中国全科医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (17): 2155-2166.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0663
所属专题: 消化系统疾病最新文章合辑; 用药最新文章合辑
谭书法1, 张磊昌2,*( ), 高强强3, 欧艳1, 黄水兰1
), 高强强3, 欧艳1, 黄水兰1
收稿日期:2023-08-10
修回日期:2024-01-13
出版日期:2024-06-15
发布日期:2024-03-22
通讯作者:
张磊昌
作者贡献:
谭书法提出研究思路,设计研究方案,负责数据收集、采集、清洗和统计学分析、绘制图表;谭书法、高强强、欧艳、黄水兰共同参与了文献的检索、筛选以及数据的提取;谭书法、张磊昌负责论文的写作及修改;张磊昌负责论文最终版本修订,对论文负责。
基金资助:
TAN Shufa1, ZHANG Leichang2,*( ), GAO Qiangqiang3, OU Yan1, HUANG Shuilan1
), GAO Qiangqiang3, OU Yan1, HUANG Shuilan1
Received:2023-08-10
Revised:2024-01-13
Published:2024-06-15
Online:2024-03-22
Contact:
ZHANG Leichang
摘要: 背景 溃疡性结肠炎(UC)是一种慢性复发和缓解性免疫介导的炎症性肠病,其治疗方式还存在争议,大约一半的患者病程发展复杂,伴有慢性活动或频繁复发的UC症状,严重影响了患者的生活质量。 目的 目前UC的治疗方式越来越多,本研究旨在比较生物制剂和小分子药物治疗UC患者的相对疗效和安全性。 方法 2名研究人员独立使用PubMed、Embase、Web of Science、Cochrane Library、中国知网、万方数据知识服务平台、维普网数据库搜索有关生物制剂和小分子药物治疗UC的随机对照试验,干预组为生物制剂或小分子药物,对照组为安慰剂。采用Cochrane偏倚风险工具、RevMan 5.4对纳入研究进行质量评价,采用R Studio进行成对分析和网络荟萃分析,采用累积排序概率图下面积(SUCRA)对各结局指标的纳入药物进行排序,以比较不同治疗方式对UC的临床疗效。 结果 共纳入25项研究,包括9 546例UC患者,10种药物干预方案(Filgotinib 100 mg、Filgotinib 200 mg、Upadacitinib、Tofacitinib、Etrolizumab、Adalimumab、Vedolizumab、Golimumab 50 mg、Golimumab 100 mg、Infliximab)。各药物对临床缓解效果的SUCRA概率排序结果显示,Upadacitinib(94.1%)>Vedolizumab(85.1%)>Tofacitinib(74.3%)>Infliximab(72.7%)>Filgotinib 200 mg(51.5%)>Golimumab 100 mg(44.3%)>Golimumab 50 mg(39.3%)>Etrolizumab(38.9%)>Adalimumab(29.8%)>Filgotinib 100 mg(18.7%)>Placebo(0.7%)。各药物对临床反应效果的SUCRA概率排序结果显示,Upadacitinib(98.4%)>Infliximab(84.4%)>Tofacitinib(67.2%)>Vedolizumab(58.4%)>Golimumab 50 mg(53.3%)>Adalimumab(34.6%)>Golimumab 100 mg(30.1%)>Placebo(0.4%)。各药物对内镜缓解效果的SUCRA概率排序结果显示,Upadacitinib(98.7%)>Tofacitinib(68.6%)>Filgotinib 200 mg(59.6%)>Adalimumab(55.2%)>Etrolizumab(46.0%)>Vedolizumab(45.9%)>Filgotinib 100 mg(23.4%)>Placebo(2.2%)。各药物对黏膜愈合效果的SUCRA概率排序结果显示,Upadacitinib(99.7%)>Tofacitinib(77.2%)>Infliximab(65.2%)>Golimumab 50 mg(46.4%)>Vedolizumab(44.4%)>Adalimumab(33.8%)>Golimumab 100 mg(31.9%)>Placebo(1.0%)。各药物不良事件风险的SUCRA概率排序结果显示,Golimumab 100 mg(96.7%)>Golimumab 50 mg(92.1%)>Placebo(68.7%)>Tofacitinib(60.8%)>Adalimumab(60.7%)>Etrolizumab(47.2%)>Upadacitinib(42.2%)>Vedolizumab(41.3%)>Infliximab(27.0%)>Filgotinib 200 mg(6.6%)>Filgotinib 100 mg(6.2%)。 结论 Upadacitinib在临床反应、临床缓解、黏膜愈合以及内镜缓解方面均展现出最佳效用,在不良事件方面Filgotinib 100 mg表现出更为安全的结果。
| 第一作者 | 发表年份(年) | 研究类型 | 国家 | 干预方式 | 例数 | 性别(男/女) | 年龄(岁) | 疾病持续时间(年) | 疾病程度 | 结局指标 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | ||||||
| HIBI[ | 2023 | RCT | 日本 | Filgotinib 100 mg | Placebo | 16 | 6 | 11/34 | 11/5 | 48±13 | 48±11 | 8.2±9.5 | 11.8±14.0 | 中度至重度活动性UC(Mayo内镜评分≥2分,直肠出血评分≥1分,大便频率亚评分≥1分,医生总体评估亚评分≥2分);总Mayo临床评分为6~12分 | 1、5 |
| HIBI[ | 2023 | RCT | 日本 | Filgotinib 200 mg | Placebo | 15 | 6 | 18/26 | 8/7 | 52±12 | 48±11 | 7.2±6.8 | 11.8±14.0 | 1、5 | |
| SCHREIBER[ | 2023 | RCT | 德国 | Filgotinib 200 mg | Placebo | 245 | 137 | 123/122 | 87/50 | 42±13.1 | 41±12.9 | 7.2±6.9 | 6.4±7.4 | 中至重度活动性UC患者(Mayo内镜评分≥2分,直肠出血评分≥1分,大便频率评分≥1分,医生总体评估评分≥2分;总梅奥临床评分为6~12分) | 1 |
| DOTAN[ | 2023 | RCT | 以色列 | Filgotinib 100 mg | Placebo | 277 | 140 | 156/121 | 89/51 | 42.3±13.3 | 41.5±12.8 | 6.7±7.4 | 6.5±7.4 | 中度至重度活动性UC的定义为Mayo内镜亚评分≥2分,直肠出血亚评分≥1分,大便频率评分≥1分,医生总体评估评分≥2分;分值相加为梅奥诊所总分6~12分 | 1 |
| DOTAN[ | 2023 | RCT | 以色列 | Filgotinib 200 mg | Placebo | 248 | 140 | 123/125 | 89/51 | 42.4±13.0 | 41.5±12.8 | 7.2±7.0 | 6.5±7.4 | 1 | |
| FEAGAN[ | 2021 | RCT | 加拿大 | Filgotinib 100 mg | Placebo | 277 | 137 | 157/120 | 87/50 | 42(13.3) | 41(12.9) | 6.7(7.4) | 6.4(7.4) | 中度至重度活动性溃疡性结肠炎内镜评分≥2分,直肠出血评分≥1分,大便频率评分≥1分,医生总体评估评分≥2分;梅奥临床总评分6~12分 | 1、3 |
| FEAGAN[ | 2021 | RCT | 加拿大 | Filgotinib 200 mg | Placebo | 245 | 137 | 123/122 | 87/50 | 42(13.1) | 41(12.9) | 7.2(6.9) | 6.4(7.4) | 1、3 | |
