中国全科医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (06): 758-764.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2023.0233
• 论著·临床质量改进 • 上一篇
彭咏怡, 吴仲平, 黄锦海, 林俊凤, 陈树冰, 郑劲平, 高怡*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-03-13
修回日期:2023-07-04
出版日期:2024-02-20
发布日期:2023-11-21
通讯作者:
高怡
基金资助:
PENG Yongyi, WU Zhongping, HUANG Jinhai, LIN Junfeng, CHEN Shubing, ZHENG Jinping, GAO Yi*( )
)
Received:2023-03-13
Revised:2023-07-04
Published:2024-02-20
Online:2023-11-21
Contact:
GAO Yi
摘要: 背景 吸入给药是慢性呼吸道疾病患者常用的给药途径。患者使用吸入给药装置的能力是影响治疗效果的关键因素。最近国内研发了一种新型吸入用药定量评估仪器,可测量在附加多种不同吸入器内置阻力条件下的吸气峰流量(PIF)和吸气容积(VI),精准评估患者使用吸入器的能力。然而目前国内外尚无关于此类吸入评估仪器的质量检测方法和通过标准。 目的 对吸入用药定量评估仪器进行质量检测,评估其检测性能,探讨该方法的应用价值。 方法 通过新型吸入用药定量评估仪器PF810模拟不同干粉吸入器内置阻力,共分为5个不同档位(R1~R5),并采用标准流量/容积模拟器对PF810的流量、容积和阻抗性能进行测试。吸气流量测试取固定容积(3.000 L)、在不同流量(在0~2.000 L/s范围内,以0.250 L/s为间隔步进取值)状态下进行。V1测试取低(0.500 L/s)、中(1.000 L/s)、高(1.500 L/s)3种流量,并在不同容积(在1.000~4.000 L范围内以1.000 L为间隔步进取值)状态下进行。采用GraphPad prism 9.0软件的Bland-Altman图法评价不同阻力档位下吸入用药定量评估仪器的PIF、VI测量值与模拟器输出的实际值之间的一致性。 结果 流量检测质量控制评估结果显示,流量检测重复度、准确度和线性度达到性能要求的百分率分别为100.00%(40/40)、95.00%(38/40)、94.29%(33/35)。R5档位1.500 L/s及以上流量下PF810准确度和线性度不符合性能检测要求,其余档位和流量下全部达标。Bland-Altman一致性检验可见,95%一致性界限(LOA)为(-0.271~0.107)L/s,96.00%(192/200)数据点在95%LOA范围内。容积检测质量控制评估结果显示,容积测试重复度、准确度和线性度的性能检测通过率均为100.00%(60/60、60/60、45/45)。Bland-Altman一致性检验可见,95%LOA为(-0.058~0.017)L,100.00%(180/180)数据点在95%LOA范围内。阻抗检测质量控制评估结果显示,吸入用药定量评估仪器PF810阻抗值与相应吸入器内置阻力之间的相对误差绝对值均<5%。 结论 本研究采用标准流量/容积模拟器对吸入用药定量评估仪器在附加不同档位吸入器内置阻力条件下的吸气流量与容积进行质量检测,方法简便可行,并可客观、科学地对该类型仪器进行性能评价与定期检测维护,值得应用与推广。
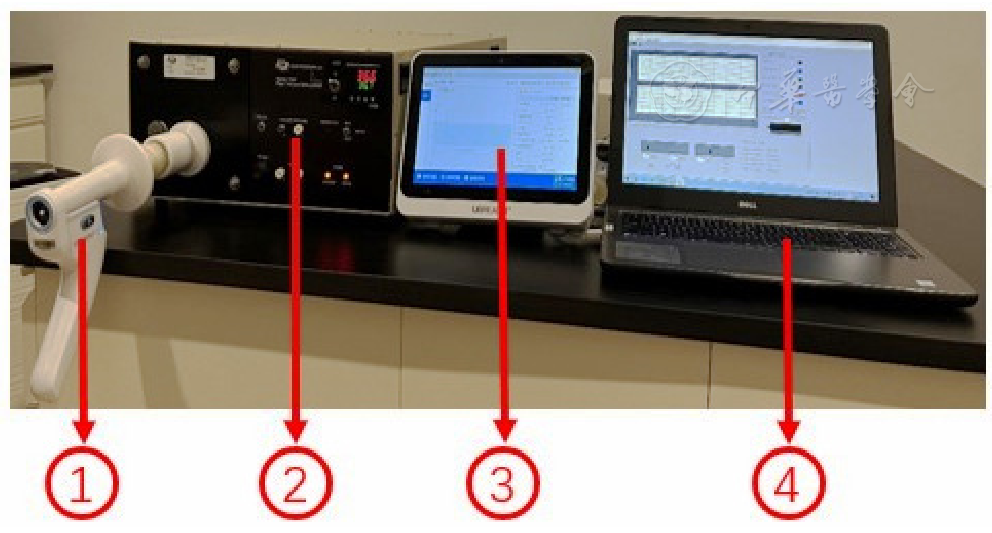

图1 实验设备连接方法注:①吸入用药定量评估仪器(PF810,优呼吸?,浙江亿联康公司),②标准流量/容积模拟器(美国Model 1120,Hans Rudolph公司),③PF810平板控制端,④标准模拟器计算机控制端。
Figure 1 Experimental equipment connection method
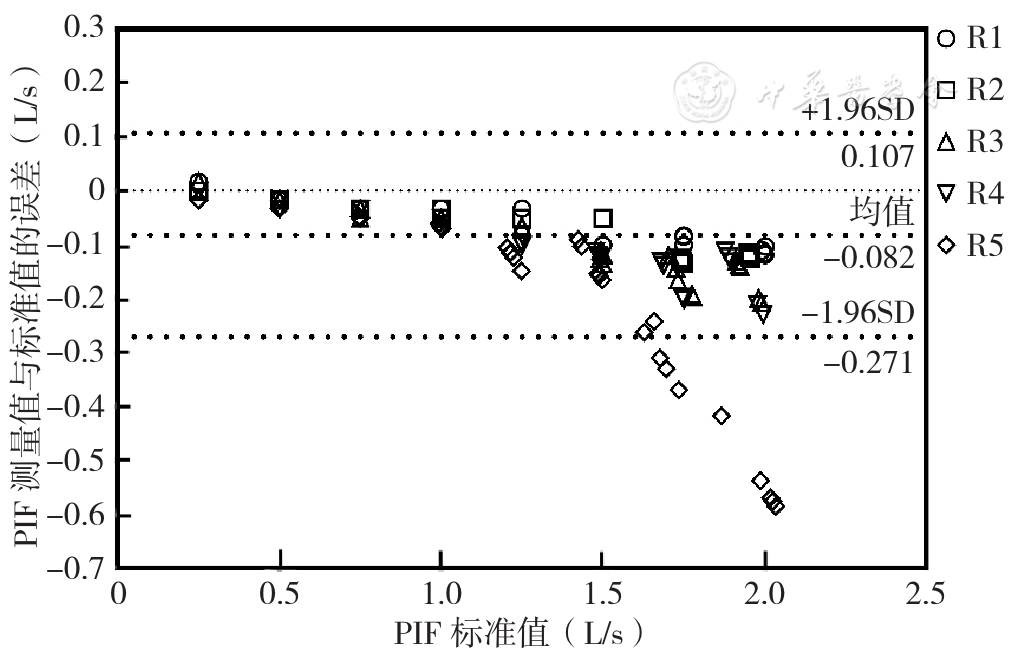
图2 吸入用药定量评估仪器PF810 PIF与标准流量/容积模拟器标准值的Bland-Altman图注:PIF=特定吸气峰流量。
Figure 2 Bland-Altman plot of the PF810 PIF and the standard value of the standard flow/volume simulator
| 阻力档位 | 流量(L/s) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.750 | 1.000 | 1.250 | 1.500 | 1.750 | 2.000 | |
| R1 | ||||||||
| 标准流量/容积模拟器PIF(L/s) | 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.750 | 1.000 | 1.250 | 1.500 | 1.750 | 1.999 |
