中国全科医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (32): 4040-4049.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0238
所属专题: 消化系统疾病最新文章合辑
杨安银1, 刘红丽2, 陈妙洋1, 郑玉凤1, 徐志远3, 杨永峰1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-04-04
修回日期:2023-08-19
出版日期:2024-11-15
发布日期:2024-08-08
通讯作者:
杨永峰
作者贡献:
杨永峰提出研究思路,制定总体研究目标;杨安银、刘红丽进行数据分析,实验操作以及文章撰写;陈妙洋、郑玉凤、徐志远进行相关文献和资料收集。
基金资助:
YANG Anyin1, LIU Hongli2, CHEN Miaoyang1, ZHENG Yufeng1, XU Zhiyuan3, YANG Yongfeng1,*( )
)
Received:2023-04-04
Revised:2023-08-19
Published:2024-11-15
Online:2024-08-08
Contact:
YANG Yongfeng
摘要: 背景 肝细胞癌是癌症相关死亡的主要原因,目前的防治形势依然严峻,对新的肝细胞癌治疗药物进行探索研究具有科学意义。 目的 通过网络药理学方法分析汉黄芩素干预肝细胞癌的作用机制,并进行体外实验验证。 方法 在TCMSP数据库中检索汉黄芩素的药物靶点,从TTD、GenCard、OMIM、DisGent数据库中收集肝细胞癌的疾病靶点。将收集的药物靶点和疾病靶点取交集,作为药物干预疾病的潜在靶点。对交集靶点运用R软件进行富集分析,使用STRING数据库和Cytoscape软件对交集靶点构建蛋白互作网络和筛选核心靶点。在GIEPA数据库对核心靶点行进一步分析。最后通过体外实验对前期分析结果进行验证:采用CCK-8试剂盒测定细胞活性;采用平板克隆形成实验测定细胞增殖;采用划痕实验测定细胞迁移;采用Western-blotting(WB)实验测定蛋白质表达水平。 结果 分析结果发现汉黄芩素的吸收、分布、代谢、排泄特性符合小分子药物成药规则并且毒性分析结果表明无毒性。收集到汉黄芩素靶点135个,肝细胞癌靶点8 238个,两者交集靶点113个。通过对构建的蛋白互作网络筛选出的前10位的核心基因进行分析,发现细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶1(CDK1)、原癌基因酪氨酸蛋白激酶Src(SRC)在肝细胞癌组织中mRNA水平较正常肝组织上调(P<0.05),并且在肝细胞癌患者中高表达与不良预后相关(P<0.05)。KEGG富集分析发现交集基因富集在PI3K/AKT信号通路上最多,分子对接结果显示汉黄芩素与CDK1、SRC结合构型活力较强。CCK-8试剂盒检测结果显示,加入汉黄芩素75.0、150.0、300.0 μmol/L组HepG2细胞活性均低于对照组(P<0.05);平板克隆形成实验结果显示,加入汉黄芩素37.5、75.0、150.0 μmol/L组HepG2细胞克隆形成数均低于对照组(P<0.05);划痕实验结果表明,加入汉黄芩素37.5、75.0、150.0 μmol/L组HepG2细胞迁移率均低于对照组(P<0.05);WB实验结果表明,加入汉黄芩素75.0、150.0 μmol/L组PI3K、P-AKT/AKT、CDK1、SRC蛋白表达水平均低于对照组(P<0.05)。 结论 汉黄芩素通过下调CDK1、SRC蛋白表达,减弱PI3K/AKT通路信号,抑制肝癌细胞增殖和迁移,诱导细胞凋亡,从而达到干预肝细胞癌发生和进展的目的。