| DANESE[ | 2022 | RCT | 印度 | Upadacitinib | Placebo | 319 | 154 | 198/121 | 97/57 | 43.0(23.0) | 44.5(23.0) | 6.6(9.6) | 6.2(8.6) | 中、重度活动性溃疡性结肠炎患者(适应Mayo评分5~9分;内镜下评分为2分或3分) | 1、2、3、4、5 |
| SANDBORN[ | 2020 | RCT | 美国 | Upadacitinib | Placebo | 47 | 46 | 23/24 | 29/17 | 41(18~75) | 40(21~67) | 6.59(0.8~43.7) | 5.19(0.4~30.8) | 中度至重度活动性UC | 1、2、3、5 |
| SANDBORN[ | 2020 | RCT | 美国 | Upadacitinib | Placebo | 49 | 46 | 30/19 | 29/17 | 41(18~75) | 40(21~67) | 4.58(0.2~43.0) | 5.19(0.4~30.8) | ||
| SANDBORN[ | 2020 | RCT | 美国 | Upadacitinib | Placebo | 52 | 46 | 31/21 | 29/17 | 42(20~72) | 40(21~67) | 6.06(0.3~27.5) | 5.19(0.4~30.8) | ||
| SANDBORN[ | 2020 | RCT | 美国 | Upadacitinib | Placebo | 56 | 46 | 37/19 | 29/17 | 37(19~74) | 40(21~67) | 6.46(0.4~23.9) | 5.19(0.4~30.8) | ||
| SANDBORN[ | 2019 | RCT | 美国 | Tofacitinib | Placebo | 938 | 282 | 557/381 | 155/127 | 41.3(13.8) | 41.4(14.4) | 8.2(7.0) | 8.2(7.8) | 中度至重度活动性UC | 5 |
| SANDBORN[ | 2018 | RCT | 美国 | Tofacitinib | Placebo | 476 | 122 | 277/199 | 77/45 | 41.3±14.1 | 41.8±15.3 | 6.5 | 6.0 | 中度至重度活动性疾病,定义为Mayo评分为6~12分,其中直肠出血评分为1~3分,内镜评分为2分或3分,Mayo评分范围为0~12分,4个评分范围均为0~3分,评分越高疾病越严重 | 1、2、3、4、5 |
| DANESE[ | 2022 | RCT | 德国 | Etrolizumab | Infliximab | 199 | 198 | 118/81 | 132/66 | 37(18~76) | 37(18~70) | 3.3(0.3~49.0) | 4.1(0.1~33.7) | 中度至重度活动性溃疡性结肠炎的成年人(定义为梅奥诊所总分为6~12分,内镜亚评分≥2分,直肠出血亚评分≥1分,大便频率亚评分≥1分) | 1 |
| VERMEIRE[ | 2014 | RCT | 比利时 | Etrolizumab | Placebo | 41 | 43 | 28/13 | 19/24 | 44.4(13.9) | 37.5(12.8) | 9.8(8.3) | 9.8(8.4) | 中、重度溃疡性结肠炎,Mayo临床评分为5分或以上(美国FDA要求≥6分) | 1、2、5 |
| RUBIN[ | 2022 | RCT | 美国 | Adalimumab | Placebo | 142 | 72 | 82/60 | 39/33 | 41.0(19~75) | 36.0(19~78) | 4.0(0.3~36.4) | 4.7(0.3~40.8) | 中度至重度活动性溃疡性结肠炎成年人(18~80岁)患者(梅奥临床总分为6~12分,内镜下亚评分≥2分,直肠出血评分≥1分,粪便频率评分≥1分) | 1、2、3、5 |
| RUBIN[ | 2022 | RCT | 美国 | Etrolizumab | Placebo | 144 | 72 | 74/70 | 39/33 | 36.5(18~79) | 36.0(19~78) | 3.4(0.4~41.9) | 4.7(0.3~40.8) | 1、2、3、5 | |
| MOTOYA[ | 2020 | RCT | 日本 | Vedolizumab | Placebo | 164 | 82 | 99/65 | 55/27 | 42.3(14.4) | 44.0(16.0) | 7.2(6.2) | 8.6(8.0) | 患者为中度至重度活动性UC,定义为基线全Mayo评分为6~12分,内窥镜评分为2分 | 1、2、4、5 |
| SANDBORN[ | 2019 | RCT | 美国 | Vedolizumab | Placebo | 106 | 56 | 65/41 | 34/22 | 38.1(13.1) | 39.4(11.7) | 8.0(6.2) | 7.4(7.1) | 患者为中度至重度活动性UC,Mayo评分为6~12分,内窥镜评分≥2分 | 1、2、3、5 |
| YAJNIK[ | 2017 | RCT | 美国 | Vedolizumab | Placebo | 334 | 78 | 187/147 | 49/29 | 44.3±5.9 | 45.0±5.5 | 8.0±6.2 | 8.0±7.1 | 中度至重度活动性UC | 2 |
| REINISCH[ | 2018 | RCT | 澳大利亚 | Golimumab 50 mg | Placebo | 93 | 96 | 47/46 | 47/49 | 40.0(12.50) | 40.8(14.83) | 7.0(7.06) | 6.7(7.51) | 中度至重度活动性UC | 5 |
| REINISCH[ | 2018 | RCT | 澳大利亚 | Golimumab 100 mg | Placebo | 477 | 96 | 285/192 | 47/49 | 40.0(12.79) | 40.8(14.83) | 6.7(6.22) | 6.7(7.51) | 5 | |
| RUTGEERTS[ | 2015 | RCT | 美国 | Golimumab 100 mg | Placebo | 214 | 77 | 127/87 | 47/30 | 41.0±14.16 | 40.9±12.58 | 6.8±6.75 | 6.8±6.59 | 中重度疾病活动(Mayo评分为6~12分,包括内镜评分≥2分) | 1、2、4、5 |
| JIANG[ | 2015 | RCT | 中国 | Infliximab | Placebo | 41 | 41 | 26/15 | 25/16 | 34.3±14.3 | 34.5±14.9 | 4.4±2.8 | 4.4±2.6 | 中、重度活动性溃疡性结肠炎,Mayo评分为6~12分,内镜评分为2分 | 1、2、4、5 |
| FEAGAN[ | 2014 | RCT | 加拿大 | Adalimumab | Placebo | 480 | 483 | 286/194 | 297/186 | 39.3(18.0±75.0) | 40.6(18.0±79.0) | 8.3(0.2±43.9) | 8.2(0.3±43.3) | 中度至重度活动性UC,定义为Mayo评分6分,内镜亚评分2分 | 5 |
| PANACCIONE[ | 2014 | RCT | 加拿大 | Infliximab | Placebo | 78 | 79 | 42/36 | 46/33 | 38.5(12.7) | 40.7(13.2) | 6.3(6.5) | 6.6(7.8) | 中度至重度UC;中度和重度疾病分别定义为Mayo评分6~8分和9~12分 | 1、5 |
| SUZUKI[ | 2014 | RCT | 日本 | Adalimumab | Placebo | 87 | 96 | 50/37 | 70/26 | 44.4±15.0 | 41.3±13.6 | 8.3±7.7 | 8.3±7.7 | 中度至重度活动性UC,定义为Mayo评分6分,内镜亚评分2分 | 1、4、5 |
| SANDBORN[ | 2014 | RCT | 美国 | Golimumab 50 mg | Placebo | 154 | 156 | 77/77 | 75/81 | 41.4±13.84 | 40.2±14.05 | 6.8±6.93 | 6.9±6.96 | 中度至重度疾病活动,定义为Mayo评分为6~12分,内窥镜评分为2分或以上 | 1、2、4、5 |
