3.0 (0.5,10.0) | ||
| 肝纤维化中风险组 | 1.50 (1.10,2.30) | 269.45 (241.14,300.34) | 9.35 (8.58,10.18)d | 1.61 (1.45,1.95)d | 23.33 (14.84,30.97) | 7.40 (6.50,7.90)d | 82.20 (64.80,105.00) | 3.0 (0.3,7.0) | ||
| 肝纤维化高风险组 | 1.60 (1.20,2.30) | 279.11 (249.86,310.68)d | 11.62 (8.13,13.32)d | 2.47 (1.54,3.04)d | 24.16 (16.63,33.59) | 7.05 (6.40,7.50)d | 94.90 (64.47,115.52) | 4.0 (0.5,10.0) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | 1.928c | 13.822c | 179.587c | 367.837c | 13.474c | 21.325c | 1.886c | 1.848c | ||
| P值 | 0.381 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.003 | <0.001 | 0.389 | 0.397 | ||
| 组别 | 初发糖尿病[例(%)] | 吸烟史[例(%)] | 饮酒史[例(%)] | 高血压[例(%)] | 肌肉质量减少[例(%)] | 糖尿病视网膜病变[例(%)] | 糖尿病肾病[例(%)] | 糖尿病周围神经病变[例(%)] | 降脂治疗[例(%)] | 降压治疗[例(%)] |
| 肝纤维化低风险组 | 542(46.6) | 308(25.0) | 158(12.8) | 656(53.1) | 142(11.5) | 177(14.3) | 150(12.1) | 317(25.7) | 219(17.7) | 273(22.1) |
| 肝纤维化中风险组 | 48(46.2) | 33(30.0) | 17(15.5) | 58(52.7) | 20(18.2)d | 23(20.9) | 16(14.5) | 37(33.6) | 26(23.6)d | 28(25.5) |
| 肝纤维化高风险组 | 34(44.7) | 22(27.8) | 9(11.4) | 51(63.7) | 17(21.5)d | 18(22.5)de | 16(20.0) | 29(36.3)d | 28(35.0)d | 21(26.3) |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.104a | 1.591a | 0.806a | 3.460a | 10.171a | 6.764a | 4.497a | 7.016a | 16.008a | 1.295a |
| P值 | 0.949 | 0.451 | 0.668 | 0.177 | 0.006 | 0.034 | 0.106 | 0.030 | <0.001 | 0.523 |
表1 不同肝纤维化风险的T2DM患者临床特征比较
Table 1 Comparison of clinical characteristics of T2DM Population with Different Liver Fibrosis Risks
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别(男/女) | 年龄(岁) | BMI[M(Q1,Q3),kg/m2] | DBP[M(Q1,Q3),mmHg] | SBP[M(Q1,Q3),mmHg] | ALT[M(Q1,Q3),U/L] | AST[M(Q1,Q3),U/L] | PLT[M(Q1,Q3),×109/L] | TBIL[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肝纤维化低风险组 | 1 235 | 837/398 | 49±11 | 26.0 (23.5,27.8) | 85.00 (78.00,92.00) | 134.38 (123.00,145.00) | 29.00 (18.00,32.00) | 22.00 (16.00,24.70) | 225.00 (191.25,265.00) | 13.06 (9.82,14.60) |
| 肝纤维化中风险组 | 110 | 72/38 | 58±7d | 25.8 (22.7,26.8) | 83.00 (75.00,90.00)d | 132.00 (122.00,139.00) | 28.00 (19.00,31.40) | 24.00 (19.00,27.00)d | 164.00 (146.00,191.00)d | 12.80 (10.30,14.04) |
| 肝纤维化高风险组 | 80 | 41/39 | 59±6d | 26.0 (23.7,27.1) | 82.29 (77.00,89.25) | 135.00 (126.00,148.75) | 31.40 (19.00,53.50)d | 26.50 (24.00,46.50)de | 151.00 (115.00,185.75)d | 13.09 (10.55,16.05) |
| 检验统计量值 | 9.310a | 49.405b | 3.854c | 6.725c | 5.800c | 6.670c | 57.165c | 219.495c | 2.701c | |
| P值 | 0.010 | <0.001 | 0.156 | 0.035 | 0.055 | 0.032 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.259 | |
