中国全科医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (03): 335-345.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0108
所属专题: 运动相关研究最新文章合辑; 肥胖最新文章合辑
收稿日期:2024-03-20
修回日期:2024-05-25
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2024-10-28
通讯作者:
谭思洁, 杨风英
作者贡献:
卢冬磊负责数据收集整理、选题、文章撰写,对整体文章负责;谭思洁负责数据收集整理、论文评估;杨风英负责论文思路、框架的把握。
基金资助:
LU Donglei1,2, TAN Sijie1,*( ), YANG Fengying3,*(
), YANG Fengying3,*( )
)
Received:2024-03-20
Revised:2024-05-25
Published:2025-01-20
Online:2024-10-28
Contact:
TAN Sijie, YANG Fengying
摘要: 背景 研究证实,超重或肥胖人群体质(体成分、心肺耐力、脂质代谢)与肥胖密切相关,并可能存在双向关联。最大脂肪氧化强度(FATmax)运动作为一种新型运动干预手段,可有效促进体质改善,但改善效果的量化关系需要进一步探讨。 目的 系统评价FATmax运动对超重或肥胖人群体质相关指标的干预效果。 方法 检索PubmMed、Web of Science、EBSCO、中国知网、维普网、万方数据知识服务平台,检索FATmax运动对超重或肥胖患者身体成分、心肺耐力、脂质代谢相关指标干预效果的随机对照试验,检索时间为2001年1月—2024年1月。基于Cochrane风险偏倚评估工具评估纳入文献的质量,Meta分析由RevMan 5.4软件完成。 结果 共纳入16项随机对照试验,包含568例超重或肥胖患者。Meta分析结果显示,与对照组相比,FATmax运动干预组身体成分[BMI:WMD=-1.82,P<0.01;体脂百分比(BFR):WMD=-2.86,P<0.01;腰臀比(WHR):WMD=-0.04,P<0.01]、心肺耐力[最大摄氧量(VO2max):WMD=3.34,P<0.01],除总胆固醇(TC)外脂质代谢状况[三酰甘油(TG):WMD=-0.24,P<0.05;高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C):WMD=0.14,P<0.05;低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C):WMD=-0.27,P<0.05]显著改善。经亚组分析得出最佳干预方案为:干预周期≥12周,3~5次/周的训练,60 min/次的跑步,以优化身体成分;而提升VO2max的最佳方案为5次/周、<60 min/次的组合运动。在脂质代谢方面,对TG的改善最佳方案为3次/周、60 min/次的跑步;对HDL-C的最佳改善方案为4次/周、60 min/次的组合运动;对LDL-C则是4次/周、>60 min/次的组合运动。 结论 FATmax运动可显著改善超重或肥胖患者BMI、BFR、WHR、VO2max、TG、HDL-C、LDL-C结局指标,但对TC并无改善作用。
中图分类号:
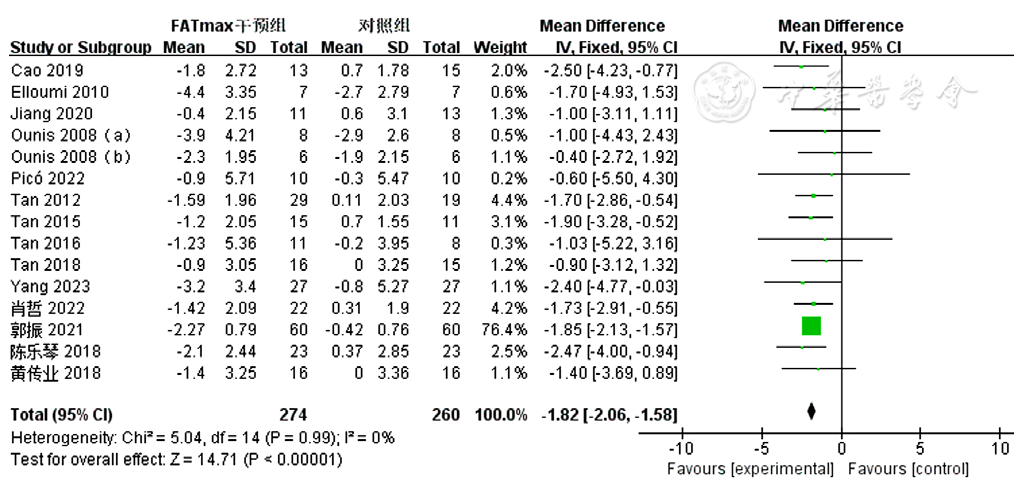
图4 FATmax运动组对超重或肥胖患者BMI影响的Meta分析森林图
Figure 4 Meta-analytsis forest plot of the effect of BMI in overweight or obese patients in the FATmax exercise cohort
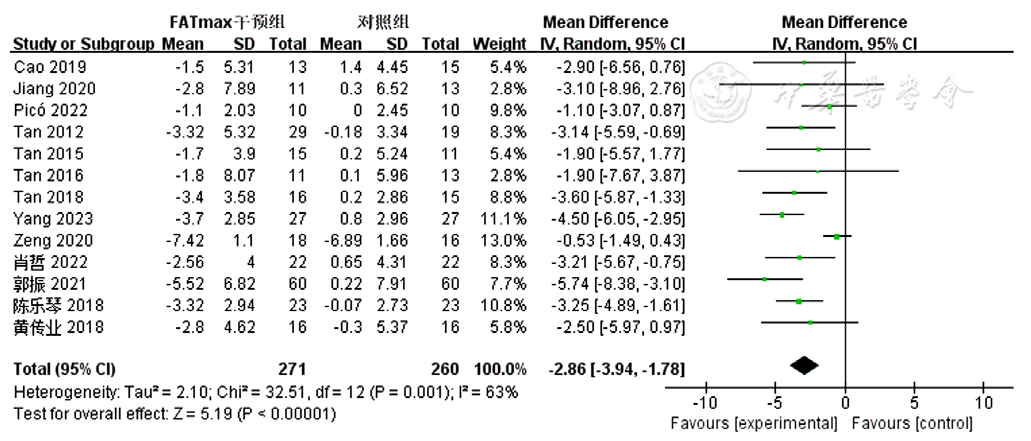
图5 FATmax运动组对超重或肥胖患者BFR影响的Meta分析森林图
Figure 5 Meta-analytsis forest plot of the effect of BFR in FATmax exercise cohort of overweight or obese patients
| 指标 | 剔除文献 | 纳入文献 | 患者数(例) | WMD(95%CI) | P值 | I2值 | P值异质性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BFR | [ | [ | 253 | -3.32(-4.02,-2.61) | <0.001 | 4% | 0.40 |
表1 BFR敏感性分析结果
Table 1 BFR sensitivity analysis results
| 指标 | 剔除文献 | 纳入文献 | 患者数(例) | WMD(95%CI) | P值 | I2值 | P值异质性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BFR | [ | [ | 253 | -3.32(-4.02,-2.61) | <0.001 | 4% | 0.40 |
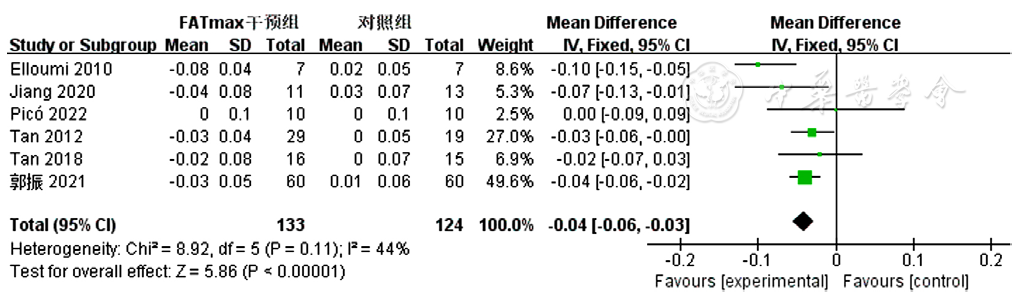
图6 FATmax运动组对超重或肥胖患者WHR影响的Meta分析森林图