| SANDBORN[ | 2014 | RCT | 美国 | Golimumab 100 mg | Placebo | 154 | 156 | 89/65 | 75/81 | 39.1±13.11 | 40.2±14.05 | 7.2±7.04 | 6.9±6.96 | 1、2、4、5 | |
| FEAGAN[ | 2013 | RCT | 加拿大 | Vedolizumab | Placebo | 225 | 149 | 132/93 | 92/57 | 40.1±13.1 | 41.2±12.5 | 6.1±5.1 | 7.1±7.2 | 活动性溃疡性结肠炎,定义为梅奥临床评分6 ~12分,乙状结肠镜评分至少为2分 | 1、2、4 |
| PARIKH[ | 2012 | RCT | 加拿大 | Vedolizumab | Placebo | 37 | 9 | 21/16 | 6/3 | 41(19~69) | 33(21~51) | 3.3(0.1~34.0) | 0.9(0.1~7.5) | 中、重度活动性溃疡性结肠炎,Mayo评分为6~12分,内镜评分为2分 | 5 |
| SANDBORN[ | 2012 | RCT | 美国 | Adalimumab | Placebo | 248 | 246 | 142/106 | 152/94 | 39.6±12.47 | 41.3±13.22 | 8.1±7.09 | 8.5±7.37 | 中度至重度活动性UC至少3个月的成年人,Mayo评分为6~12分(内窥镜评分至少为2分) | 1、2、4 |
| RUTGEERTS[ | 2012 | RCT | 比利时 | Etrolizumab | Placebo | 18 | 5 | 13/5 | 3/2 | 44(14) | 39(19) | 6.5(2~30) | 5.3(2~25) | 中度至重度疾病活动,定义为Mayo评分为6~12分 | 1、2 |
表1 纳入研究的基本特征
Table 1 Basic information of included RCTs
| 第一作者 | 发表年份(年) | 研究类型 | 国家 | 干预方式 | 例数 | 性别(男/女) | 年龄(岁) | 疾病持续时间(年) | 疾病程度 | 结局指标 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | ||||||
| HIBI[ | 2023 | RCT | 日本 | Filgotinib 100 mg | Placebo | 16 | 6 | 11/34 | 11/5 | 48±13 | 48±11 | 8.2±9.5 | 11.8±14.0 | 中度至重度活动性UC(Mayo内镜评分≥2分,直肠出血评分≥1分,大便频率亚评分≥1分,医生总体评估亚评分≥2分);总Mayo临床评分为6~12分 | 1、5 |
| HIBI[ | 2023 | RCT | 日本 | Filgotinib 200 mg | Placebo | 15 | 6 | 18/26 | 8/7 | 52±12 | 48±11 | 7.2±6.8 | 11.8±14.0 | 1、5 | |
| SCHREIBER[ | 2023 | RCT | 德国 | Filgotinib 200 mg | Placebo | 245 | 137 | 123/122 | 87/50 | 42±13.1 | 41±12.9 | 7.2±6.9 | 6.4±7.4 | 中至重度活动性UC患者(Mayo内镜评分≥2分,直肠出血评分≥1分,大便频率评分≥1分,医生总体评估评分≥2分;总梅奥临床评分为6~12分) | 1 |
| DOTAN[ | 2023 | RCT | 以色列 | Filgotinib 100 mg | Placebo | 277 | 140 | 156/121 | 89/51 | 42.3±13.3 | 41.5±12.8 | 6.7±7.4 | 6.5±7.4 | 中度至重度活动性UC的定义为Mayo内镜亚评分≥2分,直肠出血亚评分≥1分,大便频率评分≥1分,医生总体评估评分≥2分;分值相加为梅奥诊所总分6~12分 | 1 |
| DOTAN[ | 2023 | RCT | 以色列 | Filgotinib 200 mg | Placebo | 248 | 140 | 123/125 | 89/51 | 42.4±13.0 | 41.5±12.8 | 7.2±7.0 | 6.5±7.4 | 1 | |
| FEAGAN[ | 2021 | RCT | 加拿大 | Filgotinib 100 mg | Placebo | 277 | 137 | 157/120 | 87/50 | 42(13.3) | 41(12.9) | 6.7(7.4) | 6.4(7.4) | 中度至重度活动性溃疡性结肠炎内镜评分≥2分,直肠出血评分≥1分,大便频率评分≥1分,医生总体评估评分≥2分;梅奥临床总评分6~12分 | 1、3 |
| FEAGAN[ | 2021 | RCT | 加拿大 | Filgotinib 200 mg | Placebo | 245 | 137 | 123/122 | 87/50 | 42(13.1) | 41(12.9) | 7.2(6.9) | 6.4(7.4) | 1、3 | |
| DANESE[ | 2022 | RCT | 印度 | Upadacitinib | Placebo | 319 | 154 | 198/121 | 97/57 | 43.0(23.0) | 44.5(23.0) | 6.6(9.6) | 6.2(8.6) | 中、重度活动性溃疡性结肠炎患者(适应Mayo评分5~9分;内镜下评分为2分或3分) | 1、2、3、4、5 |
| SANDBORN[ | 2020 | RCT | 美国 | Upadacitinib | Placebo | 47 | 46 | 23/24 | 29/17 | 41(18~75) | 40(21~67) | 6.59(0.8~43.7) | 5.19(0.4~30.8) | 中度至重度活动性UC | 1、2、3、5 |
| SANDBORN[ | 2020 | RCT | 美国 | Upadacitinib | Placebo | 49 | 46 | 30/19 | 29/17 | 41(18~75) | 40(21~67) | 4.58(0.2~43.0) | 5.19(0.4~30.8) | ||
| SANDBORN[ | 2020 | RCT | 美国 | Upadacitinib | Placebo | 52 | 46 | 31/21 | 29/17 | 42(20~72) | 40(21~67) | 6.06(0.3~27.5) | 5.19(0.4~30.8) | ||
| SANDBORN[ | 2020 | RCT | 美国 | Upadacitinib | Placebo | 56 | 46 | 37/19 | 29/17 | 37(19~74) | 40(21~67) | 6.46(0.4~23.9) | 5.19(0.4~30.8) | ||
| SANDBORN[ | 2019 | RCT | 美国 | Tofacitinib | Placebo | 938 | 282 | 557/381 | 155/127 | 41.3(13.8) | 41.4(14.4) | 8.2(7.0) | 8.2(7.8) | 中度至重度活动性UC | 5 |
| SANDBORN[ | 2018 | RCT | 美国 | Tofacitinib | Placebo | 476 | 122 | 277/199 | 77/45 | 41.3±14.1 | 41.8±15.3 | 6.5 | 6.0 | 中度至重度活动性疾病,定义为Mayo评分为6~12分,其中直肠出血评分为1~3分,内镜评分为2分或3分,Mayo评分范围为0~12分,4个评分范围均为0~3分,评分越高疾病越严重 | 1、2、3、4、5 |
| DANESE[ | 2022 | RCT | 德国 | Etrolizumab | Infliximab | 199 | 198 | 118/81 | 132/66 | 37(18~76) | 37(18~70) | 3.3(0.3~49.0) | 4.1(0.1~33.7) | 中度至重度活动性溃疡性结肠炎的成年人(定义为梅奥诊所总分为6~12分,内镜亚评分≥2分,直肠出血亚评分≥1分,大便频率亚评分≥1分) | 1 |