| PF810 PIF(L/s) | 0.267 | 0.483 | 0.717 | 0.967 | 1.217 | 1.400 | 1.657 | 1.887 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.017 | 0.017 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | 0.017 | -0.017 | -0.033 | -0.033 | -0.033 | -0.100 | -0.094 | -0.113 |
| 相对误差(%) | 6.667 | -3.333 | -4.444 | -3.333 | -2.667 | -6.667 | -5.355 | -5.638 |
| 线性度(%) | 0 | 2.326 | 0 | 0 | 4.762 | -0.378 | 1.007 | |
| R2 | ||||||||
| 标准流量/容积模拟器PIF(L/s) | 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.750 | 1.000 | 1.250 | 1.500 | 1.746 | 1.954 |
| PF810 PIF(L/s) | 0.250 | 0.483 | 0.717 | 0.957 | 1.200 | 1.450 | 1.617 | 1.833 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.017 | 0 | 0.017 | 0 | 0 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | 0 | -0.017 | -0.033 | -0.043 | -0.050 | -0.050 | -0.129 | -0.120 |
| 相对误差(%) | 0 | -3.333 | -4.444 | -4.333 | -4.000 | -3.346 | -7.407 | -6.166 |
| 线性度(%) | 3.448 | 2.326 | 1.045 | 0.556 | 0.014 | 4.895 | -0.484 | |
| R3 | ||||||||
| 标准流量/容积模拟器PIF(L/s) | 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.750 | 1.000 | 1.250 | 1.497 | 1.726 | 1.935 |
| PF810 PIF(L/s) | 0.267 | 0.483 | 0.713 | 0.950 | 1.183 | 1.377 | 1.580 | 1.783 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0 | 0 | 0.017 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.017 | 0 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | 0.017 | -0.017 | -0.037 | -0.050 | -0.066 | -0.121 | -0.146 | -0.152 |
| 相对误差(%) | 6.667 | -3.333 | -4.889 | -5.000 | -5.303 | -8.051 | -8.438 | -7.848 |
| 线性度(%) | 0 | 2.804 | 1.404 | 1.375 | 3.942 | 1.586 | 0.351 | |
| R4 | ||||||||
| 标准流量/容积模拟器PIF(L/s) | 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.750 | 1.000 | 1.249 | 1.488 | 1.697 | 1.909 |
| PF810 PIF(L/s) | 0.250 | 0.480 | 0.717 | 0.950 | 1.153 | 1.367 | 1.550 | 1.767 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0 | 0.017 | 0 | 0 | 0.017 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | 0 | -0.020 | -0.033 | -0.050 | -0.096 | -0.121 | -0.147 | -0.142 |
| 相对误差(%) | 0 | -4.000 | -4.444 | -5.000 | -7.689 | -8.129 | -8.684 | -7.446 |