中图分类号:
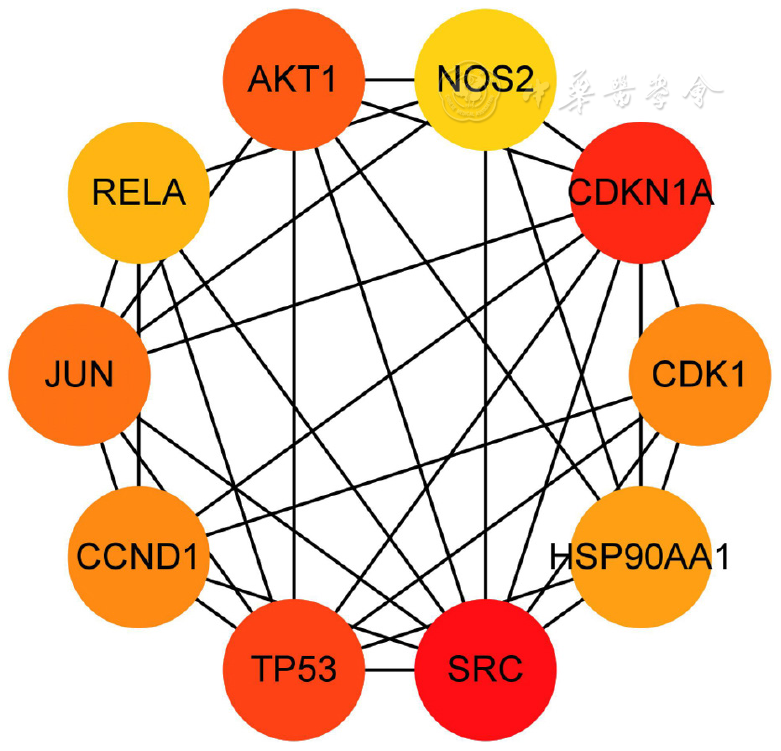
图2 TOP10核心靶点注:SRC=原癌基因酪氨酸蛋白激酶Src,HSP90AA1=热休克蛋白HSP90-α,TP53=细胞肿瘤抗原p53,CDK1=细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶1,AKT1=丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,CCND1=G1/S-特异性周期蛋白-D1,JUN=转录因子Jun,RELA=RELA原癌基因,NOS2=一氧化氮合酶,CDKN1A=细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶抑制剂1。
Figure 2 TOP10 core targets
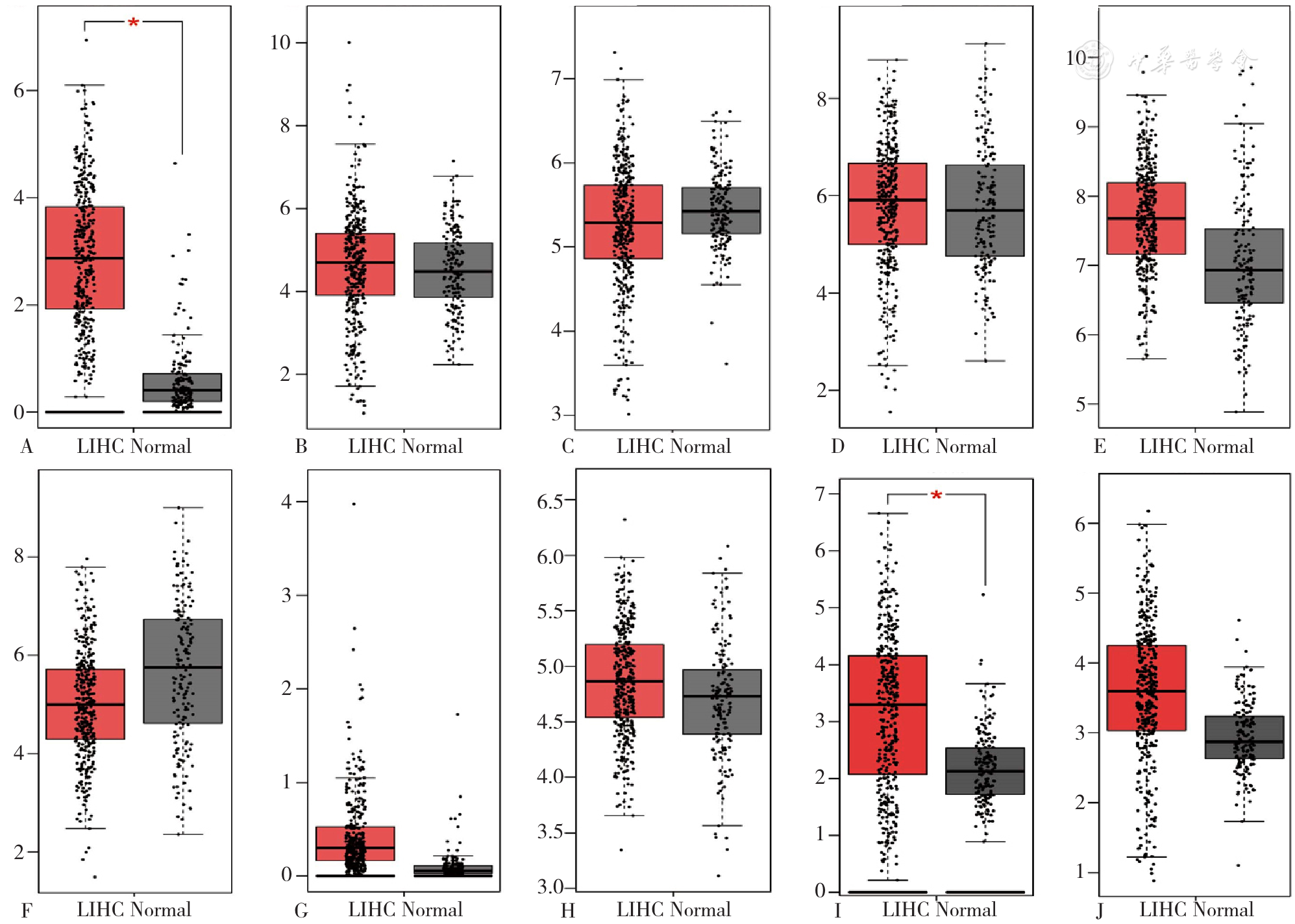
图3 GEPIA数据库验证核心靶点在肝细胞癌和正常肝组织中mRNA表达水平注:A~J分别代表CDK1、CCND1、AKT1、CDKN1A、HSP90AA1、JUN、NOS2、RELA、SRC、TP53在肝细胞癌组织和正常肝组织中的mRNA表达水平;*P<0.05,**P<0.01;LIHC=肝细胞癌,Normal=正常肝组织。
Figure 3 The GEPIA database verified the mRNA expression levels of core targets in hepatocellular carcinoma and normal liver tissues
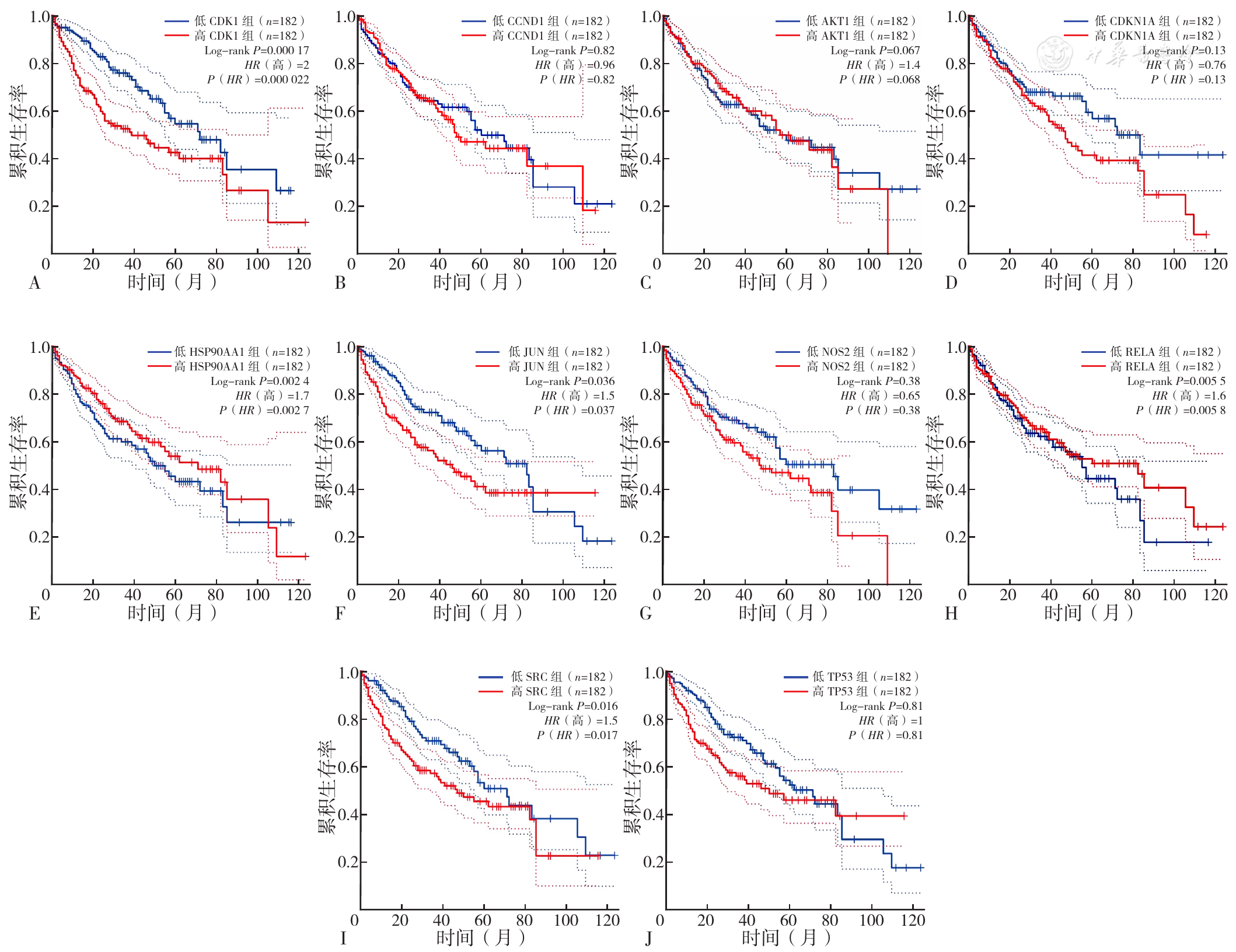
图4 GEPIA数据库对前10位核心靶点在肝细胞癌患者中的生存分析注:A为CDK1,B为CCND1,C为AKT1,D为CDKN1A,E为HSP90AA1,F为JUN,G为NOS2,H为RELA,I为SRC,J为TP53。
Figure 4 Survival analysis of TOP10 core targets in hepatocellular carcinoma patients by the GEPIA database
| 组别 | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h |
|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 1.608±0.092 | 1.473±0.086 | 1.642±0.087 |
| DMSO溶媒组 | 1.562±0.071 | 1.459±0.106 | 1.641±0.089 |
| 18.5 μmol/L | 1.344±0.112a | 1.459±0.117 | 1.655±0.101 |
| 37.5 μmol/L | 0.922±0.108a | 1.322±0.081a | 1.630±0.161 |
| 75.0 μmol/L | 0.818±0.022a | 0.976±0.081a | 1.317±0.042a |
| 150.0 μmol/L | 0.737±0.017a | 0.389±0.015a | 0.261±0.043a |
| 300.0 μmol/L | 0.637±0.018a | 0.361±0.029a | 0.223±0.036a |