| VERMEIRE[ | 2014 | RCT | 比利时 | Etrolizumab | Placebo | 41 | 43 | 28/13 | 19/24 | 44.4(13.9) | 37.5(12.8) | 9.8(8.3) | 9.8(8.4) | 中、重度溃疡性结肠炎,Mayo临床评分为5分或以上(美国FDA要求≥6分) | 1、2、5 |
| RUBIN[ | 2022 | RCT | 美国 | Adalimumab | Placebo | 142 | 72 | 82/60 | 39/33 | 41.0(19~75) | 36.0(19~78) | 4.0(0.3~36.4) | 4.7(0.3~40.8) | 中度至重度活动性溃疡性结肠炎成年人(18~80岁)患者(梅奥临床总分为6~12分,内镜下亚评分≥2分,直肠出血评分≥1分,粪便频率评分≥1分) | 1、2、3、5 |
| RUBIN[ | 2022 | RCT | 美国 | Etrolizumab | Placebo | 144 | 72 | 74/70 | 39/33 | 36.5(18~79) | 36.0(19~78) | 3.4(0.4~41.9) | 4.7(0.3~40.8) | 1、2、3、5 | |
| MOTOYA[ | 2020 | RCT | 日本 | Vedolizumab | Placebo | 164 | 82 | 99/65 | 55/27 | 42.3(14.4) | 44.0(16.0) | 7.2(6.2) | 8.6(8.0) | 患者为中度至重度活动性UC,定义为基线全Mayo评分为6~12分,内窥镜评分为2分 | 1、2、4、5 |
| SANDBORN[ | 2019 | RCT | 美国 | Vedolizumab | Placebo | 106 | 56 | 65/41 | 34/22 | 38.1(13.1) | 39.4(11.7) | 8.0(6.2) | 7.4(7.1) | 患者为中度至重度活动性UC,Mayo评分为6~12分,内窥镜评分≥2分 | 1、2、3、5 |
| YAJNIK[ | 2017 | RCT | 美国 | Vedolizumab | Placebo | 334 | 78 | 187/147 | 49/29 | 44.3±5.9 | 45.0±5.5 | 8.0±6.2 | 8.0±7.1 | 中度至重度活动性UC | 2 |
| REINISCH[ | 2018 | RCT | 澳大利亚 | Golimumab 50 mg | Placebo | 93 | 96 | 47/46 | 47/49 | 40.0(12.50) | 40.8(14.83) | 7.0(7.06) | 6.7(7.51) | 中度至重度活动性UC | 5 |
| REINISCH[ | 2018 | RCT | 澳大利亚 | Golimumab 100 mg | Placebo | 477 | 96 | 285/192 | 47/49 | 40.0(12.79) | 40.8(14.83) | 6.7(6.22) | 6.7(7.51) | 5 | |
| RUTGEERTS[ | 2015 | RCT | 美国 | Golimumab 100 mg | Placebo | 214 | 77 | 127/87 | 47/30 | 41.0±14.16 | 40.9±12.58 | 6.8±6.75 | 6.8±6.59 | 中重度疾病活动(Mayo评分为6~12分,包括内镜评分≥2分) | 1、2、4、5 |
| JIANG[ | 2015 | RCT | 中国 | Infliximab | Placebo | 41 | 41 | 26/15 | 25/16 | 34.3±14.3 | 34.5±14.9 | 4.4±2.8 | 4.4±2.6 | 中、重度活动性溃疡性结肠炎,Mayo评分为6~12分,内镜评分为2分 | 1、2、4、5 |
| FEAGAN[ | 2014 | RCT | 加拿大 | Adalimumab | Placebo | 480 | 483 | 286/194 | 297/186 | 39.3(18.0±75.0) | 40.6(18.0±79.0) | 8.3(0.2±43.9) | 8.2(0.3±43.3) | 中度至重度活动性UC,定义为Mayo评分6分,内镜亚评分2分 | 5 |
| PANACCIONE[ | 2014 | RCT | 加拿大 | Infliximab | Placebo | 78 | 79 | 42/36 | 46/33 | 38.5(12.7) | 40.7(13.2) | 6.3(6.5) | 6.6(7.8) | 中度至重度UC;中度和重度疾病分别定义为Mayo评分6~8分和9~12分 | 1、5 |
| SUZUKI[ | 2014 | RCT | 日本 | Adalimumab | Placebo | 87 | 96 | 50/37 | 70/26 | 44.4±15.0 | 41.3±13.6 | 8.3±7.7 | 8.3±7.7 | 中度至重度活动性UC,定义为Mayo评分6分,内镜亚评分2分 | 1、4、5 |
| SANDBORN[ | 2014 | RCT | 美国 | Golimumab 50 mg | Placebo | 154 | 156 | 77/77 | 75/81 | 41.4±13.84 | 40.2±14.05 | 6.8±6.93 | 6.9±6.96 | 中度至重度疾病活动,定义为Mayo评分为6~12分,内窥镜评分为2分或以上 | 1、2、4、5 |
| SANDBORN[ | 2014 | RCT | 美国 | Golimumab 100 mg | Placebo | 154 | 156 | 89/65 | 75/81 | 39.1±13.11 | 40.2±14.05 | 7.2±7.04 | 6.9±6.96 | 1、2、4、5 | |
| FEAGAN[ | 2013 | RCT | 加拿大 | Vedolizumab | Placebo | 225 | 149 | 132/93 | 92/57 | 40.1±13.1 | 41.2±12.5 | 6.1±5.1 | 7.1±7.2 | 活动性溃疡性结肠炎,定义为梅奥临床评分6 ~12分,乙状结肠镜评分至少为2分 | 1、2、4 |
| PARIKH[ | 2012 | RCT | 加拿大 | Vedolizumab | Placebo | 37 | 9 | 21/16 | 6/3 | 41(19~69) | 33(21~51) | 3.3(0.1~34.0) | 0.9(0.1~7.5) | 中、重度活动性溃疡性结肠炎,Mayo评分为6~12分,内镜评分为2分 | 5 |
| SANDBORN[ | 2012 | RCT | 美国 | Adalimumab | Placebo | 248 | 246 | 142/106 | 152/94 | 39.6±12.47 | 41.3±13.22 | 8.1±7.09 | 8.5±7.37 | 中度至重度活动性UC至少3个月的成年人,Mayo评分为6~12分(内窥镜评分至少为2分) | 1、2、4 |
| RUTGEERTS[ | 2012 | RCT | 比利时 | Etrolizumab | Placebo | 18 | 5 | 13/5 | 3/2 | 44(14) | 39(19) | 6.5(2~30) | 5.3(2~25) | 中度至重度疾病活动,定义为Mayo评分为6~12分 | 1、2 |
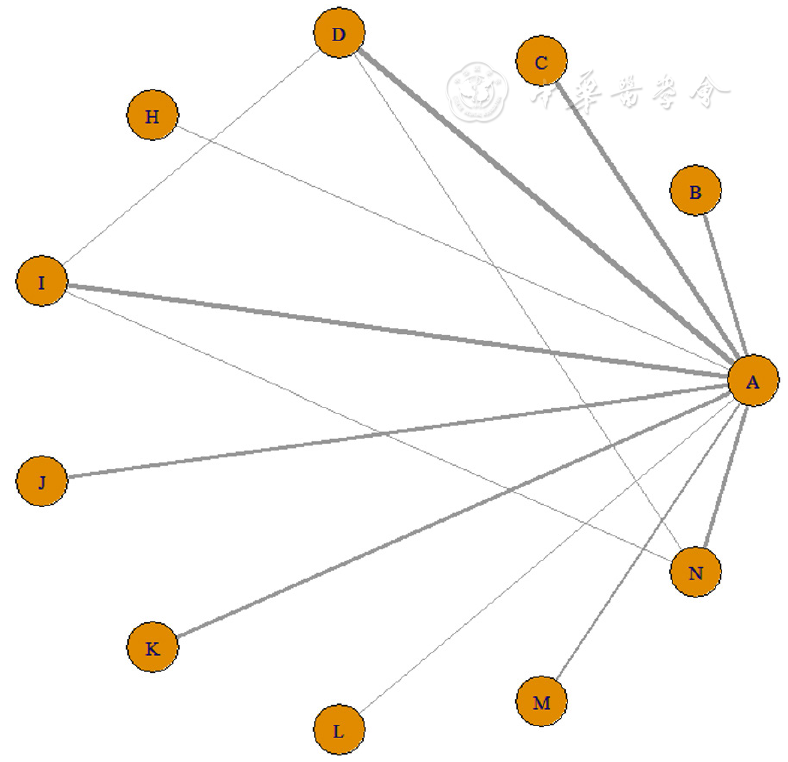
图3 临床缓解率的网络证据图注:A=Placebo,B=Filgotinib 100 mg,C=Filgotinib 200 mg,D=Upadacitinib,H=Tofacitinib,I=Etrolizumab,J=Adalimumab,K=Vedolizumab,L=Golimumab 50 mg,M=Golimumab 100 mg,N=Infliximab。
Figure 3 Network diagram for clinical remission rates
| 干预措施 | Placebo | Filgotinib 100 mg | Filgotinib 200 mg | Upadacitinib | Tofacitinib | Etrolizumab | Adalimumab | Vedolizumab | Golimumab 50 mg | Golimumab 100 mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filgotinib 100 mg | -0.25 (-0.59~0.06) | |||||||||
