中国全科医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (15): 1871-1877.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2024.0057
陈伊静, 许琪, 刘忠典, 覃玲巧, 陈淑萍, 唐薇婷, 钟秋安*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-19
修回日期:2024-05-07
出版日期:2025-05-20
发布日期:2025-03-21
通讯作者:
钟秋安
作者贡献:
陈伊静提出主要研究目标,负责研究的构思与设计,研究的实施,撰写论文;许琪、刘忠典进行数据的收集与整理,统计学处理,图、表的绘制与展示;陈伊静、陈淑萍负责实验指标的检测;覃玲巧、唐薇婷进行论文的修订;钟秋安负责文章的质量控制与审查,对文章整体负责,监督管理。
基金资助:
CHEN Yijing, XU Qi, LIU Zhongdian, QIN Lingqiao, CHEN Shuping, TANG Weiting, ZHONG Qiuan*( )
)
Received:2024-03-19
Revised:2024-05-07
Published:2025-05-20
Online:2025-03-21
Contact:
ZHONG Qiuan
摘要: 背景 动脉粥样硬化(AS)是心血管病主要的病理基础,以血管内皮炎症为主要特征,因而靶向炎症相关机制是防治AS的关键。 目的 研究己糖胺生物合成通路(HBP)对黏附分子的影响及其在血管内皮炎症中的调控作用。 方法 2022年8—12月,将24只SPF级C57BL/6雌性小鼠按体质量以随机区组设计方法分为对照组、6-重氮-5-氧代-L-正亮氨酸(DON)组、高脂饮食(HFD)组、HFD+DON组。各组小鼠给予相应干预措施15周后,收集小鼠的血清及主动脉组织。使用生化试剂盒检测干预前后小鼠的血脂水平,采用HE染色法检测主动脉根部的病理变化,并通过免疫荧光染色、ELISA和蛋白质印迹法检测细胞间黏附分子1(ICAM-1)和血管细胞黏附分子1(VCAM-1)的表达水平。 结果 干预15周后,与对照组相比,HFD组LDL-C、TC水平显著性上升,而HDL-C显著降低(P<0.05);HFD组与HFD+DON组之间的血脂水平无变化(P>0.05)。HE染色结果显示,HFD组血管内膜增厚,血管平滑肌形态异常,结构紊乱,并可见大量的泡沫细胞。HFD+DON组的小鼠平滑肌细胞排列整齐,内皮细胞层连续,泡沫细胞数量明显减少,细胞间隙基本正常。免疫荧光染色、ELISA和蛋白质印迹法结果均显示,与HFD组相比,HFD+DON组的ICAM-1、VCAM-1蛋白表达下调。 结论 抑制HBP具有下调黏附分子ICAM-1、VCAM-1表达,改善血管内皮炎症的作用。
中图分类号:
| 组别 | 只数 | LDL-C | TC | HDL-C | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干预前 | 干预15周后 | t配对值 | P值 | 干预前 | 干预15周后 | t配对值 | P值 | 干预前 | 干预15周后 | t配对值 | P值 | ||
| 对照组 | 6 | 0.096±0.002 | 0.624±0.183 | 7.101 | 0.000 9 | 0.149±0.011 | 2.421±0.617 | 7.528 | 0.001 7 | 3.183±0.489 | 1.979±0.358 | 6.036 | 0.001 8 |
| DON组 | 6 | 0.099±0.005 | 0.583±0.157 | 7.487 | 0.000 7 | 0.158±0.006 | 2.493±0.286 | 26.787 | <0.001 | 2.593±0.820 | 1.812±0.351 | 2.131 | 0.100 1 |
| HFD组 | 6 | 0.095±0.002 | 2.522±0.747ab | 7.208 | 0.000 4 | 0.149±0.015 | 5.149±1.838ab | 5.419 | 0.005 6 | 2.929±0.929 | 0.283±0.190ab | 5.220 | 0.006 4 |
| HFD+DON组 | 6 | 0.098±0.004 | 2.541±0.646ab | 9.231 | 0.000 3 | 0.151±0.010 | 5.181±1.151ab | 11.597 | 0.000 3 | 3.038±0.327 | 0.387±0.429ab | 12.715 | 0.000 2 |