| F值 | 148.5 | 178.1 | 271.2 |
| P值 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 |
表1 汉黄芩素处理后HepG2细胞活性(±s,n=3)
Table 1 Activity of HepG2 cells treated with wogonin
| 组别 | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h |
|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 1.608±0.092 | 1.473±0.086 | 1.642±0.087 |
| DMSO溶媒组 | 1.562±0.071 | 1.459±0.106 | 1.641±0.089 |
| 18.5 μmol/L | 1.344±0.112a | 1.459±0.117 | 1.655±0.101 |
| 37.5 μmol/L | 0.922±0.108a | 1.322±0.081a | 1.630±0.161 |
| 75.0 μmol/L | 0.818±0.022a | 0.976±0.081a | 1.317±0.042a |
| 150.0 μmol/L | 0.737±0.017a | 0.389±0.015a | 0.261±0.043a |
| 300.0 μmol/L | 0.637±0.018a | 0.361±0.029a | 0.223±0.036a |
| F值 | 148.5 | 178.1 | 271.2 |
| P值 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 |
| 组别 | 18.5 μmol/L | 37.5 μmol/L | 75.0 μmol/L | 150.0 μmol/L | 300.0 μmol/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2细胞活性 | 83.45±2.96 | 57.67±9.28 | 51.18±4.56 | 45.97±3.35 | 39.71±2.90 |
| LO2细胞活性 | 113.41±5.68 | 108.77±4.54 | 106.06±4.54 | 82.75±3.92 | 61.92±3.33 |
| t值 | 10.06 | 11.06 | 17.57 | 15.96 | 11.23 |
| P值 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 |
表2 汉黄芩素处理24 h后,相同浓度下HepG2细胞与LO2细胞活性比较(±s,n=3)
Table 2 Comparison of the activity of HepG2 cells and LO2 cells at the same concentration after 24 h treatment with wogonin
| 组别 | 18.5 μmol/L | 37.5 μmol/L | 75.0 μmol/L | 150.0 μmol/L | 300.0 μmol/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2细胞活性 | 83.45±2.96 | 57.67±9.28 | 51.18±4.56 | 45.97±3.35 | 39.71±2.90 |
| LO2细胞活性 | 113.41±5.68 | 108.77±4.54 | 106.06±4.54 | 82.75±3.92 | 61.92±3.33 |