| Filgotinib 200 mg | -0.55 (-0.77~-0.35) | -0.30 (-0.69~0.08) | ||||||||
| Upadacitinib | -1.08 (-1.41~-0.77) | -0.83 (-1.29~-0.37) | -0.53 (-0.92~-0.15) | |||||||
| Tofacitinib | -0.83 (-1.54~-0.25) | -0.58 (-1.34~0.09) | -0.28 (-1.01~0.34) | 0.25 (-0.52~0.92) | ||||||
| Etrolizumab | -0.45 (-0.78~-0.13) | -0.20 (-0.66~0.26) | 0.09 (-0.29~0.49) | 0.63 (0.30~0.96) | 0.38 (-0.28~1.15) | |||||
| Adalimumab | -0.38 (-0.60~-0.17) | -0.13 (-0.51~0.26) | 0.17 (-0.12~0.47) | 0.70 (0.31~1.09) | 0.45 (-0.16~1.19) | 0.07 (-0.31~0.46) | ||||
| Vedolizumab | -0.94 (-1.36~-0.57) | -0.69 (-1.21~-0.19) | -0.38 (-0.85~0.04) | 0.14 (-0.37~0.64) | -0.10 (-0.82~0.68) | -0.49 (-1.00~0.01) | -0.56 (-1.02~-0.12) | |||
| Golimumab 50 mg | -0.45 (-0.82~-0.09) | -0.20 (-0.68~0.28) | 0.10 (-0.32~0.51) | 0.63 (0.15~1.12) | 0.38 (-0.30~1.17) | 0.002 (-0.49~0.49) | -0.07 (-0.49~0.34) | 0.49 (-0.03~1.03) | ||
| Golimumab 100 mg | -0.49 (-0.83~-0.18) | -0.24 (-0.71~0.21) | 0.05 (-0.33~0.43) | 0.58 (0.13~1.04) | 0.34 (-0.33~1.11) | -0.04 (-0.50~0.41) | -0.11 (-0.51~0.26) | 0.44 (-0.05~0.96) | -0.04 (-0.53~0.43) | |
| Infliximab | -0.77 (-1.09~-0.46) | -0.51 (-0.96~-0.06) | -0.21 (-0.59~0.15) | 0.31 (0.02~0.62) | 0.06 (-0.60~0.83) | -0.31 (-0.67~0.04) | -0.38 (-0.76~-0.01) | 0.17 (-0.31~0.68) | -0.31 (-0.79~0.15) | -0.27 (-0.72~0.17) |
表2 不同干预措施对UC临床缓解率比较的网状Meta分析结果[logOR(95%CI)]
Table 2 Network meta-analysis of the clinical remission rates of different types of intervention regimens
| 干预措施 | Placebo | Filgotinib 100 mg | Filgotinib 200 mg | Upadacitinib | Tofacitinib | Etrolizumab | Adalimumab | Vedolizumab | Golimumab 50 mg | Golimumab 100 mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filgotinib 100 mg | -0.25 (-0.59~0.06) | |||||||||
| Filgotinib 200 mg | -0.55 (-0.77~-0.35) | -0.30 (-0.69~0.08) | ||||||||
| Upadacitinib | -1.08 (-1.41~-0.77) | -0.83 (-1.29~-0.37) | -0.53 (-0.92~-0.15) | |||||||
| Tofacitinib | -0.83 (-1.54~-0.25) | -0.58 (-1.34~0.09) | -0.28 (-1.01~0.34) | 0.25 (-0.52~0.92) | ||||||
| Etrolizumab | -0.45 (-0.78~-0.13) | -0.20 (-0.66~0.26) | 0.09 (-0.29~0.49) | 0.63 (0.30~0.96) | 0.38 (-0.28~1.15) | |||||
| Adalimumab | -0.38 (-0.60~-0.17) | -0.13 (-0.51~0.26) | 0.17 (-0.12~0.47) | 0.70 (0.31~1.09) | 0.45 (-0.16~1.19) | 0.07 (-0.31~0.46) | ||||
| Vedolizumab | -0.94 (-1.36~-0.57) | -0.69 (-1.21~-0.19) | -0.38 (-0.85~0.04) | 0.14 (-0.37~0.64) | -0.10 (-0.82~0.68) | -0.49 (-1.00~0.01) | -0.56 (-1.02~-0.12) | |||
| Golimumab 50 mg | -0.45 (-0.82~-0.09) | -0.20 (-0.68~0.28) | 0.10 (-0.32~0.51) | 0.63 (0.15~1.12) | 0.38 (-0.30~1.17) | 0.002 (-0.49~0.49) | -0.07 (-0.49~0.34) | 0.49 (-0.03~1.03) | ||
| Golimumab 100 mg | -0.49 (-0.83~-0.18) | -0.24 (-0.71~0.21) | 0.05 (-0.33~0.43) | 0.58 (0.13~1.04) | 0.34 (-0.33~1.11) | -0.04 (-0.50~0.41) | -0.11 (-0.51~0.26) | 0.44 (-0.05~0.96) | -0.04 (-0.53~0.43) | |
| Infliximab | -0.77 (-1.09~-0.46) | -0.51 (-0.96~-0.06) | -0.21 (-0.59~0.15) | 0.31 (0.02~0.62) | 0.06 (-0.60~0.83) | -0.31 (-0.67~0.04) | -0.38 (-0.76~-0.01) | 0.17 (-0.31~0.68) | -0.31 (-0.79~0.15) | -0.27 (-0.72~0.17) |
| 干预措施 | Placebo | Upadacitinib | Tofacitinib | Etrolizumab | Adalimumab | Vedolizumab | Golimumab 50 mg | Golimumab 100 mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upadacitinib | -1.05(-1.28~-0.83) | |||||||
| Tofacitinib | -0.50(-0.79~-0.26) | 0.54(0.17~0.89) | ||||||
| Etrolizumab | -0.20(-0.40~-0.01) | 0.84(0.55~1.14) | 0.30(-0.01~0.65) | |||||
| Adalimumab | -0.28(-0.43~-0.13) | 0.76(0.49~1.04) | 0.22(-0.06~0.55) | -0.08(-0.32~0.16) | ||||
| Vedolizumab | -0.43(-0.64~-0.23) | 0.61(0.31~0.91) | 0.076(-0.25~0.42) | -0.23(-0.50~0.05) | -0.14(-0.40~0.10) | |||