| 线性度(%) | 4.167 | 1.860 | 1.754 | 3.994 | 1.820 | 1.708 | -0.298 | |
| R5 | ||||||||
| 标准流量/容积模拟器PIF(L/s) | 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.750 | 0.999 | 1.215 | 1.456 | 1.680 | 1.987 |
| PF810 PIF(L/s) | 0.233 | 0.467 | 0.700 | 0.933 | 1.100 | 1.333 | 1.373 | 1.450 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.017 | 0.033 | 0 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | -0.017 | -0.033 | -0.050 | -0.066 | -0.115 | -0.123 | -0.306 | -0.537 |
| 相对误差(%) | -6.667 | -6.667 | -6.692 | -6.573 | -9.480 | -8.450 | -18.235 | -27.040 |
| 线性度(%) | 3.571 | 2.410 | 1.657 | 4.503 | 0.590 | 13.340 | 15.940 | |
表1 吸入用药定量评估仪器PF810流量检测质量控制评估结果
Table 1 Quality control evaluation results of PF810 flow test for inhalation drug quantitative assessment instrument
| 阻力档位 | 流量(L/s) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.750 | 1.000 | 1.250 | 1.500 | 1.750 | 2.000 | |
| R1 | ||||||||
| 标准流量/容积模拟器PIF(L/s) | 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.750 | 1.000 | 1.250 | 1.500 | 1.750 | 1.999 |
| PF810 PIF(L/s) | 0.267 | 0.483 | 0.717 | 0.967 | 1.217 | 1.400 | 1.657 | 1.887 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.017 | 0.017 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | 0.017 | -0.017 | -0.033 | -0.033 | -0.033 | -0.100 | -0.094 | -0.113 |
| 相对误差(%) | 6.667 | -3.333 | -4.444 | -3.333 | -2.667 | -6.667 | -5.355 | -5.638 |
| 线性度(%) | 0 | 2.326 | 0 | 0 | 4.762 | -0.378 | 1.007 | |
| R2 | ||||||||
| 标准流量/容积模拟器PIF(L/s) | 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.750 | 1.000 | 1.250 | 1.500 | 1.746 | 1.954 |
| PF810 PIF(L/s) | 0.250 | 0.483 | 0.717 | 0.957 | 1.200 | 1.450 | 1.617 | 1.833 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.017 | 0 | 0.017 | 0 | 0 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | 0 | -0.017 | -0.033 | -0.043 | -0.050 | -0.050 | -0.129 | -0.120 |
| 相对误差(%) | 0 | -3.333 | -4.444 | -4.333 | -4.000 | -3.346 | -7.407 | -6.166 |
| 线性度(%) | 3.448 | 2.326 | 1.045 | 0.556 | 0.014 | 4.895 | -0.484 | |
| R3 | ||||||||
| 标准流量/容积模拟器PIF(L/s) | 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.750 | 1.000 | 1.250 | 1.497 | 1.726 | 1.935 |