| 组别 | DBIL[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | HDL-C[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | LDL-C[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | TC[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | TG[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | HbA1c[M(Q1,Q3),%] | 空腹C肽[M(Q1,Q3),pmol/L] | FBG[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | ||
| 肝纤维化低风险组 | 2.70 (2.00,3.00) | 1.10 (0.95,1.20) | 2.87 (2.50,3.25) | 4.93 (4.40,5.41) | 1.90 (1.23,2.41) | 8.40 (7.10,10.00) | 645.00 (461.25,870.90) | 8.07 (6.6,10.79) | ||
| 肝纤维化中风险组 | 2.80 (2.40,3.40)d | 1.10 (0.94,1.26) | 2.78 (2.45,3.07) | 4.77 (4.22,5.25) | 1.71 (1.12,2.30) | 9.00 (7.37,10.10) | 621.80 (456.00,875.00) | 8.06 (6.09,9.78) | ||
| 肝纤维化高风险组 | 2.83 (2.47,3.62)d | 1.13 (0.97,1.27) | 2.59 (1.92,2.95)d | 4.53 (3.81,5.05)d | 1.64 (1.05,2.14) | 9.50 (8.70,10.40)d | 646.00 (471.00,853.50) | 7.43 (6.17,10.40) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | 16.154c | 1.538c | 16.614c | 15.364c | 5.407c | 10.741c | 0.391c | 2.943c | ||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.463 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.067 | 0.005 | 0.822 | 0.230 | ||
| 组别 | HOMA2-IR [M(Q1,Q3)] | UAP [M(Q1,Q3),dB/m] | LSM[M(Q1,Q3),kPa] | FIB4 [M(Q1,Q3)] | FRS[M(Q1,Q3),分] | SMI[M(Q1,Q3),kg/m2] | VFA[M(Q1,Q3),cm2] | 病程[M(Q1,Q3),年] | ||
| 肝纤维化低风险组 | 1.70 (1.20,2.40) | 263.55 (232.27,294.08) | 7.12 (5.68,8.78) | 0.94 (0.70,1.20) | 16.49 (9.88,26.43) | 7.50 (6.80,8.10) | 90.70 (67.72,113.00) | 3.0 (0.5,10.0) | ||
| 肝纤维化中风险组 | 1.50 (1.10,2.30) | 269.45 (241.14,300.34) | 9.35 (8.58,10.18)d | 1.61 (1.45,1.95)d | 23.33 (14.84,30.97) | 7.40 (6.50,7.90)d | 82.20 (64.80,105.00) | 3.0 (0.3,7.0) | ||
| 肝纤维化高风险组 | 1.60 (1.20,2.30) | 279.11 (249.86,310.68)d | 11.62 (8.13,13.32)d | 2.47 (1.54,3.04)d | 24.16 (16.63,33.59) | 7.05 (6.40,7.50)d | 94.90 (64.47,115.52) | 4.0 (0.5,10.0) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | 1.928c | 13.822c | 179.587c | 367.837c | 13.474c | 21.325c | 1.886c | 1.848c | ||
| P值 | 0.381 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.003 | <0.001 | 0.389 | 0.397 | ||
| 组别 | 初发糖尿病[例(%)] | 吸烟史[例(%)] | 饮酒史[例(%)] | 高血压[例(%)] | 肌肉质量减少[例(%)] | 糖尿病视网膜病变[例(%)] | 糖尿病肾病[例(%)] | 糖尿病周围神经病变[例(%)] | 降脂治疗[例(%)] | 降压治疗[例(%)] |
| 肝纤维化低风险组 | 542(46.6) | 308(25.0) | 158(12.8) | 656(53.1) | 142(11.5) | 177(14.3) | 150(12.1) | 317(25.7) | 219(17.7) | 273(22.1) |
| 肝纤维化中风险组 | 48(46.2) | 33(30.0) | 17(15.5) | 58(52.7) | 20(18.2)d | 23(20.9) | 16(14.5) | 37(33.6) | 26(23.6)d | 28(25.5) |
| 肝纤维化高风险组 | 34(44.7) | 22(27.8) | 9(11.4) | 51(63.7) | 17(21.5)d | 18(22.5)de | 16(20.0) | 29(36.3)d | 28(35.0)d | 21(26.3) |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.104a | 1.591a | 0.806a | 3.460a | 10.171a | 6.764a | 4.497a | 7.016a | 16.008a | 1.295a |
| P值 | 0.949 | 0.451 | 0.668 | 0.177 | 0.006 | 0.034 | 0.106 | 0.030 | <0.001 | 0.523 |