| t值 | 10.06 | 11.06 | 17.57 | 15.96 | 11.23 |
| P值 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 |
| 组别 | 18.5 μmol/L | 37.5 μmol/L | 75.0 μmol/L | 150.0 μmol/L | 300.0 μmol/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2细胞活性 | 95.23±4.91 | 91.97±2.40 | 51.05±2.83 | 24.11±1.30 | 13.90±0.80 |
| LO2细胞活性 | 99.26±9.30 | 90.04±8.39 | 66.62±9.30 | 26.48±1.75 | 24.62±2.47 |
| t值 | 0.857 | 0.496 | 3.587 | 2.428 | 9.237 |
| P值 | 0.416 | 0.633 | 0.007 | 0.041 | <0.001 |
表3 汉黄芩素处理48 h后,相同浓度下HepG2细胞与LO2细胞活性比较(±s,n=3)
Table 3 Comparison of the activity of HepG2 cells and LO2 cells at the same concentration after 48 h treatment with wogonin
| 组别 | 18.5 μmol/L | 37.5 μmol/L | 75.0 μmol/L | 150.0 μmol/L | 300.0 μmol/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2细胞活性 | 95.23±4.91 | 91.97±2.40 | 51.05±2.83 | 24.11±1.30 | 13.90±0.80 |
| LO2细胞活性 | 99.26±9.30 | 90.04±8.39 | 66.62±9.30 | 26.48±1.75 | 24.62±2.47 |
| t值 | 0.857 | 0.496 | 3.587 | 2.428 | 9.237 |
| P值 | 0.416 | 0.633 | 0.007 | 0.041 | <0.001 |
| 组别 | 18.5 μmol/L | 37.5 μmol/L | 75.0 μmol/L | 150.0 μmol/L | 300.0 μmol/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2细胞活性 | 79.08±5.85 | 72.73±1.50 | 65.80±2.43 | 37.89±2.68 | 26.71±2.74 |
| LO2细胞活性 | 100.79±3.38 | 99.17±7.47 | 80.32±3.23 | 41.55±1.97 | 34.45±3.76 |
| t值 | 7.182 | 7.764 | 8.029 | 2.460 | 3.721 |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.039 | 0.005 |
表4 汉黄芩素处理72 h后,相同浓度下HepG2细胞与LO2细胞活性比较(±s,n=3)
Table 4 Comparison of the activity of HepG2 cells and LO2 cells at the same concentration after 72 h treatment with wogonin