| F值 | 1.530 | 28.780 | 0.620 | 11.370 | 0.570 | 43.50 | |||||||
| P值 | 0.235 | <0.001 | 0.609 | <0.001 | 0.640 | <0.001 | |||||||
表1 4组小鼠血脂水平比较(±s,mmol/L)
Table 1 Comparison of blood lipid levels in 4 groups of mice
| 组别 | 只数 | LDL-C | TC | HDL-C | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干预前 | 干预15周后 | t配对值 | P值 | 干预前 | 干预15周后 | t配对值 | P值 | 干预前 | 干预15周后 | t配对值 | P值 | ||
| 对照组 | 6 | 0.096±0.002 | 0.624±0.183 | 7.101 | 0.000 9 | 0.149±0.011 | 2.421±0.617 | 7.528 | 0.001 7 | 3.183±0.489 | 1.979±0.358 | 6.036 | 0.001 8 |
| DON组 | 6 | 0.099±0.005 | 0.583±0.157 | 7.487 | 0.000 7 | 0.158±0.006 | 2.493±0.286 | 26.787 | <0.001 | 2.593±0.820 | 1.812±0.351 | 2.131 | 0.100 1 |
| HFD组 | 6 | 0.095±0.002 | 2.522±0.747ab | 7.208 | 0.000 4 | 0.149±0.015 | 5.149±1.838ab | 5.419 | 0.005 6 | 2.929±0.929 | 0.283±0.190ab | 5.220 | 0.006 4 |
| HFD+DON组 | 6 | 0.098±0.004 | 2.541±0.646ab | 9.231 | 0.000 3 | 0.151±0.010 | 5.181±1.151ab | 11.597 | 0.000 3 | 3.038±0.327 | 0.387±0.429ab | 12.715 | 0.000 2 |
| F值 | 1.530 | 28.780 | 0.620 | 11.370 | 0.570 | 43.50 | |||||||
| P值 | 0.235 | <0.001 | 0.609 | <0.001 | 0.640 | <0.001 | |||||||
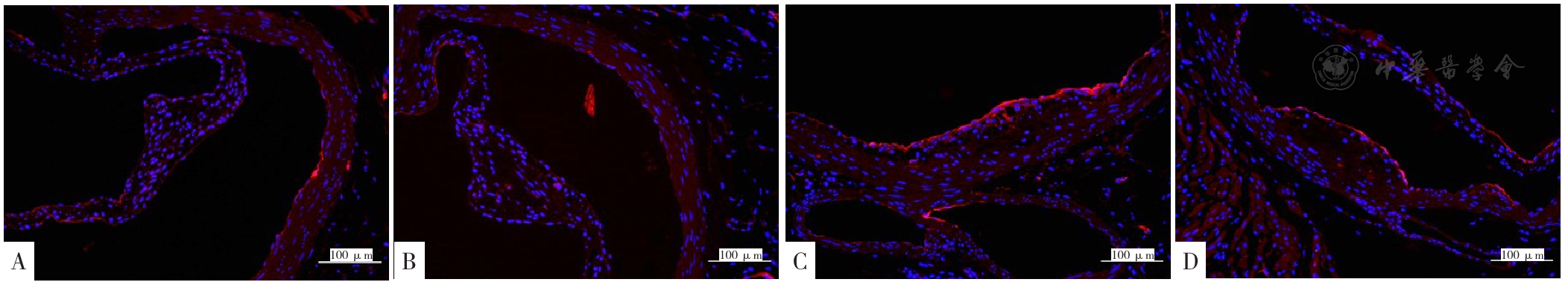
图2 4组小鼠主动脉根部横截面ICAM-1的表达(×200)注:A为对照组,B为DON组,C为HFD组,D为HFD+DON组;红色高亮为ICAM-1染色阳性。
Figure 2 Expression of ICAM-1 in cross-section of aortic root in 4 groups of mice

图3 4组小鼠主动脉根部横截面VCAM-1的表达(×200)注:A为对照组,B为DON组,C为HFD组,D为HFD+DON组;红色高亮为VCAM-1染色阳性。
Figure 3 Expression of VCAM-1 in cross-section of aortic root in 4 groups of mice
| 组别 | 只数 | ICAM-1 | VCAM-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 6 | 1 778.618±221.922 | 1 701.446±451.229 |
| DON组 | 6 | 1 337.773±302.284 | 1 786.358±390.094 |
| HFD组 | 6 | 2 003.233±763.840b | 2 269.460±427.058a |
| HFD+DON组 | 6 | 826.039±241.942abc | 1 326.899±242.623bc |
| F值 | 7.760 | 5.069 | |
| P值 | 0.003 | 0.011 |
表2 4组小鼠血清黏附分子ICAM-1、VCAM-1水平比较(±s,pg/mL)
Table 2 Comparison of serum adhesion molecules ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in 4 groups of mice