| 项目 | 例数 | 肝纤维化低风险 | 肝纤维化中风险 | 肝纤维化高风险 | χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 55.764 | <0.001 | ||||
| ≤60岁 | 1 072 | 971(90.6) | 59(5.5) | 42(3.9) | ||
| >60岁 | 353 | 264(74.8) | 51(14.5) | 38(10.7) | ||
| BMI | 6.778 | 0.148 | ||||
| <24 kg/m2 | 427 | 365(85.5) | 38(8.9) | 24(5.6) | ||
| 24~28 kg/m2 | 670 | 573(85.5) | 57(8.5) | 40(6.0) | ||
| >28 kg/m2 | 328 | 297(90.5) | 15(4.6) | 16(4.9) | ||
| HbA1c | 14.386 | 0.006 | ||||
| <7% | 339 | 303(89.3) | 25(7.4) | 11(3.3) | ||
| 7%~9% | 517 | 450(87.1) | 45(8.7) | 22(4.2) | ||
| >9% | 569 | 482(84.7) | 40(7.0) | 47(8.3) | ||
| 肝酶异常 | 14.486 | <0.001 | ||||
| 否 | 692 | 616(89.0) | 53(7.7) | 23(3.3) | ||
| 是 | 733 | 619(84.4) | 57(7.8) | 57(7.8) | ||
| 合并肌肉质量减少 | 10.170 | 0.006 | ||||
| 否 | 1 245 | 1 093(87.8) | 90(7.2) | 62(5.0) | ||
| 是 | 180 | 142(78.8) | 20(11.2) | 18(10.0) | ||
表2 不同亚组T2DM患者的肝纤维化风险发生率比较[例(%)]
Table 2 Comparison of the incidence of liver fibrosis risk in different subgroups of T2DM patients
| 项目 | 例数 | 肝纤维化低风险 | 肝纤维化中风险 | 肝纤维化高风险 | χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 55.764 | <0.001 | ||||
| ≤60岁 | 1 072 | 971(90.6) | 59(5.5) | 42(3.9) | ||
| >60岁 | 353 | 264(74.8) | 51(14.5) | 38(10.7) | ||
| BMI | 6.778 | 0.148 | ||||
| <24 kg/m2 | 427 | 365(85.5) | 38(8.9) | 24(5.6) | ||
| 24~28 kg/m2 | 670 | 573(85.5) | 57(8.5) | 40(6.0) | ||
| >28 kg/m2 | 328 | 297(90.5) | 15(4.6) | 16(4.9) | ||
| HbA1c | 14.386 | 0.006 | ||||
| <7% | 339 | 303(89.3) | 25(7.4) | 11(3.3) | ||
| 7%~9% | 517 | 450(87.1) | 45(8.7) | 22(4.2) | ||
| >9% | 569 | 482(84.7) | 40(7.0) | 47(8.3) | ||
| 肝酶异常 | 14.486 | <0.001 | ||||
| 否 | 692 | 616(89.0) | 53(7.7) | 23(3.3) | ||
| 是 | 733 | 619(84.4) | 57(7.8) | 57(7.8) | ||
| 合并肌肉质量减少 | 10.170 | 0.006 | ||||
| 否 | 1 245 | 1 093(87.8) | 90(7.2) | 62(5.0) | ||
| 是 | 180 | 142(78.8) | 20(11.2) | 18(10.0) | ||
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别(男/女) | 年龄(岁) | BMI[M(Q1,Q3),kg/m2] | DBP[M(Q1,Q3),mmHg] | SBP[M(Q1,Q3),mmHg] | ALT[M(Q1,Q3),U/L] | AST[M(Q1,Q3),U/L] | PLT[M(Q1,Q3),×109/L] | TBIL[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 心肝低危组 | 214 | 122/92 | 38±10 | 26.01 (23.37,27.98) | 82.00 (74.00,90.00) | 125.00 (115.00,138.00) | 23.00 (17.00,43.50) | 22.00 (16.00,30.50) | 236.50 (194.00,273.50) | 11.90 (9.35,16.75) |
| 心高肝低危组 | 1 021 | 715/306d | 52±10d | 26.01 (23.56,27.74) | 85.19 (79.00,92.00)d | 135.09 (126.00,146.00)d | 29.00 (18.00,31.40) | 22.00 (16.00,24.70) | 223.00 (191.00,262.00)d | 13.10 (9.98,14.34) |
| 心肝高危组 | 178 | 107/71e | 59±5de | 24.99 (22.24,26.43) | 82.58 (76.00,90.00)e | 133.00 (124.00,144.50)d | 30.00 (19.00,34.50) | 24.70 (21.00,29.50)de | 161.00 (137.00,188.00)de | 12.90 (10.35,14.95) |