Figure 6 Forest plot of Meta-analysis of the effect of WHR in FATmax exercise cohort of overweight or obese patients
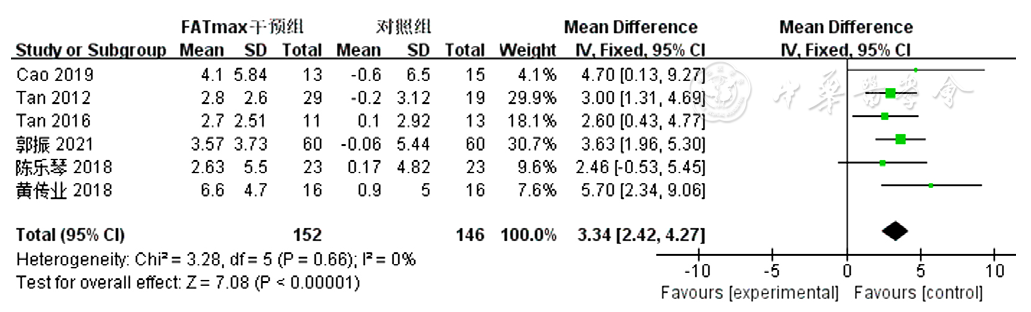
图7 FATmax运动组对超重或肥胖患者VO2max影响的Meta分析森林图
Figure 7 Meta-analytsis forest plot of the effect of VO2max in overweight or obese patients in the FATmax exercise cohort
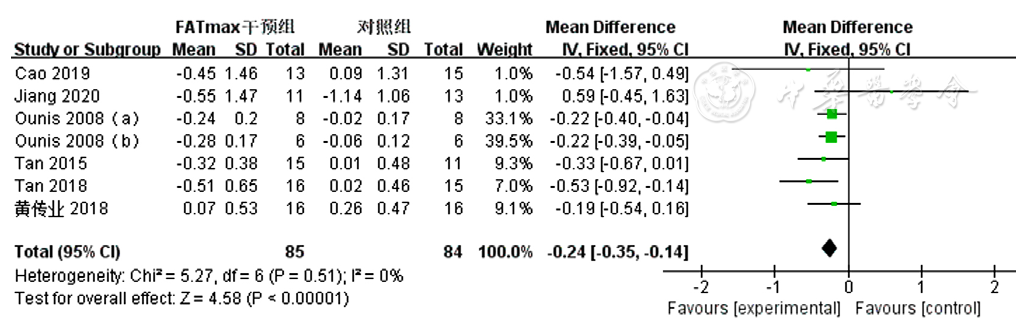
图8 FATmax运动组对超重或肥胖患者TG影响的Meta分析森林图
Figure 8 Meta-analytsis forest plot of the effect of TG in overweight or obese patients in the FATmax exercise cohort
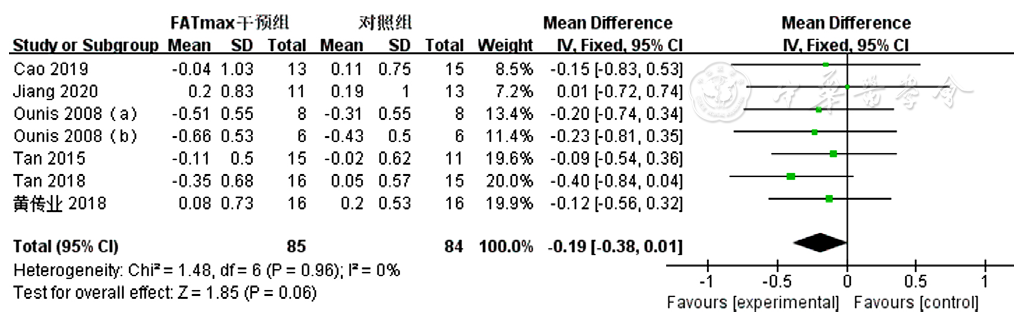
图9 FATmax运动组对超重或肥胖患者TC影响的Meta分析森林图
Figure 9 Meta-analytsis forest plot of the effect of TC in overweight or obese patients in the FATmax exercise cohort
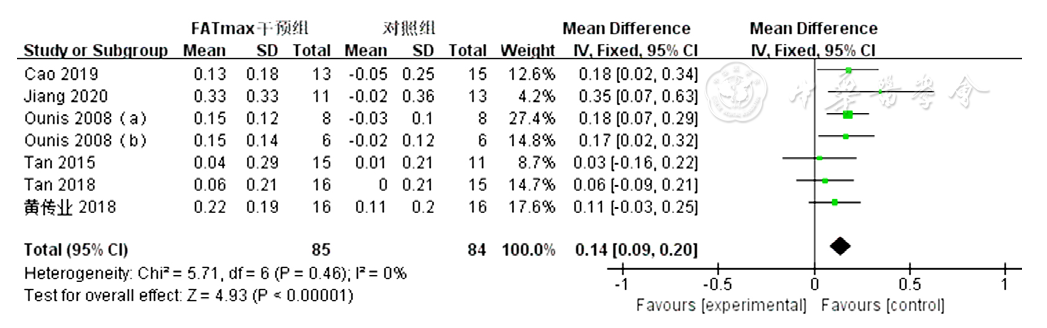
图10 FATmax运动组对超重或肥胖患者HDL-C影响的Meta分析森林图
Figure 10 Meta-analytsis forest plot of the effect of HDL-C in overweight or obese patients in the FATmax exercise cohort
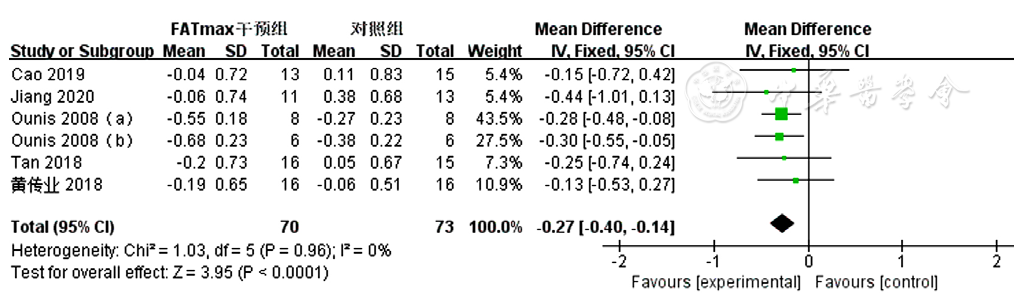
图11 FATmax运动组对超重或肥胖患者LDL-C影响的Meta分析森林图
Figure 11 Forest plot of Meta-analysis of the effect of LDL-C in FATmax exercise cohort of overweight or obese patients
| 指标 | 影响因素 | 分组 | 研究数量(篇) | 研究对象(例) | WMD(95%CI) | P值 | 异质性 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2值(%) | P值 | |||||||
| BMI | 干预周期 | ≥12周 | 9 | 191 | -1.86(-2.11~-1.60) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.93 |
| <12周 | 6 | 83 | -1.53(-2.26~-0.8) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.94 | ||
| 训练频率 | 3次/周 | 6 | 107 | -1.85(-2.49~-1.22) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.77 | |
| 4次/周 | 6 | 80 | -1.55(-2.42~-0.67) | 0.000 5 | 0 | 0.88 | ||
| 5次/周 | 3 | 87 | -1.84(-2.11~-1.57) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.86 | ||
| 单次干预时长 | >60 min | 4 | 31 | -0.85(-2.42~0.71) | 0.290 | 0 | 0.93 | |
| 60 min | 10 | 227 | -1.85(-2.10~-1.60) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.97 | ||
| <60 min | 1 | 16 | -1.40(-3.11~0.31) | 0.110 | ||||
| 运动形式 | 跑步 | 9 | 204 | -1.83(-2.08~-1.58) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.97 | |
| 组合运动 | 6 | 70 | -1.63(-2.61~-0.64) | 0.001 | 0 | 0.77 | ||
| BFR | 干预周期 | ≥12周 | 9 | 191 | -3.37(-4.15~-2.59) | 0.000 1 | 29 | 0.19 |
| <12周 | 3 | 62 | -3.07(-4.73~-1.41) | 0.000 3 | 0 | 0.92 | ||
| 训练频率 | 3次/周 | 6 | 107 | -3.16(-4.21~-2.11) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.99 | |
| 4次/周 | 3 | 59 | -2.99(-5.12~-0.85) | <0.001 | 72 | 0.03 | ||