| 组别 | 只数 | ICAM-1 | VCAM-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 6 | 1 778.618±221.922 | 1 701.446±451.229 |
| DON组 | 6 | 1 337.773±302.284 | 1 786.358±390.094 |
| HFD组 | 6 | 2 003.233±763.840b | 2 269.460±427.058a |
| HFD+DON组 | 6 | 826.039±241.942abc | 1 326.899±242.623bc |
| F值 | 7.760 | 5.069 | |
| P值 | 0.003 | 0.011 |
| 组别 | 只数 | ICAM-1 | VCAM-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 3 | 1.000±0 | 1.000±0 |
| DON组 | 3 | 1.087±0.428 | 0.759±0.066 |
| HFD组 | 3 | 1.243±0.272 | 1.325±0.181ab |
| HFD+DON组 | 3 | 1.158±0.335 | 0.900±0.105c |
| F值 | 0.58 | 19.30 | |
| P值 | 0.639 | <0.001 |
表3 4组小鼠主动脉组织ICAM-1、VCAM-1蛋白表达比较(±s)
Table 3 Comparison of protein expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in aortic tissues of the 4 groups of mice
| 组别 | 只数 | ICAM-1 | VCAM-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 3 | 1.000±0 | 1.000±0 |
| DON组 | 3 | 1.087±0.428 | 0.759±0.066 |
| HFD组 | 3 | 1.243±0.272 | 1.325±0.181ab |
| HFD+DON组 | 3 | 1.158±0.335 | 0.900±0.105c |
| F值 | 0.58 | 19.30 | |
| P值 | 0.639 | <0.001 |
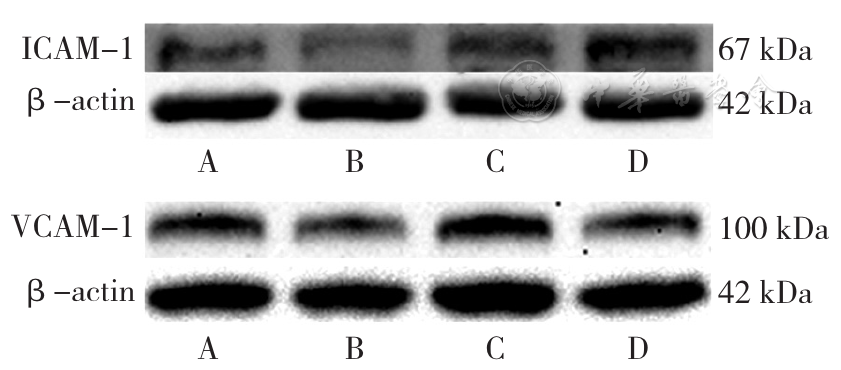
图4 4组小鼠主动脉组织ICAM-1、VCAM-1蛋白表达情况注:A为对照组,B为DON组,C为HFD组,D为HFD+DON组;ICAM-1=细胞间黏附分子1,VCAM-1=血管细胞黏附分子1。
Figure 4 Protein expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in aortic tissues of the 4 groups of mice
| [1] |
《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2022》编写组. 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2022》要点解读[J]. 中国心血管杂志,2023,28(4):297-312. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5410.2023.04.001.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
高丽君,齐晓勇,王秀萍,等. 瑞舒伐他汀对颈动脉粥样硬化患者血脂和颈动脉斑块的影响[J]. 中国全科医学,2011,14(36):4153-4156. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2011.36.012.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
苏敏,钟翠平. 动脉粥样硬化病变中黏附分子ICAM-1、VCAM-1及E-selectin的表达[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2009,31(11):1066-1068. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-5404.2009.11.020.