| 组别 | 18.5 μmol/L | 37.5 μmol/L | 75.0 μmol/L | 150.0 μmol/L | 300.0 μmol/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2细胞活性 | 79.08±5.85 | 72.73±1.50 | 65.80±2.43 | 37.89±2.68 | 26.71±2.74 |
| LO2细胞活性 | 100.79±3.38 | 99.17±7.47 | 80.32±3.23 | 41.55±1.97 | 34.45±3.76 |
| t值 | 7.182 | 7.764 | 8.029 | 2.460 | 3.721 |
| P值 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.039 | 0.005 |
| 组别 | HepG2细胞克隆形成数 | HepG2细胞迁移率 |
|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 95.67±4.51 | 33.83±3.05 |
| 37.5 μmol/L | 74.00±3.00a | 18.98±0.45a |
| 75.0 μmol/L | 39.67±2.52a | 8.54±2.39a |
| 150.0 μmol/L | 9.67±2.52a | 5.06±1.89a |
| F值 | 410.0 | 106.7 |
| P值 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 |
表5 HepG2细胞克隆形成集落数和汉黄芩素处理后细胞迁移率比较(±s,n=3)
Table 5 Comparison of clone-forming colonies in HepG2 cells and cell migration rate after wogonin treatment
| 组别 | HepG2细胞克隆形成数 | HepG2细胞迁移率 |
|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 95.67±4.51 | 33.83±3.05 |
| 37.5 μmol/L | 74.00±3.00a | 18.98±0.45a |
| 75.0 μmol/L | 39.67±2.52a | 8.54±2.39a |
| 150.0 μmol/L | 9.67±2.52a | 5.06±1.89a |
| F值 | 410.0 | 106.7 |
| P值 | <0.000 1 | <0.000 1 |
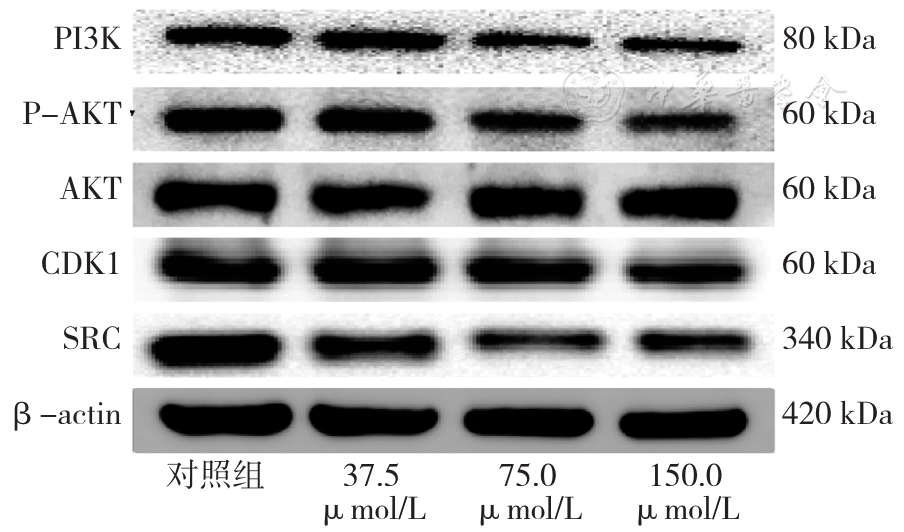
图10 汉黄芩素下调核心靶点SRC、CDK1蛋白表达水平和降低PI3K/AKT通路信号
Figure 10 Wogonin down-regulates the expression of core targets of SRC,CDK1 protein and decreases PI3K/AKT pathway signaling
| 组别 | PI3K | P-AKT/AKT | CDK1 | SRC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 0.674±0.021 | 1.141±0.178 | 0.716±0.121 | 0.747±0.065 |