| 检验统计量值 | 18.194a | 236.010b | 3.069c | 19.169c | 45.088c | 2.775c | 41.765c | 210.040c | 0.598c | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.216 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.250 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.742 | |
| 组别 | DBIL[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | HDL-C[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | LDL-C[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | TC[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | TG[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | HbA1c[M(Q1,Q3),%] | 空腹C肽[M(Q1,Q3),pmol/L] | FBG[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | ||
| 心肝低危组 | 2.60 (1.90,3.85) | 1.08 (0.92,1.26) | 2.68 (2.02,3.25) | 4.53 (3.84,5.33) | 1.47 (0.99,2.27) | 7.50 (5.80,8.35) | 670.00 (482.50,879.50) | 7.94 (6.18,10.42) | ||
| 心高肝低危组 | 2.70 (2.10,2.99) | 1.10 (0.96,1.18) | 2.89 (2.60,3.26)d | 4.97 (4.55,5.43)d | 1.97 (1.33,2.42)d | 8.70 (7.40,10.20)d | 637.00 (454.00,870.60) | 8.08 (6.67,10.87) | ||
| 心肝高危组 | 2.81 (2.40,3.46)de | 1.11 (0.95,1.23) | 2.72 (2.24,3.04)e | 4.71 (4.15,5.20)e | 1.71 (1.12,2.29) | 9.10 (7.70,10.25)d | 630.00 (459.00,860.00) | 7.71 (5.99,9.91) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | 14.518c | 1.232c | 26.542c | 41.208c | 27.819c | 89.588c | 1.105c | 6.189c | ||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.540 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.575 | 0.103 | ||
| 组别 | HOMA2-IR [M(Q1,Q3)] | UAP [M(Q1,Q3),dB/m] | LSM [M(Q1,Q3),kPa] | FIB4 [M(Q1,Q3)] | FRS [M(Q1,Q3),分] | SMI [M(Q1,Q3),kg/m2] | VFA [M(Q1,Q3),cm2] | 病程[M(Q1,Q3),年] | ||
| 心肝低危组 | 1.70 (1.20,2.40) | 256.34 (229.25,298.91) | 7.44 (5.55,9.25) | 0.69 (0.50,0.95) | 6.35 (4.13,8.71) | 7.44 (6.68,8.03) | 94.90 (72.17,113.30) | 2.0 (0.5,10.0) | ||
| 心高肝低危组 | 1.70 (1.20,2.40) | 263.71 (232.94,292.13) | 7.09 (5.72,8.68) | 0.99 (0.75,1.22)d | 20.00 (13.17,28.94)d | 7.50 (6.90,8.10) | 89.30 (66.60,112.90) | 3.0 (0.5,10.0) | ||
| 心肝高危组 | 1.50 (1.20,2.30) | 269.75 (241.69,304.78)de | 9.80 (8.57,11.37)de | 1.70 (1.46,2.38)de | 24.15 (17.05,33.67)de | 7.30 (6.40,7.80)e | 86.60 (66.50,112.15) | 3.0 (0.3,8.0) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | 1.499c | 10.627c | 179.494c | 411.137c | 427.583c | 16.849c | 2.406c | 1.639c | ||
| P值 | 0.473 | 0.005 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.300 | 0.441 | ||
| 组别 | 初发糖尿病[例(%)] | 吸烟[例(%)] | 饮酒[例(%)] | 高血压[例(%)] | 肌肉质量减少[例(%)] | 糖尿病视网膜病变[例(%)] | 糖尿病肾病[例(%)] | 糖尿病周围神经病变[例(%)] | 降脂治疗[例(%)] | 降压治疗[例(%)] |
| 心肝低危组 | 95(47.50) | 47(22.1) | 35(16.40) | 72(33.60) | 27(12.70) | 38(17.80) | 18(8.40) | 39(18.20) | 32(15.00) | 48(22.40) |
| 心高肝低危组 | 447(46.40) | 261(25.6) | 123(12.00) | 584(57.20)d | 115(11.30) | 193(18.90) | 132(12.90)d | 278(27.30)d | 187(18.30) | 225(22.00) |