| Golimumab 50 mg | -0.40(-0.70~-0.12) | 0.64(0.27~1.00) | 0.10(-0.28~0.50) | -0.20(-0.54~0.14) | -0.12(-0.45~0.19) | 0.02(-0.32~0.37) | ||
| Golimumab 100 mg | -0.24(-0.49~-0.01) | 0.80(0.47~1.12) | 0.26(-0.08~0.62) | -0.04(-0.35~0.25) | 0.03(-0.24~0.31) | 0.18(-0.12~0.49) | 0.15(-0.21~0.52) | |
| Infliximab | -0.75(-1.24~-0.36) | 0.30(-0.23~0.75) | -0.24(-0.79~0.24) | -0.54(-1.07~-0.10) | -0.46(-0.97~-0.05) | -0.31(-0.84~0.12) | -0.34(-0.92~0.14) | -0.50(-1.03~-0.04) |
表3 不同干预措施对UC临床反应比较的网状Meta分析结果[logOR(95%CI)]
Table 3 Network meta-analysis of the clinical response of different types of intervention regimens
| 干预措施 | Placebo | Upadacitinib | Tofacitinib | Etrolizumab | Adalimumab | Vedolizumab | Golimumab 50 mg | Golimumab 100 mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upadacitinib | -1.05(-1.28~-0.83) | |||||||
| Tofacitinib | -0.50(-0.79~-0.26) | 0.54(0.17~0.89) | ||||||
| Etrolizumab | -0.20(-0.40~-0.01) | 0.84(0.55~1.14) | 0.30(-0.01~0.65) | |||||
| Adalimumab | -0.28(-0.43~-0.13) | 0.76(0.49~1.04) | 0.22(-0.06~0.55) | -0.08(-0.32~0.16) | ||||
| Vedolizumab | -0.43(-0.64~-0.23) | 0.61(0.31~0.91) | 0.076(-0.25~0.42) | -0.23(-0.50~0.05) | -0.14(-0.40~0.10) | |||
| Golimumab 50 mg | -0.40(-0.70~-0.12) | 0.64(0.27~1.00) | 0.10(-0.28~0.50) | -0.20(-0.54~0.14) | -0.12(-0.45~0.19) | 0.02(-0.32~0.37) | ||
| Golimumab 100 mg | -0.24(-0.49~-0.01) | 0.80(0.47~1.12) | 0.26(-0.08~0.62) | -0.04(-0.35~0.25) | 0.03(-0.24~0.31) | 0.18(-0.12~0.49) | 0.15(-0.21~0.52) | |
| Infliximab | -0.75(-1.24~-0.36) | 0.30(-0.23~0.75) | -0.24(-0.79~0.24) | -0.54(-1.07~-0.10) | -0.46(-0.97~-0.05) | -0.31(-0.84~0.12) | -0.34(-0.92~0.14) | -0.50(-1.03~-0.04) |
| 干预措施 | Placebo | Filgotinib 100 mg | Filgotinib 200 mg | Upadacitinib | Tofacitinib | Etrolizumab | Adalimumab |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filgotinib 100 mg | -0.49(-1.59~0.42) | ||||||
| Filgotinib 200 mg | -1.25(-2.35~-0.41) | -0.75(-2.19~0.61) | |||||
| Upadacitinib | -3.10(-4.94~-1.89) | -2.62(-4.67~-0.92) | -1.86(-3.88~-0.22) | ||||
| Tofacitinib | -1.54(-3.33~-0.32) | -1.05(-3.01~0.61) | -0.28(-2.27~1.33) | 1.57(-0.54~3.71) | |||
| Etrolizumab | -0.99(-1.67~-0.41) | -0.49(-1.63~0.73) | 0.26(-0.81~1.49) | 2.11(0.71~4.02) | 0.55(-0.86~2.44) | ||
| Adalimumab | -1.14(-1.81~-0.58) | -0.65(-1.78~0.58) | 0.10(-0.96~1.33) | 1.96(0.56~3.88) | 0.39(-0.99~2.27) | -0.15(-1.03~0.73) | |
| Vedolizumab | -0.99(-1.57~-0.50) | -0.49(-1.60~0.69) | 0.25(-0.76~1.46) | 2.11(0.75~3.99) | 0.55(-0.82~2.39) | -0.003(-0.83~0.82) | 0.10(-0.66~0.98) |
表4 不同干预措施对UC内镜缓解比较的网状Meta分析结果[logOR(95%CI)]
Table 4 Network meta-analysis of the endoscopic remission of different types of intervention regimens
| 干预措施 | Placebo | Filgotinib 100 mg | Filgotinib 200 mg | Upadacitinib | Tofacitinib | Etrolizumab | Adalimumab |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filgotinib 100 mg | -0.49(-1.59~0.42) | ||||||
| Filgotinib 200 mg | -1.25(-2.35~-0.41) | -0.75(-2.19~0.61) | |||||
| Upadacitinib | -3.10(-4.94~-1.89) | -2.62(-4.67~-0.92) | -1.86(-3.88~-0.22) | ||||
| Tofacitinib | -1.54(-3.33~-0.32) | -1.05(-3.01~0.61) | -0.28(-2.27~1.33) | 1.57(-0.54~3.71) | |||
| Etrolizumab | -0.99(-1.67~-0.41) | -0.49(-1.63~0.73) | 0.26(-0.81~1.49) | 2.11(0.71~4.02) | 0.55(-0.86~2.44) | ||
| Adalimumab | -1.14(-1.81~-0.58) | -0.65(-1.78~0.58) | 0.10(-0.96~1.33) | 1.96(0.56~3.88) | 0.39(-0.99~2.27) | -0.15(-1.03~0.73) | |
| Vedolizumab | -0.99(-1.57~-0.50) | -0.49(-1.60~0.69) | 0.25(-0.76~1.46) | 2.11(0.75~3.99) | 0.55(-0.82~2.39) | -0.003(-0.83~0.82) | 0.10(-0.66~0.98) |
| 干预措施 | Placebo | Upadacitinib | Tofacitinib | Adalimumab | Vedolizumab | Golimumab 50 mg | Golimumab 100 mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upadacitinib | -2.27(-4.18~-1.03) | ||||||