| 5次/周 | 3 | 87 | -3.99(-6.49~-1.50) | <0.01 | 29 | 0.24 | ||
| 单次干预时长 | >60 min | 1 | 10 | -1.10(-3.07~0.87) | 0.270 | |||
| 60 min | 10 | 227 | -3.70(-4.47~-2.92) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.79 | ||
| <60 min | 1 | 16 | -2.50(-5.97~0.97) | 0.160 | ||||
| 运动形式 | 跑步 | 9 | 204 | -3.83(-4.71~-2.95) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.75 | |
| 组合运动 | 3 | 49 | -2.39(-3.57~-1.20) | <0.001 | 26 | 0.26 | ||
| WHR | 干预周期 | ≥12周 | 4 | 97 | -0.04(-0.06~-0.02) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.65 |
| <12周 | 2 | 36 | -0.06(-0.13~0.01) | 0.07 | 84 | 0.01 | ||
| 训练频率 | 3次/周 | 3 | 56 | -0.03(-0.06~-0.01) | 0.003 | 0 | 0.43 | |
| 4次/周 | 2 | 17 | -0.06(-0.15~-0.04) | 0.250 | 74 | 0.05 | ||
| 5次/周 | 1 | 60 | -0.04(-0.06~-0.02) | <0.001 | ||||
| 单次干预时长 | >60 min | 2 | 17 | -0.02(-0.06~0.02) | 0.310 | 0 | 0.58 | |
| 60 min | 4 | 116 | -0.05(-0.08~-0.02) | 0.005 | 60 | 0.06 | ||
| <60 min | ||||||||
| 运动形式 | 跑步 | 4 | 116 | -0.04(-0.05~-0.02) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.60 | |
| 组合运动 | 2 | 17 | -0.06(-0.15~0.04) | 0.250 | 74 | 0.05 | ||
| VO2max | 干预周期 | ≥12周 | 4 | 112 | 3.80(2.52~5.08) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.53 |
| <12周 | 2 | 40 | 2.85(1.51~4.18) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.78 | ||
| 训练频率 | 3次/周 | 3 | 65 | 3.04(1.64~4.44) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.72 | |
| 4次/周 | ||||||||
| 5次/周 | 3 | 87 | 3.58(2.35~4.81) | <0.001 | 14 | 0.31 | ||
| 单次干预时长 | >60 min | |||||||
| 60 min | 5 | 136 | 3.28(2.21~4.36) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.74 | ||
| <60 min | 1 | 16 | 5.70(2.34~9.06) | 0.000 9 | ||||
| 运动形式 | 跑步 | 4 | 113 | 3.23(2.21~4.25) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.80 | |
| 组合运动 | 2 | 39 | 3.70(-0.06~7.46) | 0.050 | 64 | 0.09 | ||
| TG | 干预周期 | ≥12周 | 5 | 71 | -0.31(-0.51~-0.11) | 0.002 | 15 | 0.32 |
| <12周 | 2 | 14 | -0.22(-0.34~-0.10) | 0.000 4 | 0 | 1.00 | ||
| 训练频率 | 3次/周 | 4 | 55 | -0.37(-0.61~-0.12) | 0.003 | 26 | 0.26 | |
| 4次/周 | 2 | 14 | -0.22(-0.34~-0.10) | 0.000 4 | 0 | 1.00 | ||
| 5次/周 | 1 | 16 | -0.19(-0.54~0.16) | 0.280 | ||||
| 单次干预时长 | >60 min | 2 | 14 | -0.22(-0.34~-0.10) | 0.000 4 | 0 | 1.00 | |
| 60 min | 4 | 55 | -0.37(-0.61~-0.12) | 0.003 | 26 | 0.26 | ||
| <60 min | 1 | 16 | -0.19(-0.54~0.16) | 0.28 | ||||