| 心肝高危组 | 76(45.00) | 52(29.4) | 26(14.70) | 107(60.50)d | 32(18.10)e | 39(22.00) | 31(17.50)d | 62(35.00)de | 54(28.40)de | 48(27.10) |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.528a | 2.727a | 5.296a | 43.797a | 6.509a | 1.299a | 7.991a | 14.012a | 13.437a | 2.223a |
| P值 | 0.913 | 0.436 | 0.151 | <0.001 | 0.039 | 0.522 | 0.018 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.329 |
表3 不同肝纤维化风险人群根据CVD风险进一步分层的临床特征比较
Table 3 Different liver fibrosis risk populations further categorized based on cardiovascular disease risk
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别(男/女) | 年龄(岁) | BMI[M(Q1,Q3),kg/m2] | DBP[M(Q1,Q3),mmHg] | SBP[M(Q1,Q3),mmHg] | ALT[M(Q1,Q3),U/L] | AST[M(Q1,Q3),U/L] | PLT[M(Q1,Q3),×109/L] | TBIL[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 心肝低危组 | 214 | 122/92 | 38±10 | 26.01 (23.37,27.98) | 82.00 (74.00,90.00) | 125.00 (115.00,138.00) | 23.00 (17.00,43.50) | 22.00 (16.00,30.50) | 236.50 (194.00,273.50) | 11.90 (9.35,16.75) |
| 心高肝低危组 | 1 021 | 715/306d | 52±10d | 26.01 (23.56,27.74) | 85.19 (79.00,92.00)d | 135.09 (126.00,146.00)d | 29.00 (18.00,31.40) | 22.00 (16.00,24.70) | 223.00 (191.00,262.00)d | 13.10 (9.98,14.34) |
| 心肝高危组 | 178 | 107/71e | 59±5de | 24.99 (22.24,26.43) | 82.58 (76.00,90.00)e | 133.00 (124.00,144.50)d | 30.00 (19.00,34.50) | 24.70 (21.00,29.50)de | 161.00 (137.00,188.00)de | 12.90 (10.35,14.95) |
| 检验统计量值 | 18.194a | 236.010b | 3.069c | 19.169c | 45.088c | 2.775c | 41.765c | 210.040c | 0.598c | |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.216 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.250 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.742 | |
| 组别 | DBIL[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | HDL-C[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | LDL-C[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | TC[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | TG[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | HbA1c[M(Q1,Q3),%] | 空腹C肽[M(Q1,Q3),pmol/L] | FBG[M(Q1,Q3),mmol/L] | ||
| 心肝低危组 | 2.60 (1.90,3.85) | 1.08 (0.92,1.26) | 2.68 (2.02,3.25) | 4.53 (3.84,5.33) | 1.47 (0.99,2.27) | 7.50 (5.80,8.35) | 670.00 (482.50,879.50) | 7.94 (6.18,10.42) | ||
| 心高肝低危组 | 2.70 (2.10,2.99) | 1.10 (0.96,1.18) | 2.89 (2.60,3.26)d | 4.97 (4.55,5.43)d | 1.97 (1.33,2.42)d | 8.70 (7.40,10.20)d | 637.00 (454.00,870.60) | 8.08 (6.67,10.87) | ||
| 心肝高危组 | 2.81 (2.40,3.46)de | 1.11 (0.95,1.23) | 2.72 (2.24,3.04)e | 4.71 (4.15,5.20)e | 1.71 (1.12,2.29) | 9.10 (7.70,10.25)d | 630.00 (459.00,860.00) | 7.71 (5.99,9.91) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | 14.518c | 1.232c | 26.542c | 41.208c | 27.819c | 89.588c | 1.105c | 6.189c | ||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.540 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.575 | 0.103 | ||