| Tofacitinib | -0.72(-1.20~-0.31) | 1.55(0.19~3.52) | |||||
| Adalimumab | -0.31(-0.50~-0.12) | 1.96(0.70~3.87) | 0.41(-0.04~0.92) | ||||
| Vedolizumab | -0.38(-0.64~-0.14) | 1.89(0.61~3.80) | 0.33(-0.14~0.87) | -0.07(-0.38~0.23) | |||
| Golimumab 50 mg | -0.40(-0.89~0.05) | 1.87(0.51~3.82) | 0.32(-0.32~0.98) | -0.09(-0.61~0.40) | -0.02(-0.56~0.51) | ||
| Golimumab 100 mg | -0.28(-0.60~0.01) | 1.98(0.69~3.92) | 0.43(-0.08~0.99) | 0.02(-0.34~0.37) | 0.09(-0.29~0.48) | 0.11(-0.44~0.68) | |
| Infliximab | -0.54(-0.86~-0.26) | 1.72(0.44~3.65) | 0.17(-0.34~0.72) | -0.23(-0.60~0.10) | -0.16(-0.55~0.21) | -0.14(-0.70~0.41) | -0.26(-0.69~0.15) |
表5 不同干预措施对UC黏膜愈合比较的网状Meta分析结果[logOR(95%CI)]
Table 5 Network meta-analysis of the mucosal healing of different types of intervention regimens
| 干预措施 | Placebo | Upadacitinib | Tofacitinib | Adalimumab | Vedolizumab | Golimumab 50 mg | Golimumab 100 mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upadacitinib | -2.27(-4.18~-1.03) | ||||||
| Tofacitinib | -0.72(-1.20~-0.31) | 1.55(0.19~3.52) | |||||
| Adalimumab | -0.31(-0.50~-0.12) | 1.96(0.70~3.87) | 0.41(-0.04~0.92) | ||||
| Vedolizumab | -0.38(-0.64~-0.14) | 1.89(0.61~3.80) | 0.33(-0.14~0.87) | -0.07(-0.38~0.23) | |||
| Golimumab 50 mg | -0.40(-0.89~0.05) | 1.87(0.51~3.82) | 0.32(-0.32~0.98) | -0.09(-0.61~0.40) | -0.02(-0.56~0.51) | ||
| Golimumab 100 mg | -0.28(-0.60~0.01) | 1.98(0.69~3.92) | 0.43(-0.08~0.99) | 0.02(-0.34~0.37) | 0.09(-0.29~0.48) | 0.11(-0.44~0.68) | |
| Infliximab | -0.54(-0.86~-0.26) | 1.72(0.44~3.65) | 0.17(-0.34~0.72) | -0.23(-0.60~0.10) | -0.16(-0.55~0.21) | -0.14(-0.70~0.41) | -0.26(-0.69~0.15) |
| 干预措施 | Placebo | Filgotinib 100 mg | Filgotinib 200 mg | Upadacitinib | Tofacitinib | Etrolizumab | Adalimumab | Vedolizumab | Golimumab 50 mg | Golimumab 100 mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filgotinib 100 mg | 2.24 (0.23~5.58) | |||||||||
| Filgotinib 200 mg | 2.18 (0.21~5.43) | -0.05 (-3.88~3.73) | ||||||||
| Upadacitinib | 0.10 (8.31~0.20) | -2.14 (-5.47~-0.13) | -2.08 (-5.33~-0.10) | |||||||
| Tofacitinib | 0.02 (-0.15~0.18) | -2.22 (-5.56~-0.20) | -2.16 (-5.41~-0.17) | -0.07 (-0.28~0.11) | ||||||
| Etrolizumab | 0.08 (-0.10~0.27) | -2.16 (-5.49~-0.14) | -2.09 (-5.35~-0.11) | -0.01 (-0.23~0.19) | 0.06 (-0.18~0.32) | |||||
| Adalimumab | 0.02 (-0.12~0.16) | -2.22 (-5.56~-0.20) | -2.16 (-5.42~-0.17) | -0.07 (-0.25~0.09) | 0.001 (-0.21~0.22) | -0.06 (-0.30~0.17) | ||||
| Vedolizumab | 0.11 (-0.05~0.27) | -2.13 (-5.47~-0.11) | -2.07 (-5.32~-0.08) | 0.01 (-0.18~0.19) | 0.09 (-0.14~0.32) | 0.02 (-0.22~0.27) | 0.08 (-0.12~0.30) | |||
| Golimumab 50 mg | -0.18 (-0.30~-0.06) | -2.42 (-5.76~-0.41) | -2.37 (-5.62~-0.38) | -0.28 (-0.44~-0.12) | -0.20 (-0.40~0.01) | -0.27 (-0.49~-0.04) | -0.20 (-0.39~-0.01) | -0.29 (-0.49~-0.09) | ||
| Golimumab 100 mg | -0.22 (-0.33~-0.12) | -2.47 (-5.82~-0.46) | -2.41 (-5.67~-0.43) | -0.32 (-0.47~-0.18) | -0.25 (-0.44~-0.04) | -0.31 (-0.53~-0.10) | -0.25 (-0.42~-0.07) | -0.34 (-0.52~-0.14) | -0.04 (-0.20~0.11) | |
| Infliximab | 0.24 (-0.03~0.52) | -1.99 (-5.33~0.03) | -1.94 (-5.20~0.05) | 0.14 (-0.15~0.44) | 0.22 (-0.10~0.55) | 0.15 (-0.17~0.49) | 0.22 (-0.08~0.53) | 0.13 (-0.18~0.45) | 0.42 (0.12~0.73) | 0.47 (0.17~0.77) |
表6 不同干预措施对UC不良事件比较的网状Meta分析结果[logOR(95%CI)]
Table 6 Network meta-analysis of the adverse events of different types of intervention regimens
| 干预措施 | Placebo | Filgotinib 100 mg | Filgotinib 200 mg | Upadacitinib | Tofacitinib | Etrolizumab | Adalimumab | Vedolizumab | Golimumab 50 mg | Golimumab 100 mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filgotinib 100 mg | 2.24 (0.23~5.58) | |||||||||
| Filgotinib 200 mg | 2.18 (0.21~5.43) | -0.05 (-3.88~3.73) | ||||||||