| PF810 PIF(L/s) | 0.267 | 0.483 | 0.713 | 0.950 | 1.183 | 1.377 | 1.580 | 1.783 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0 | 0 | 0.017 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.017 | 0 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | 0.017 | -0.017 | -0.037 | -0.050 | -0.066 | -0.121 | -0.146 | -0.152 |
| 相对误差(%) | 6.667 | -3.333 | -4.889 | -5.000 | -5.303 | -8.051 | -8.438 | -7.848 |
| 线性度(%) | 0 | 2.804 | 1.404 | 1.375 | 3.942 | 1.586 | 0.351 | |
| R4 | ||||||||
| 标准流量/容积模拟器PIF(L/s) | 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.750 | 1.000 | 1.249 | 1.488 | 1.697 | 1.909 |
| PF810 PIF(L/s) | 0.250 | 0.480 | 0.717 | 0.950 | 1.153 | 1.367 | 1.550 | 1.767 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0 | 0.017 | 0 | 0 | 0.017 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | 0 | -0.020 | -0.033 | -0.050 | -0.096 | -0.121 | -0.147 | -0.142 |
| 相对误差(%) | 0 | -4.000 | -4.444 | -5.000 | -7.689 | -8.129 | -8.684 | -7.446 |
| 线性度(%) | 4.167 | 1.860 | 1.754 | 3.994 | 1.820 | 1.708 | -0.298 | |
| R5 | ||||||||
| 标准流量/容积模拟器PIF(L/s) | 0.250 | 0.500 | 0.750 | 0.999 | 1.215 | 1.456 | 1.680 | 1.987 |
| PF810 PIF(L/s) | 0.233 | 0.467 | 0.700 | 0.933 | 1.100 | 1.333 | 1.373 | 1.450 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.017 | 0.033 | 0 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | -0.017 | -0.033 | -0.050 | -0.066 | -0.115 | -0.123 | -0.306 | -0.537 |
| 相对误差(%) | -6.667 | -6.667 | -6.692 | -6.573 | -9.480 | -8.450 | -18.235 | -27.040 |
| 线性度(%) | 3.571 | 2.410 | 1.657 | 4.503 | 0.590 | 13.340 | 15.940 | |
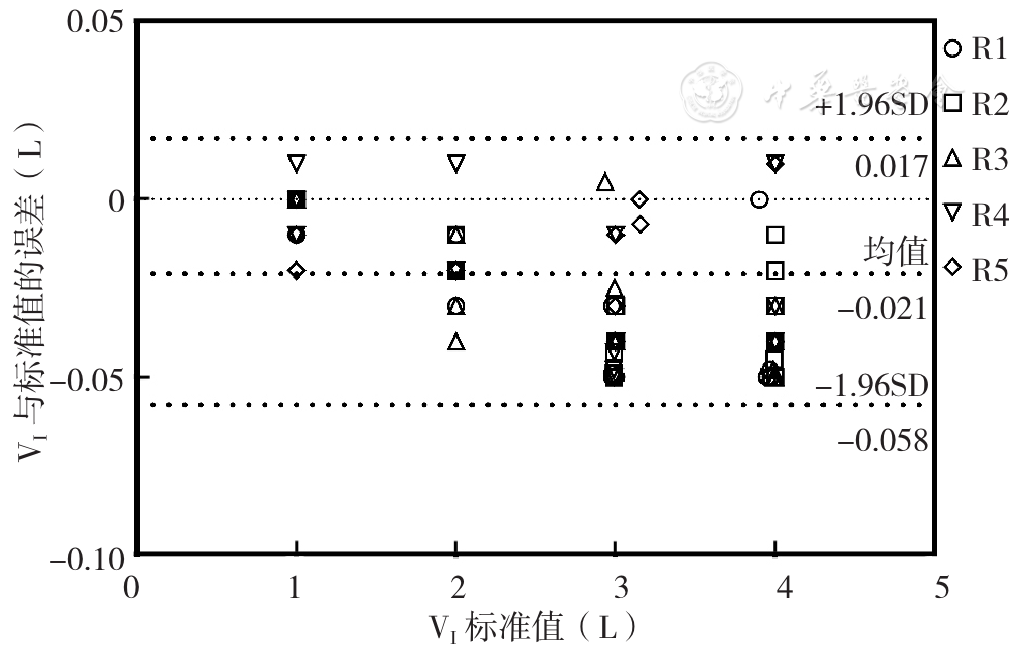
图3 吸入用药定量评估仪器PF810 VI与标准流量/容积模拟器标准值的Bland-Altman图注:V1=吸气容积
Figure 3 Blan-altman plot of the PF810 VI instrument for quantitative evaluation of inhaled medication and the standard value of the standard flow/volume simulator
| 流量 | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.000 L | 2.000 L | 3.000 L | 4.000 L | 1.000 L | 2.000 L | 3.000 L | 4.000 L | 1.000 L | 2.000 L | 3.000 L | 4.000 L | 1.000 L | 2.000 L | 3.000 L | 4.000 L | 1.000 L | 2.000 L | 3.000 L | 4.000 L | |