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [1] | 田珂, 冷秋枫, 吕晶, 苗国英, 王新慧, 谢辉, 刘渠, 姚春霞. 二甲双胍通过NLRP3炎症小体通路对皮肤角质形成细胞增殖和凋亡的双向调节研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(06): 742-750. |
| [2] | 杨灿, 李宁, 李雪菲, 赵力, 徐浩, 施杞, 王拥军, 梁倩倩. 脏痹方治疗类风湿关节炎间质性肺疾病小鼠关节炎及肺脏并发症的疗效研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(24): 3015-3022. |
| [3] | 秦芳, 马甜甜, 于子夫, 刘西花. 有氧运动抑制炎症反应改善ApoE-/-动脉粥样硬化小鼠心肌纤维化机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(05): 557-562. |
| [4] | 李媛, 木艳玲, 薛孟周. 青蒿琥酯调控NLRP3/ASC/Caspase-1信号通路减轻脑出血小鼠炎症及保护神经功能的作用研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4194-4202. |
| [5] | 陈铿, 邓翼遥, 尚顺来, 李清刚, 陈香美. 复方肾怡治疗狼疮肾炎小鼠的疗效及对补体旁路途径激活的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(26): 3298-3307. |
| [6] | 程经纬, 柳杨青, 汪艳芳. 肌肉生长抑制素基因敲除对2型糖尿病小鼠白色脂肪棕色化及相关基因表达的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(21): 2610-2617. |
| [7] | 张玉双, 于富洋, 吴忠冰, 王一然, 李晶. 食管鳞癌原位模型小鼠肠道菌群分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(08): 945-951. |
| [8] | 陈绍华,王沁筠,吴昌桂,赵啸,徐浩,施杞,梁倩倩. 当归拈痛汤治疗急性痛风性关节炎疗效和作用机制的小鼠实验研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(24): 3116-3121. |
| [9] | 王岩,黄仲夏,胡婉莉,魏宇君,王林月. 血管细胞黏附分子-1和激活素A对多发性骨髓瘤的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(17): 2185-2191. |
| [10] | 余雷,杨云霜,李延晖,刘晓辰,杜磊,王思念,张蓉. 补肾解毒方对放射致小鼠胸腺损伤的防护作用研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2020, 23(9): 1164-1168. |
| [11] | 常全,张娜娜,马冬. 髓系KLF5基因缺失小鼠腹主动脉瘤形成的生物信息学分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2020, 23(6): 692-698. |
| [12] | 张燕*,范晓翔,章美武,庄鲁辉,毛达峰. LRC5调节转化生长因子-β1诱导的肝星状细胞活化及逆转对肝纤维化的影响[J]. 中国全科医学, 2020, 23(24): 3051-3059. |
| [13] | 李洪涛,林煜森,邹小玲,李文娟,孟平,张天托. CpG寡聚脱氧核苷酸对变应性联合气道疾病气道重塑的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2019, 22(26): 3191-3197. |
| [14] | 张娜,刘学芳,蒋时红,王琦,田燕歌. 益肺逐积方联合环磷酰胺对Lewis肺癌小鼠模型肿瘤体积及免疫功能的影响[J]. 中国全科医学, 2018, 21(30): 3753-3756. |
| [15] | 徐利,葛琼翔,林国强. 温和灸对肛门瘙痒模型小鼠背根节TRPV1表达的影响[J]. 中国全科医学, 2018, 21(30): 3749-3752. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