| 运动形式 | 跑步 | 4 | 55 | -0.37(-0.61~-0.12) | 0.003 | 26 | 0.26 | |
| 组合运动 | 3 | 30 | -0.22(-0.33~-0.10) | 0.000 2 | 0 | 0.99 | ||
| HDL-C | 干预周期 | ≥12周 | 5 | 71 | 0.12(0.04~0.19) | 0.002 | 15 | 0.32 |
| <12周 | 2 | 14 | 0.18(0.09~0.26) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.91 | ||
| 训练频率 | 3次/周 | 4 | 55 | 0.12(0.03~0.21) | 0.008 | 36 | 0.20 | |
| 4次/周 | 2 | 14 | 0.18(0.09~0.26) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.91 | ||
| 5次/周 | 1 | 16 | 0.11(-0.03~0.25) | 0.110 | ||||
| 单次干预时长 | >60 min | 2 | 14 | 0.18(0.09~0.26) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.91 | |
| 60 min | 4 | 55 | 0.12(0.03~0.21) | 0.008 | 36 | 0.20 | ||
| <60 min | 1 | 16 | 0.11(-0.03~0.25) | 0.110 | ||||
| 运动形式 | 跑步 | 4 | 55 | 0.12(0.03~0.21) | 0.008 | 36 | 0.20 | |
| 组合运动 | 3 | 30 | 0.16(0.08~0.23) | <0.01 | 0 | 0.72 | ||
| LDL-C | 干预周期 | ≥12周 | 4 | 56 | -0.22(-0.47~0.03) | 0.080 | 0 | 0.84 |
| <12周 | 2 | 14 | -0.29(-0.45~-0.13) | 0.000 4 | 0 | 0.90 | ||
| 训练频率 | 3次/周 | 3 | 40 | -0.28(-0.59~0.04) | 0.080 | 0 | 0.77 | |
| 4次/周 | 2 | 14 | -0.29(-0.45~-0.13) | 0.000 4 | 0 | 0.90 | ||
| 5次/周 | 1 | 16 | -0.13(-0.53~0.27) | 0.530 | ||||
| 单次干预时长 | >60 min | 2 | 14 | -0.29(-0.45~-0.13) | 0.000 4 | 0 | 0.90 | |
| 60 min | 3 | 40 | -0.28(-0.59~0.04) | 0.080 | 0 | 0.77 | ||
| <60 min | 1 | 16 | -0.13(-0.53~0.27) | 0.530 | ||||
| 运动形式 | 跑步 | 3 | 40 | -0.28(-0.59~0.04) | 0.080 | 0 | 0.77 | |
| 组合运动 | 3 | 30 | -0.27(-0.40~-0.12) | 0.000 4 | 0 | 0.77 | ||
表2 各结局指标敏感性及亚组分析结果
Table 2 Sensitivity and subgroup analysis results of various outcome indicators
| 指标 | 影响因素 | 分组 | 研究数量(篇) | 研究对象(例) | WMD(95%CI) | P值 | 异质性 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2值(%) | P值 | |||||||
| BMI | 干预周期 | ≥12周 | 9 | 191 | -1.86(-2.11~-1.60) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.93 |
| <12周 | 6 | 83 | -1.53(-2.26~-0.8) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.94 | ||
| 训练频率 | 3次/周 | 6 | 107 | -1.85(-2.49~-1.22) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.77 | |
| 4次/周 | 6 | 80 | -1.55(-2.42~-0.67) | 0.000 5 | 0 | 0.88 | ||
| 5次/周 | 3 | 87 | -1.84(-2.11~-1.57) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.86 | ||
| 单次干预时长 | >60 min | 4 | 31 | -0.85(-2.42~0.71) | 0.290 | 0 | 0.93 | |
| 60 min | 10 | 227 | -1.85(-2.10~-1.60) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.97 | ||