| Upadacitinib | 0.10 (8.31~0.20) | -2.14 (-5.47~-0.13) | -2.08 (-5.33~-0.10) | |||||||
| Tofacitinib | 0.02 (-0.15~0.18) | -2.22 (-5.56~-0.20) | -2.16 (-5.41~-0.17) | -0.07 (-0.28~0.11) | ||||||
| Etrolizumab | 0.08 (-0.10~0.27) | -2.16 (-5.49~-0.14) | -2.09 (-5.35~-0.11) | -0.01 (-0.23~0.19) | 0.06 (-0.18~0.32) | |||||
| Adalimumab | 0.02 (-0.12~0.16) | -2.22 (-5.56~-0.20) | -2.16 (-5.42~-0.17) | -0.07 (-0.25~0.09) | 0.001 (-0.21~0.22) | -0.06 (-0.30~0.17) | ||||
| Vedolizumab | 0.11 (-0.05~0.27) | -2.13 (-5.47~-0.11) | -2.07 (-5.32~-0.08) | 0.01 (-0.18~0.19) | 0.09 (-0.14~0.32) | 0.02 (-0.22~0.27) | 0.08 (-0.12~0.30) | |||
| Golimumab 50 mg | -0.18 (-0.30~-0.06) | -2.42 (-5.76~-0.41) | -2.37 (-5.62~-0.38) | -0.28 (-0.44~-0.12) | -0.20 (-0.40~0.01) | -0.27 (-0.49~-0.04) | -0.20 (-0.39~-0.01) | -0.29 (-0.49~-0.09) | ||
| Golimumab 100 mg | -0.22 (-0.33~-0.12) | -2.47 (-5.82~-0.46) | -2.41 (-5.67~-0.43) | -0.32 (-0.47~-0.18) | -0.25 (-0.44~-0.04) | -0.31 (-0.53~-0.10) | -0.25 (-0.42~-0.07) | -0.34 (-0.52~-0.14) | -0.04 (-0.20~0.11) | |
| Infliximab | 0.24 (-0.03~0.52) | -1.99 (-5.33~0.03) | -1.94 (-5.20~0.05) | 0.14 (-0.15~0.44) | 0.22 (-0.10~0.55) | 0.15 (-0.17~0.49) | 0.22 (-0.08~0.53) | 0.13 (-0.18~0.45) | 0.42 (0.12~0.73) | 0.47 (0.17~0.77) |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
马清林,杜丽东,臧凯宏,等. 溃疡性结肠炎研究进展概述[J]. 医药论坛杂志,2020,41(1):175-176,封3.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
柴昕浩,刘俊. 小分子Janus激酶抑制剂在炎症性肠病中的应用[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2020,30(16):50-54. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2020.16.009.
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
许馨文,周群燕,陈中霞,等. 生物制剂治疗中重度溃疡性结肠炎的研究进展[J]. 胃肠病学,2021,26(6):363-367.
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [1] | 郑博月, 付积艺, 吴佳霏, 王珺, 李慧. 卡非佐米治疗多发性骨髓瘤的疗效及安全性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3806-3814. |
| [2] | 全家霖, 朱琳, 苏煜, 陈泽恺, 陈梓淇, 张卓凡. 运动方式对超重或肥胖儿童青少年执行功能改善效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3422-3431. |
| [3] | 李浩, 李江涛, 刘丹, 王建军. 贝利尤单抗和阿尼鲁单抗及泰它西普治疗系统性红斑狼疮疗效和安全性的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2924-2933. |
| [4] | 何芸, 范焕芳, 马盼, 许绍青, 杨柳, 金明哲, 张明蕊, 陈佳琪. 不同针灸治疗方式干预乳腺癌术后上肢淋巴水肿效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1788-1794. |
| [5] | 朱胜杰, 刁华琼, 杭晓屹, 孙文军. 不同中成药注射液治疗后循环缺血性眩晕效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1795-1808. |
| [6] | 迟洵, 刘思思, 陈巧, 胡玥, 王伟仙. 不同营养筛查工具对肝硬化患者营养筛查适用性的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(11): 1395-1402. |
| [7] | 谷明宇, 秦廷廷, 乔昆, 白欣苑, 王尧, 杨宇彤, 李星明. 中国基层高血压管理模式的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(10): 1265-1272. |
| [8] | 刘浏, 徐文航, 吕宾, 范一宏. 维得利珠单抗与乌司奴单抗作为初治生物制剂在中重度活动期克罗恩病患者中的疗效比较研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(08): 948-953. |
| [9] | 郭佳, 曹春梅, 刘国纯, 郑满, 朱芮含, 龙伟. 不同运动方式对失眠患者睡眠影响效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(35): 4376-4387. |
| [10] | 黄腾佳, 曹曦, 陈蕾, 李子滢, 秦莉花. 非药物治疗脑卒中后肩手综合征有效性的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(23): 2921-2930. |
| [11] | 王婷, 王海燕, 富文俊. 不同针灸疗法治疗慢性萎缩性胃炎效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(23): 2913-2920. |
| [12] | 吴凯瑞, 叶宇, 李娇月, 裴蓓, 李学军, 程红亮. 脾胃培源方加减联合针刺治疗慢性萎缩性胃炎伴肠化生效果的多中心临床随机对照试验[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(20): 2466-2475. |
| [13] | 白鑫, 武新宇, 赵尊, 柳舒心, 刘斯淼, 薛宇航, 徐俊玲, 高永举. 131I治疗血清甲状腺球蛋白抗体阳性分化型甲状腺癌远处转移的疗效研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(15): 1833-1837. |
| [14] | 牛靖元, 陈会生, 于嘉祥, 崔钰. 川芎嗪类注射液辅助治疗急性缺血性脑卒中疗效的贝叶斯网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(14): 1761-1774. |
| [15] | 张翼升, 唐福波, 孙亚如, 钟远鸣, 李智斐. 经皮内镜后路经椎间孔腰椎椎间融合术联合高度可调钛质融合器治疗腰椎滑脱合并腰椎管狭窄症的临床疗效分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(35): 4464-4471. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