| 0.500 L/s | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 均值VI(L) | 0.993 | 1.980 | 2.960 | 3.900 | 1.000 | 1.980 | 2.967 | 3.977 | 1.000 | 1.960 | 2.960 | 3.960 | 0.990 | 2.010 | 2.943 | 3.967 | 1.000 | 1.980 | 2.970 | 4.010 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0.010 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.010 | 0.030 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.020 | 0 | 0 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | -0.007 | -0.020 | -0.040 | -0.033 | 0 | -0.020 | -0.033 | -0.023 | 0 | -0.040 | -0.040 | -0.040 | -0.010 | 0.010 | -0.047 | -0.033 | 0 | -0.020 | -0.030 | 0.010 |
| 相对误差(%) | -0.667 | -1.000 | -1.333 | -0.847 | 0 | -1.000 | -1.111 | -0.583 | 0 | -2.000 | -1.333 | -1.000 | -1.000 | 0.500 | -1.572 | -0.833 | 0 | -1.000 | -1.000 | 0.250 |
| 线性度(%) | 0.889 | 0.800 | -0.192 | 1.333 | 0.533 | 0.286 | 2.667 | 0 | 0 | -1.333 | 2.284 | -0.391 | 1.333 | 0.400 | -1.143 | |||||
| 1.000 L/s | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 均值VI(L) | 1.000 | 1.983 | 2.950 | 3.960 | 1.000 | 1.980 | 2.943 | 3.950 | 1.000 | 1.990 | 2.960 | 3.970 | 1.010 | 2.010 | 2.990 | 4.010 | 1.000 | 1.980 | 2.960 | 3.960 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0 | 0.010 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.010 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | 0 | -0.017 | -0.043 | -0.040 | 0 | -0.020 | -0.047 | -0.048 | 0 | -0.010 | -0.040 | -0.030 | 0.010 | 0.010 | -0.010 | 0.010 | 0 | -0.020 | -0.040 | -0.040 |
| 相对误差(%) | 0 | -0.833 | -1.448 | -1.000 | 0 | -1.000 | -1.583 | -1.209 | 0 | -0.500 | -1.333 | -0.750 | 1.000 | 0.500 | -0.333 | 0.250 | 0 | -1.000 | -1.333 | -1.000 |
| 线性度(%) | 1.111 | 1.068 | -0.095 | 1.333 | 1.095 | -0.029 | 0.667 | 1.200 | -0.286 | 0 | 0.800 | -0.762 | 1.333 | 0.800 | 0 | |||||
| 1.500 L/s | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 均值VI(L) | 1.000 | 1.970 | 2.930 | 3.920 | 1.000 | 1.990 | 2.970 | 3.970 | 1.000 | 1.970 | 2.940 | 3.940 | 1.000 | 1.980 | 2.960 | 3.970 | 0.983 | 1.980 | 2.990 | 3.150 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.010 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | 0 | -0.030 | -0.049 | -0.049 | 0 | -0.010 | -0.030 | -0.030 | 0 | -0.030 | -0.020 | -0.049 | 0 | -0.020 | -0.040 | -0.030 | -0.017 | -0.020 | -0.010 | -0.002 |