| <60 min | 1 | 16 | -1.40(-3.11~0.31) | 0.110 | ||||
| 运动形式 | 跑步 | 9 | 204 | -1.83(-2.08~-1.58) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.97 | |
| 组合运动 | 6 | 70 | -1.63(-2.61~-0.64) | 0.001 | 0 | 0.77 | ||
| BFR | 干预周期 | ≥12周 | 9 | 191 | -3.37(-4.15~-2.59) | 0.000 1 | 29 | 0.19 |
| <12周 | 3 | 62 | -3.07(-4.73~-1.41) | 0.000 3 | 0 | 0.92 | ||
| 训练频率 | 3次/周 | 6 | 107 | -3.16(-4.21~-2.11) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.99 | |
| 4次/周 | 3 | 59 | -2.99(-5.12~-0.85) | <0.001 | 72 | 0.03 | ||
| 5次/周 | 3 | 87 | -3.99(-6.49~-1.50) | <0.01 | 29 | 0.24 | ||
| 单次干预时长 | >60 min | 1 | 10 | -1.10(-3.07~0.87) | 0.270 | |||
| 60 min | 10 | 227 | -3.70(-4.47~-2.92) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.79 | ||
| <60 min | 1 | 16 | -2.50(-5.97~0.97) | 0.160 | ||||
| 运动形式 | 跑步 | 9 | 204 | -3.83(-4.71~-2.95) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.75 | |
| 组合运动 | 3 | 49 | -2.39(-3.57~-1.20) | <0.001 | 26 | 0.26 | ||
| WHR | 干预周期 | ≥12周 | 4 | 97 | -0.04(-0.06~-0.02) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.65 |
| <12周 | 2 | 36 | -0.06(-0.13~0.01) | 0.07 | 84 | 0.01 | ||
| 训练频率 | 3次/周 | 3 | 56 | -0.03(-0.06~-0.01) | 0.003 | 0 | 0.43 | |
| 4次/周 | 2 | 17 | -0.06(-0.15~-0.04) | 0.250 | 74 | 0.05 | ||
| 5次/周 | 1 | 60 | -0.04(-0.06~-0.02) | <0.001 | ||||
| 单次干预时长 | >60 min | 2 | 17 | -0.02(-0.06~0.02) | 0.310 | 0 | 0.58 | |
| 60 min | 4 | 116 | -0.05(-0.08~-0.02) | 0.005 | 60 | 0.06 | ||
| <60 min | ||||||||
| 运动形式 | 跑步 | 4 | 116 | -0.04(-0.05~-0.02) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.60 | |
| 组合运动 | 2 | 17 | -0.06(-0.15~0.04) | 0.250 | 74 | 0.05 | ||
| VO2max | 干预周期 | ≥12周 | 4 | 112 | 3.80(2.52~5.08) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.53 |
| <12周 | 2 | 40 | 2.85(1.51~4.18) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.78 | ||
| 训练频率 | 3次/周 | 3 | 65 | 3.04(1.64~4.44) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.72 | |
| 4次/周 | ||||||||
| 5次/周 | 3 | 87 | 3.58(2.35~4.81) | <0.001 | 14 | 0.31 | ||
| 单次干预时长 | >60 min | |||||||
| 60 min | 5 | 136 | 3.28(2.21~4.36) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.74 | ||
| <60 min | 1 | 16 | 5.70(2.34~9.06) | 0.000 9 | ||||
| 运动形式 | 跑步 | 4 | 113 | 3.23(2.21~4.25) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.80 | |
| 组合运动 | 2 | 39 | 3.70(-0.06~7.46) | 0.050 | 64 | 0.09 | ||