| 组别 | HOMA2-IR [M(Q1,Q3)] | UAP [M(Q1,Q3),dB/m] | LSM [M(Q1,Q3),kPa] | FIB4 [M(Q1,Q3)] | FRS [M(Q1,Q3),分] | SMI [M(Q1,Q3),kg/m2] | VFA [M(Q1,Q3),cm2] | 病程[M(Q1,Q3),年] | ||
| 心肝低危组 | 1.70 (1.20,2.40) | 256.34 (229.25,298.91) | 7.44 (5.55,9.25) | 0.69 (0.50,0.95) | 6.35 (4.13,8.71) | 7.44 (6.68,8.03) | 94.90 (72.17,113.30) | 2.0 (0.5,10.0) | ||
| 心高肝低危组 | 1.70 (1.20,2.40) | 263.71 (232.94,292.13) | 7.09 (5.72,8.68) | 0.99 (0.75,1.22)d | 20.00 (13.17,28.94)d | 7.50 (6.90,8.10) | 89.30 (66.60,112.90) | 3.0 (0.5,10.0) | ||
| 心肝高危组 | 1.50 (1.20,2.30) | 269.75 (241.69,304.78)de | 9.80 (8.57,11.37)de | 1.70 (1.46,2.38)de | 24.15 (17.05,33.67)de | 7.30 (6.40,7.80)e | 86.60 (66.50,112.15) | 3.0 (0.3,8.0) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | 1.499c | 10.627c | 179.494c | 411.137c | 427.583c | 16.849c | 2.406c | 1.639c | ||
| P值 | 0.473 | 0.005 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.300 | 0.441 | ||
| 组别 | 初发糖尿病[例(%)] | 吸烟[例(%)] | 饮酒[例(%)] | 高血压[例(%)] | 肌肉质量减少[例(%)] | 糖尿病视网膜病变[例(%)] | 糖尿病肾病[例(%)] | 糖尿病周围神经病变[例(%)] | 降脂治疗[例(%)] | 降压治疗[例(%)] |
| 心肝低危组 | 95(47.50) | 47(22.1) | 35(16.40) | 72(33.60) | 27(12.70) | 38(17.80) | 18(8.40) | 39(18.20) | 32(15.00) | 48(22.40) |
| 心高肝低危组 | 447(46.40) | 261(25.6) | 123(12.00) | 584(57.20)d | 115(11.30) | 193(18.90) | 132(12.90)d | 278(27.30)d | 187(18.30) | 225(22.00) |
| 心肝高危组 | 76(45.00) | 52(29.4) | 26(14.70) | 107(60.50)d | 32(18.10)e | 39(22.00) | 31(17.50)d | 62(35.00)de | 54(28.40)de | 48(27.10) |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.528a | 2.727a | 5.296a | 43.797a | 6.509a | 1.299a | 7.991a | 14.012a | 13.437a | 2.223a |
| P值 | 0.913 | 0.436 | 0.151 | <0.001 | 0.039 | 0.522 | 0.018 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.329 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
中华医学会内分泌学分会,中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国成人2型糖尿病合并非酒精性脂肪性肝病管理专家共识[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志,2021,37(7):589-598.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Summary of revisions:standards of medical care in diabetes-2022[J]. Diabetes Care,2022,45(Suppl 1):S4-7.
|
| [6] |
中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2021,13(4):315-409.
|
| [7] |
中华医学会肝病学分会脂肪肝和酒精性肝病学组. 中国非酒精性脂肪性肝病诊疗指南(2010年修订版)[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2012,4(7):4-10.
|
| [8] |
中华医学会肝病学分会,中华医学会消化病学分会,中华医学会感染病学分会. 肝纤维化诊断及治疗共识(2019年)[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志,2019,22(6):793-803.
|
| [9] |
仲维莉,邹国良. 初发与血糖控制不佳的2型糖尿病患者应用门冬胰岛素30注射液强化治疗的效果及安全性比较[J]. 中国医药,2019,14(2):242-245. DOI:10.3760/j.issn.1673-4777.2019.02.021.
|
| [10] |
翁心植,邱鹤庚. 世界卫生组织(WHO)关于吸烟情况调查方法标准化的建议(节译)[J]. 心肺血管病杂志,1984(1):21-26.