| 相对误差(%) | 0 | -1.500 | -1.656 | -1.243 | 0 | -0.500 | -1.000 | -0.750 | 0 | -1.500 | -0.676 | -1.237 | 0 | -1.000 | -1.333 | -0.750 | -1.667 | -1.000 | -0.333 | -0.047 |
| 线性度(%) | 2.000 | 0.777 | 0 | 0.667 | 0.800 | 0 | 2.000 | -0.403 | 0.844 | 1.333 | 0.800 | -0.286 | 0.222 | -0.400 | -0.249 | |||||
表2 吸入用药定量评估仪器PF810容量检测质量控制评估结果
Table 2 Quality control evaluation results of PF810 volume test for inhalation drug quantitative assessment instrument
| 流量 | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.000 L | 2.000 L | 3.000 L | 4.000 L | 1.000 L | 2.000 L | 3.000 L | 4.000 L | 1.000 L | 2.000 L | 3.000 L | 4.000 L | 1.000 L | 2.000 L | 3.000 L | 4.000 L | 1.000 L | 2.000 L | 3.000 L | 4.000 L | |
| 0.500 L/s | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 均值VI(L) | 0.993 | 1.980 | 2.960 | 3.900 | 1.000 | 1.980 | 2.967 | 3.977 | 1.000 | 1.960 | 2.960 | 3.960 | 0.990 | 2.010 | 2.943 | 3.967 | 1.000 | 1.980 | 2.970 | 4.010 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0.010 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.010 | 0.030 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.020 | 0 | 0 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | -0.007 | -0.020 | -0.040 | -0.033 | 0 | -0.020 | -0.033 | -0.023 | 0 | -0.040 | -0.040 | -0.040 | -0.010 | 0.010 | -0.047 | -0.033 | 0 | -0.020 | -0.030 | 0.010 |
| 相对误差(%) | -0.667 | -1.000 | -1.333 | -0.847 | 0 | -1.000 | -1.111 | -0.583 | 0 | -2.000 | -1.333 | -1.000 | -1.000 | 0.500 | -1.572 | -0.833 | 0 | -1.000 | -1.000 | 0.250 |
| 线性度(%) | 0.889 | 0.800 | -0.192 | 1.333 | 0.533 | 0.286 | 2.667 | 0 | 0 | -1.333 | 2.284 | -0.391 | 1.333 | 0.400 | -1.143 | |||||
| 1.000 L/s | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 均值VI(L) | 1.000 | 1.983 | 2.950 | 3.960 | 1.000 | 1.980 | 2.943 | 3.950 | 1.000 | 1.990 | 2.960 | 3.970 | 1.010 | 2.010 | 2.990 | 4.010 | 1.000 | 1.980 | 2.960 | 3.960 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0 | 0.010 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.010 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | 0 | -0.017 | -0.043 | -0.040 | 0 | -0.020 | -0.047 | -0.048 | 0 | -0.010 | -0.040 | -0.030 | 0.010 | 0.010 | -0.010 | 0.010 | 0 | -0.020 | -0.040 | -0.040 |