| TG | 干预周期 | ≥12周 | 5 | 71 | -0.31(-0.51~-0.11) | 0.002 | 15 | 0.32 |
| <12周 | 2 | 14 | -0.22(-0.34~-0.10) | 0.000 4 | 0 | 1.00 | ||
| 训练频率 | 3次/周 | 4 | 55 | -0.37(-0.61~-0.12) | 0.003 | 26 | 0.26 | |
| 4次/周 | 2 | 14 | -0.22(-0.34~-0.10) | 0.000 4 | 0 | 1.00 | ||
| 5次/周 | 1 | 16 | -0.19(-0.54~0.16) | 0.280 | ||||
| 单次干预时长 | >60 min | 2 | 14 | -0.22(-0.34~-0.10) | 0.000 4 | 0 | 1.00 | |
| 60 min | 4 | 55 | -0.37(-0.61~-0.12) | 0.003 | 26 | 0.26 | ||
| <60 min | 1 | 16 | -0.19(-0.54~0.16) | 0.28 | ||||
| 运动形式 | 跑步 | 4 | 55 | -0.37(-0.61~-0.12) | 0.003 | 26 | 0.26 | |
| 组合运动 | 3 | 30 | -0.22(-0.33~-0.10) | 0.000 2 | 0 | 0.99 | ||
| HDL-C | 干预周期 | ≥12周 | 5 | 71 | 0.12(0.04~0.19) | 0.002 | 15 | 0.32 |
| <12周 | 2 | 14 | 0.18(0.09~0.26) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.91 | ||
| 训练频率 | 3次/周 | 4 | 55 | 0.12(0.03~0.21) | 0.008 | 36 | 0.20 | |
| 4次/周 | 2 | 14 | 0.18(0.09~0.26) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.91 | ||
| 5次/周 | 1 | 16 | 0.11(-0.03~0.25) | 0.110 | ||||
| 单次干预时长 | >60 min | 2 | 14 | 0.18(0.09~0.26) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.91 | |
| 60 min | 4 | 55 | 0.12(0.03~0.21) | 0.008 | 36 | 0.20 | ||
| <60 min | 1 | 16 | 0.11(-0.03~0.25) | 0.110 | ||||
| 运动形式 | 跑步 | 4 | 55 | 0.12(0.03~0.21) | 0.008 | 36 | 0.20 | |
| 组合运动 | 3 | 30 | 0.16(0.08~0.23) | <0.01 | 0 | 0.72 | ||
| LDL-C | 干预周期 | ≥12周 | 4 | 56 | -0.22(-0.47~0.03) | 0.080 | 0 | 0.84 |
| <12周 | 2 | 14 | -0.29(-0.45~-0.13) | 0.000 4 | 0 | 0.90 | ||
| 训练频率 | 3次/周 | 3 | 40 | -0.28(-0.59~0.04) | 0.080 | 0 | 0.77 | |
| 4次/周 | 2 | 14 | -0.29(-0.45~-0.13) | 0.000 4 | 0 | 0.90 | ||
| 5次/周 | 1 | 16 | -0.13(-0.53~0.27) | 0.530 | ||||
| 单次干预时长 | >60 min | 2 | 14 | -0.29(-0.45~-0.13) | 0.000 4 | 0 | 0.90 | |
| 60 min | 3 | 40 | -0.28(-0.59~0.04) | 0.080 | 0 | 0.77 | ||
| <60 min | 1 | 16 | -0.13(-0.53~0.27) | 0.530 | ||||
| 运动形式 | 跑步 | 3 | 40 | -0.28(-0.59~0.04) | 0.080 | 0 | 0.77 | |
| 组合运动 | 3 | 30 | -0.27(-0.40~-0.12) | 0.000 4 | 0 | 0.77 | ||
| [1] | |
| [2] |
冷正清,阿力木江·依米提·塔尔肯. 中国2014—2020年7~12岁儿童生长趋势及超重肥胖状况分析[J]. 中国全科医学,2024,27(1):36-44,58. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0203.
|
| [3] | |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
GBD Diabetes Collaborators. Global,regional,and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021,with projections of prevalence to 2050:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021[J]. Lancet,2023,402(10397):203-234. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01301-6.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