|
| [11] |
曹清明,王蔚婕,张琳,等. 中国居民平衡膳食模式的践行——《中国居民膳食指南(2022)》解读[J]. 食品与机械,2022,38(6):22-29. DOI:10.13652/j.spjx.1003.5788.2022.60050.
|
| [12] |
刘娟,丁清清,周白瑜,等. 中国老年人肌少症诊疗专家共识(2021)[J]. 中华老年医学杂志,2021,40(8):943-952. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-9026.2021.08.001.
|
| [13] |
中华医学会肝病学分会,中华医学会消化病学分会,中华医学会感染病学分会. 肝纤维化诊断及治疗共识(2019年)[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志,2019,27(9):657-667.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
Americal College of Cardiology, Americal Heart Association. Reprint:2013 AHA/ACC guideline on lifestyle management to reduce cardiovascular risk[J]. J Am Pharm Assoc,2014,54(1):e2. DOI:10.1331/japha.2014.14501.
|
| [16] |
中国血脂管理指南修订联合专家委员会. 中国血脂管理指南(2023年)[J]. 中国循环杂志,2023,38(3):237-271. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2023.03.001.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [1] | 卓莉莉, 瞿欢佳, 张秋玲. 2型糖尿病与肥胖对纤维化4指数筛查非酒精性脂肪性肝病早期肝纤维化影响的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(11): 1354-1360. |
| [2] | 李弈晴, 程桂荣, 许浪, 胡晨璐, 李春利, 李露寒. 生活方式在心血管代谢性疾病患病时长与轻度认知功能障碍关联中的作用研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(11): 1329-1335. |
| [3] | 孔晓倩, 王婧怡, 王莉, 毛婷, 夏文婧, 施雁. 山区农村老年人急性心脑血管事件目击情境真实体验的质性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(11): 1342-1346. |
| [4] | 郑晓梦, 周旋, 孙雨, 范苗, 金依依, 朱素燕. 心血管代谢性共病患者的临床特征及用药特点研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(09): 1061-1064. |
| [5] | 王媛, 肖斐, 张宇馨, 周恩慧, 钟建琴, 胡宇欣, 洪峰. 少数民族特色饮食与心血管疾病的关系:基于西南区域少数民族聚集地世居自然人群队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(06): 688-696. |
| [6] | 刘明波, 何新叶, 杨晓红, 王增武. 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2023》要点解读[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(01): 20-38. |
| [7] | 李婕, 丁虎. 脂蛋白a在心血管疾病中的研究新进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(36): 4505-4514. |
| [8] | 张俊, 罗雯, 王绿娅, 杨娅, 陈彦. 综合医院血脂管理门诊模式建设探索与实践[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(36): 4527-4533. |
| [9] | 张龙, 李建平. 立足分级诊疗的血脂异常管控体系的建立与推广[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(36): 4493-4497. |
| [10] | 周伊恒, 杨梓钰, 吕垚, 刘力滴, 沈灿, 廖晓阳, 贾禹. 《人工智能在心血管疾病中的应用科学声明》解读[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(35): 4353-4357. |
| [11] | 李一光, 刘荷君, 赵锦鹏, 冯焱, 徐银兰. 碳水化合物对心血管疾病风险因素影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(34): 4341-4349. |
| [12] | 刘忠典, 许琪, 陈伊静, 覃玲巧, 陈淑萍, 唐薇婷, 钟秋安. 心血管疾病中高风险人群颈动脉粥样硬化的识别:基于机器学习的预测模型及验证[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(30): 3763-3771. |
| [13] | 任凌萱, 卢子琪, 齐威, 冯志杰. 基于单细胞转录组学测序的巨噬细胞在肝硬化-肝癌疾病进展中的功能研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(29): 3654-3663. |
| [14] | 郁海东, 潘苗苗, 顾红琴, 刘涛, 戴洁, 刘玲华, 侯俊平, 杨丽, 施美芳, 赵超. 社区老年人抑郁和认知状况与营养代谢的关联性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(28): 3540-3545. |
| [15] | 左仲琪, 王宇, 靳艳, 张庆伟, 袁彬彬, 沈赛娅, 王菲, 于漫. 心血管疾病风险早期预警评估工具的范围综述[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(27): 3440-3445. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