| 37.5 μmol/L | 0.610±0.010 | 0.992±0.156 | 0.637±0.104 | 0.709±0.077 |
| 75.0 μmol/L | 0.514±0.059a | 0.774±0.105a | 0.454±0.110a | 0.559±0.037a |
| 150.0 μmol/L | 0.488±0.050a | 0.686±0.053a | 0.358±0.037a | 0.462±0.056a |
| F值 | 13.64 | 7.335 | 8.324 | 14.25 |
| P值 | 0.001 6 | 0.011 0 | 0.007 7 | 0.001 4 |
表6 HepG2细胞PI3K/AKT信号通路和CDK1、SRC蛋白表达(±s,n=3)
Table 6 PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and CDK1,SRC protein expression levels in HepG2 cells
| 组别 | PI3K | P-AKT/AKT | CDK1 | SRC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 0.674±0.021 | 1.141±0.178 | 0.716±0.121 | 0.747±0.065 |
| 37.5 μmol/L | 0.610±0.010 | 0.992±0.156 | 0.637±0.104 | 0.709±0.077 |
| 75.0 μmol/L | 0.514±0.059a | 0.774±0.105a | 0.454±0.110a | 0.559±0.037a |
| 150.0 μmol/L | 0.488±0.050a | 0.686±0.053a | 0.358±0.037a | 0.462±0.056a |
| F值 | 13.64 | 7.335 | 8.324 | 14.25 |
| P值 | 0.001 6 | 0.011 0 | 0.007 7 | 0.001 4 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [1] | 陈超, 陈天翔, 刘钱伟, 张秩, 王欢欢, 吴平平, 高磊, 于照祥. 基于加权基因共表达网络和癌症基因组图谱临床数据分析并鉴定肝细胞癌的Hub基因研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(32): 4050-4059. |
| [2] | 麦尔哈巴·麦麦提艾力, 张凯楠, 赵辉, 亚库甫·托合提, 叶建蔚, 吕国栋. 血清聚腺苷二磷酸核糖聚合酶2作为潜在的肝细胞癌诊断标志物的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(32): 4060-4065. |
| [3] | 胡灵溪, 李妹, 付艺伟, 路丽霞, 马晓萱, 王荣琦, 南月敏. 血清血管内皮生长因子对肝动脉化疗栓塞单独/联合靶免治疗在中晚期肝癌临床疗效中的评估价值[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(32): 4033-4039. |
| [4] | 张林, 高锦, 吴明华, 王广梅. 通脑饮治疗急性脑梗死的临床疗效及作用机制研究:基于网络药理学和分子对接技术[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(23): 2904-2912. |