谭思洁,郭振,曹立全,等. 9~10岁肥胖男童最大脂肪氧化强度运动减重处方的研究[J]. 体育科学,2016,36(9):36-39,53. DOI:10.16469/j.css.201609005.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
肖哲,朱欢,胡江平,等. 10周有氧运动和有氧结合抗阻运动对肥胖大学生微循环功能的影响及机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2022,25(19):2349-2355,2362. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0118.
|
| [26] |
郭振,谭思洁. 持续12周运动减重方案对青年男性肥胖者心肺机能影响的研究[J]. 天津体育学院学报,2021,36(4):490-496. DOI:10.13297/j.cnki.issn1005-0000.2021.04.018.
|
| [27] |
陈乐琴. 16周有氧健身操运动干预对超重女大学生脂肪氧化动力学影响研究[J]. 沈阳体育学院学报,2018,37(5):87-91. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-0560.2018.05.015.
|
| [28] |
黄传业,潘明玲,章岚,等. 最大脂肪氧化强度运动对超重/肥胖青年男子动脉硬度的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2018,37(1):3-9. DOI:10.16038/j.1000-6710.2018.01.001.
|
| [29] |
郝丽鑫,张兵,王惠君,等. 1989—2018年我国15个省(自治区、直辖市)18~35岁成年人超重和肥胖变化趋势及流行特征[J]. 环境与职业医学,2022,39(5):471-477. DOI:10.11836/JEOM21386.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
李盈盈,黄丽,彭莉. 肥胖女大学生最大脂肪氧化强度研究[J]. 中国学校卫生,2021,42(9):1407-1410,1414. DOI:10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2021.09.032.
|
| [33] |
彭永,朱欢,杨梅,等. 12周FATmax运动对肥胖型非酒精性脂肪肝患者血糖血脂及肝功能的影响[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2022,41(3):648-658. DOI:10.13417/j.gab.041.000648.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
江唐军,伍晓艳,陶芳标. 运动干预对青少年心血管代谢健康保护作用的Meta分析[J]. 现代预防医学,2023,50(19):3525-3533. DOI:10.20043/j.cnki.MPM.202212195.
|
| [36] |
赵婉婷,刘洵,庞家祺,等. FATmax运动对肥胖老年人体质及心血管机能影响的研究[J]. 体育科学,2016,36(12):48-52,76. DOI:10.16469/j.css.201612006.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
肖义然,张蓝天,邱俊强,等. 运动改善老年人心肺功能存在剂量效应的系统综述与Meta分析[J]. 中国体育科技,2022,58(7):48-59. DOI:10.16470/j.csst.2021102.
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
陈伟伟,高润霖,刘力生,等. 《中国心血管病报告2016》概要[J]. 中国循环杂志,2017,32(6):521-530.
|
| [41] |
高思垚,吕万刚,聂应军. 不同运动方式对中国超重或肥胖人群代谢指标影响的元分析[J]. 中国体育科技,2021,57(10):46-54,69. DOI:10.16470/j.csst.2020019.
|
| [42] |
李嘉豪,李佳锦,陶宽,等. 健步走对中老年人血脂代谢影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2022,41(12):983-992. DOI:10.16038/j.1000-6710.2022.12.006.
|
| [43] |
谭思洁,徐冬青,曹立全,等. FATmax运动干预中年女性非酒精性脂肪肝的研究[J]. 天津体育学院学报,2015,30(3):185-189. DOI:10.13297/j.cnki.issn1005-0000.2015.03.001.