| 相对误差(%) | 0 | -0.833 | -1.448 | -1.000 | 0 | -1.000 | -1.583 | -1.209 | 0 | -0.500 | -1.333 | -0.750 | 1.000 | 0.500 | -0.333 | 0.250 | 0 | -1.000 | -1.333 | -1.000 |
| 线性度(%) | 1.111 | 1.068 | -0.095 | 1.333 | 1.095 | -0.029 | 0.667 | 1.200 | -0.286 | 0 | 0.800 | -0.762 | 1.333 | 0.800 | 0 | |||||
| 1.500 L/s | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 均值VI(L) | 1.000 | 1.970 | 2.930 | 3.920 | 1.000 | 1.990 | 2.970 | 3.970 | 1.000 | 1.970 | 2.940 | 3.940 | 1.000 | 1.980 | 2.960 | 3.970 | 0.983 | 1.980 | 2.990 | 3.150 |
| 重复度(L/s) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.010 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 绝对误差(L/s) | 0 | -0.030 | -0.049 | -0.049 | 0 | -0.010 | -0.030 | -0.030 | 0 | -0.030 | -0.020 | -0.049 | 0 | -0.020 | -0.040 | -0.030 | -0.017 | -0.020 | -0.010 | -0.002 |
| 相对误差(%) | 0 | -1.500 | -1.656 | -1.243 | 0 | -0.500 | -1.000 | -0.750 | 0 | -1.500 | -0.676 | -1.237 | 0 | -1.000 | -1.333 | -0.750 | -1.667 | -1.000 | -0.333 | -0.047 |
| 线性度(%) | 2.000 | 0.777 | 0 | 0.667 | 0.800 | 0 | 2.000 | -0.403 | 0.844 | 1.333 | 0.800 | -0.286 | 0.222 | -0.400 | -0.249 | |||||
| PF810模拟阻力档位 | 阻抗值[kPa1/2·(L·min)-1] | 相对误差(%) |
|---|---|---|
| 低阻力 | ||
| R2 | 0.025 | -0.70 |
| 准纳器(Accuhaler®/Diskus®) | 0.025 | |
| 中阻力 | ||
| R3 | 0.035 | -3.72 |
| 都保(Turbuhaler®) | 0.036 | |
| 高阻力 | ||
| R5 | 0.043 | 1.94 |
| 吸乐(HandiHaler®) | 0.042 |
表3 吸入用药定量评估仪器PF810模拟阻力与DPI吸入器内置阻力对比
Table 3 Comparison of simulated resistance of PF810 and internal resistance of DPI inhaler for inhalation drug quantitative assessment instrument
| PF810模拟阻力档位 | 阻抗值[kPa1/2·(L·min)-1] | 相对误差(%) |
|---|---|---|
| 低阻力 | ||
| R2 | 0.025 | -0.70 |
| 准纳器(Accuhaler®/Diskus®) | 0.025 | |
| 中阻力 | ||
| R3 | 0.035 | -3.72 |
| 都保(Turbuhaler®) | 0.036 | |
| 高阻力 | ||
| R5 | 0.043 | 1.94 |
| 吸乐(HandiHaler®) | 0.042 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
ISO. 26782:2009 Anaesthetic and respiratory equipment-Spirometers intended for the measurement of time forced expired volumes in humans[EB/OL]. [2023-03-09].