| [5] | 张芸, 蔡欣奕, 丁靖诺, 陆圣威, 陈萃英, 吴婷婷, 张军利, 赵卫峰. 寡糖链、甲胎蛋白对乙型肝炎病毒相关肝细胞癌风险筛查与诊断价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(15): 1855-1860. |
| [6] | 刁翯, 白文佩, 赵立东. 左慈丸的化学成分及治疗围绝经期听力损失的作用机制研究:基于网络药理学与分子对接技术[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(12): 1493-1503. |
| [7] | 宁麟, 孙建光. 芪术化积方治疗肝细胞癌癌前病变患者的随机对照研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(03): 335-342. |
| [8] | 路丽霞, 王荣琦. 原发性肝癌基层筛查与健康监测管理的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(36): 4505-4509. |
| [9] | 张康, 赵婷婷, 张波, 高梦琦, 李昱熹, 王邵鹏, 赵文景. 基于网络药理学探究布地奈德治疗IgA肾病的作用机制[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(35): 4453-4458. |
| [10] | 叶坤, 雷敏, 谢欣, 郑晖, 陈敏, 余曙光. 基于网络药理学与分子对接技术探讨黄芪建中汤治疗腹泻型肠易激综合征的作用机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(15): 1814-1824. |
| [11] | 孙凯,朱立国,魏戌,银河,李秋月,秦晓宽,杨博文. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS结合网络药理学的壮腰通络方延缓腰椎间盘退行性病变的化学成分及作用机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(35): 4437-4446. |
| [12] | 吴忱思,赵乐,吴建华,王英南,张风宾,高立明,赵林,张卫国,张瑞星. 乙型肝炎病毒S区基因突变对乙型肝炎病毒相关性肝细胞癌患者预后的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2019, 22(15): 1807-1811. |
| [13] | 李丽艳1,褚丽娟1,赵伟2,郭云志1,申国强1,王晓燕3,周顺科4. 钆贝葡胺双功能对比一站式MRI成像对肝细胞癌的诊断价值分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2018, 21(9): 1124-1129. |
| [14] | 赵昆1,徐菊英2,许青1,3*,朱忠政3*. 染色体8q拷贝数变异与肝细胞癌患者术后总生存期的相关性及其靶基因筛选[J]. 中国全科医学, 2018, 21(18): 2190-2195. |
| [15] | 黄伍奎,张曦,刘墨,王海林,阿不拉江,顾朋,樊喜文,杨树法. 肝细胞癌源性肾上腺转移瘤经导管动脉化疗栓塞治疗时供血动脉情况分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2016, 19(15): 1848-1851. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