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
叶国鸿,汪正毅,许建生,等. 运动与血脂的研究进展[J]. 北京体育大学学报,2004,27(7):933-935. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-3612.2004.07.024.
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
高洪,刘伟长. 健身长跑对中老年人血脂代谢的影响[J]. 辽宁师范大学学报(自然科学版),2003,26(3):295-296. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1735.2003.03.020.
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
刘善云,王丽,何玉秀. 有氧运动和抗阻练习对中老年女性血脂异常患者血脂、超敏C反应蛋白和免疫球蛋白的干预作用[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2008,27(1):84-87. DOI:10.16038/j.1000-6710.2008.01.002.
|
| [50] |
黄亚茹,纪环,葛小川,等. 4周运动配合饮食控制对肥胖青少年体成分、血脂的影响及相关调控机理[J]. 中国体育科技,2013,49(1):46-51. DOI:10.16470/j.csst.2013.01.008.
|
| [51] |
汲智勇,杜晓平,符谦. 七周有氧运动对高脂膳食大鼠体脂和血脂的影响[J]. 沈阳体育学院学报,2010,29(4):69-73. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-0560.2010.04.017.
|
| [52] |
诸骏仁,高润霖,赵水平,等. 中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)[J]. 中国循环杂志,2016,31(10):937-953.
|
| [53] |
董宏,王荣辉,戴俊. 不同剂量运动对静坐少动中年女性心血管健康的影响[J]. 北京体育大学学报,2018,41(2):65-72. DOI:10.19582/j.cnki.11-3785/g8.2018.02.010.
|
| [1] | 张鹏, 刘力滴, 张颖, 杨梓钰, 刘长明, 唐以俊, 廖晓阳, 贾禹. 2024意大利《成人超重、肥胖和代谢合并症行为治疗抵抗的管理指南》解读与启示[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3747-3752. |
| [2] | 卢冬磊, 杨风英, 冯展鹏, 曹立全, 谭思洁. 同期训练可改善伴有超重或肥胖2型糖尿病患者的健康效应:一项Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3410-3421. |
| [3] | 朱晨, 余嘉文, 江昊, 甘盼盼, 夏天, 徐海涛, 杜瀛瀛. 消化系统肿瘤血脂特征对正常相位角的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3385-3390. |
| [4] | 全家霖, 朱琳, 苏煜, 陈泽恺, 陈梓淇, 张卓凡. 运动方式对超重或肥胖儿童青少年执行功能改善效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3422-3431. |
| [5] | 张宇诺, 李瑞斌, 王玮. 血清Nesfatin-1和Ghrelin水平与糖脂代谢及2型糖尿病的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3264-3270. |
| [6] | 向心月, 张冰青, 欧阳煜钦, 汤文娟, 冯文焕. 短期内科门诊减重对肥胖患者动脉粥样硬化性心血管疾病风险的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3229-3239. |
| [7] | 魏云鸿, 杨莉, 王玉路, 叶秋芳, 代安妮, 何燕. 肥胖相关性高血压患者不同运动阶段心肺功能的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2972-2978. |
| [8] | 石小天, 王珊, 杨华昱, 杨一帆, 李旭, 马清. 中国老年人体重指数和死亡的相关性:一项队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2791-2797. |
| [9] | 杨菲, 韩正, 付晓雅, 顾瀚东, 顾可羿, 王为强. 体重正常人群中身体圆度指数与心血管代谢性共病的相关性研究:三酰甘油葡萄糖乘积指数的中介作用[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2798-2805. |
| [10] | 王爽, 吴树法, 令垚, 谭茜蔚, 曹汝岱, 曾慧婷, 孔丹莉, 丁元林, 于海兵. 基于代谢组学探究非脂质代谢物在肥胖与糖尿病视网膜病变间的中介作用:孟德尔随机化研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2625-2634. |
| [11] | 梁恒妙, 黄锶哲, 陈玉婷, 刘策, 王慧君, 杜庆锋. 健康体检人群血尿酸水平与胰岛素抵抗程度关系的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2635-2642. |
| [12] | 金彦, 杨洋, 王璐璐, 郑清婉, 李新艳, 张宁. 减重代谢手术后运动训练对2型糖尿病合并肥胖患者心肺功能的影响:一项随机对照试验[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2611-2617. |
| [13] | 李春贤, 刘安诺. 成年人肥胖和脂质相关指标对代谢综合征的影响及预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2595-2603. |
| [14] | 潘姚佳, 傅方琳, 韩正, 孙梦, 顾怀聪, 王为强. 肥胖类型与心血管代谢性共病的关系:基于不同性别的中年居民[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(18): 2285-2293. |
| [15] | 黄志杰, 麦志华, 王皓翔, 何煜明, 邓巧妍, 戴燃然, 周志衡. 老年"三高"共患情况和家庭功能的现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(16): 2001-2010. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