|
| [24] |
国家食品药品监督管理总局. 麻醉和呼吸设备评价自主呼吸者肺功能的呼气峰值流量计:YY/T 1438—2016[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2017.
|
| [25] |
国家药品监督管理局. 麻醉和呼吸设备用于测量人体时间用力呼气量的肺量计:YY/T 1804—2021[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2021.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
23747-2016 U-EI. Anaesthetic and respiratory equipment - Peak expiratory flow meters for the assessment of pulmonary function in spontaneously breathing humans(ISO 23747:2015)[S].
|
| [29] |
中国医学装备协会呼吸病学专委会吸入治疗与呼吸康复学组,中国慢性阻塞性肺疾病联盟. 稳定期慢性气道疾病吸入装置规范应用中国专家共识[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志,2019,42(4):241-253. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-0939.2019.04.001.
|
| [30] |
|
| [1] | 王雪婷, 蒋祎. 1990—2019年金砖国家慢性阻塞性肺疾病疾病负担研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(09): 1118-1125. |
| [2] | 袁泉, 陆海英, 王怡, 刘韵霄, 余家琴, 田丰兆, 李瑶. 远程医疗管理在老年中重度慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者稳定期呼吸康复中的效果:一项随机对照研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(06): 711-716. |
| [3] | 王婧, 王慧, 宋仕群, 吉广荷, 郭亚坤, 要丹柠, 赵书晗, 李多多, 夏如玉, 张立山. 口服中药治疗慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重随机对照试验的文献特征及结局指标研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(02): 226-232. |
| [4] | 慢性阻塞性肺疾病中西医结合管理专家共识写作组. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病中西医结合管理专家共识(2023版)[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(35): 4359-4371. |
| [5] | 刘健, 张天一, 艾力扎提·艾则孜, 常蕊静, 张建立, 王婉, 姜鹏. 外科口罩和N95口罩对慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者心肺功能的影响:一项随机交叉对照试验[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(24): 3028-3032. |
| [6] | 沈俊希, 朱星, 陈云志, 李文. 肺部、肠道菌群及其相互作用与慢性阻塞性肺疾病发生发展的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(20): 2548-2554. |
| [7] | 梁振宇, 王凤燕, 陈子正, 陈荣昌. 2023年GOLD慢性阻塞性肺疾病诊断、管理及预防全球策略更新要点解读[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(11): 1287-1298. |
| [8] | 王通, 权海善, 田博文, 李莹, 崔倩倩, 刘瑶, 朱花花. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者疲劳研究的范围综述[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(07): 893-902. |
| [9] | 刘建材, 郑涵尹, 潘卉, 叶灵兰, 李传芬. 农村地区基层慢性病管理人员对慢性阻塞性肺疾病认知的调查研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(07): 877-885. |
| [10] | 王益德, 李争, 李风森. 从脂肪组织的内分泌功能角度探讨其在慢性阻塞性肺疾病中的作用机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(06): 754-759. |
| [11] | 胡奕卿, 方继伟, 刘焕兵. 肺功能检查技术如何在基层医疗卫生服务中更好地应用——附重点问题专家解答[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(05): 532-540. |
| [12] | 石伟娟, 王凤燕, 杨宇琼, 谢清秀, 李玉琪, 李时悦, 陈荣昌, 张冬莹, 郑劲平, 梁振宇. 新型冠状病毒感染疫情对慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者急性加重频率的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(05): 550-556. |
| [13] | 白亚虎, 高胜寒, 纪思禹, 尚金钰, 董延春, 宁康. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病向"前"发展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(03): 268-273. |
| [14] | 郭栋伟, 张鹏飞, 任明君, 廖丽君, 黄茹妍, 罗湘蓉. 银杏叶提取物防治慢性阻塞性肺疾病的机制研究:基于PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路调控肺泡巨噬细胞自噬[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(03): 293-303. |
| [15] | 黄桃, 罗娜, 罗松, 徐钦. 具有双通道通气和恒定泄气量功能的新型无创正压通气面罩治疗慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重合并CO2潴留患者的临床效果研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(03): 343-347. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





