中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (16): 2027-2035.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0690
收稿日期:2022-10-12
修回日期:2023-03-21
出版日期:2023-06-05
发布日期:2023-03-30
通讯作者:
黄蛟灵
基金资助:Received:2022-10-12
Revised:2023-03-21
Published:2023-06-05
Online:2023-03-30
Contact:
HUANG Jiaoling
摘要: 背景 新型冠状病毒感染(简称新冠感染)疫情防控期间,基层卫生是防控的"第一道防线"。各国学术界对新冠感染期间基层卫生工作进行了广泛的研究,但基层卫生制度不同导致研究侧重点有差异。 目的 了解新冠感染背景下国内与国际上基层卫生相关研究的进展、热点、趋势及差异性,为该领域进一步研究提供参考。 方法 于2022-07-05,检索新冠感染发生后中国知网(CNKI)与Web of science(WOS)核心数据库收录的基层卫生相关研究的文献,检索时间范围均限定为2020-01-01至2022-06-30,纳入CNKI文献282篇、WOS文献1 755篇。利用CiteSpace软件进行可视化分析,实现作者共现分析,关键词共现、聚类、时间线分析,关键词突现分析。 结果 从文献时序分布上看国内相关研究文献量在疫情发生初期增速较快,后增速逐渐下降,趋于平缓;国际上研究起始稍滞后,但保持较高增速至今。作者合作以小团队与个人为主,无大规模跨团队合作。国内研究热点偏重疫情防控相关体制及机制探讨与管理实践,国际研究关注疫情影响下就医方式的转变、患者就医需求的满足。国内与国际上的研究均重点关注疫情影响下发生的心理问题。 结论 新冠感染背景下国内与国际的基层卫生相关研究既有共通点也各有侧重,国内研究在不断细化、多样化的进程中可吸收国际经验,重视相关研究力量建设,健全该领域知识体系,积极利用信息化技术完善疫情下基层卫生的服务体系。
图1 新冠感染背景下基层卫生相关文献检索流程注:新冠感染=新型冠状病毒感染,CNKI=中国知网,WOS=Web of science
Figure 1 Flow chart of the search for literature on primary healthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic
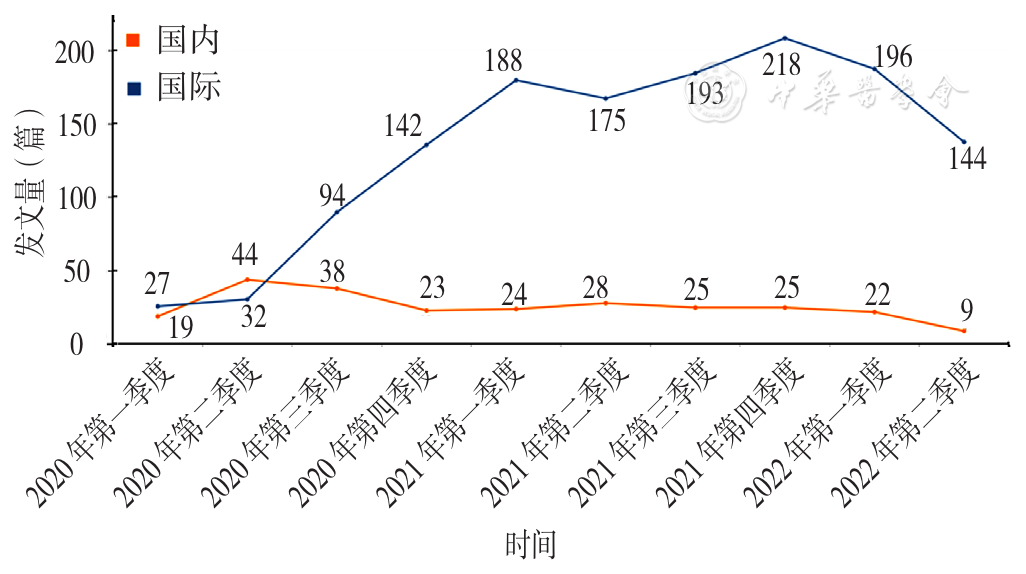
图3 新冠感染背景下国内与国际相关研究的发文量趋势
Figure 3 Seasonal trends in the number of domestic and international studies on primary healthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic published during 2020 to 2022
| 序号 | 国内文献 | 国际文献 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 关键词 | 词频(次) | 中心度 | 关键词 | 词频(次) | 中心度 | |
| 1 | 疫情防控 | 62 | 0.55 | impact | 124 | 0.12 |
| 2 | 医务人员 | 55 | 0.31 | covid 19 | 80 | 0.11 |
| 3 | 新冠疫情 | 54 | 0.39 | care | 77 | 0.10 |
| 4 | 基层医院 | 18 | 0.29 | health | 66 | 0.13 |
| 5 | 全科医生 | 17 | 0.09 | risk | 58 | 0.17 |
| 6 | 防治原则 | 11 | 0.00 | mental health | 52 | 0.15 |
| 7 | 皮肤问题 | 11 | 0.00 | depression | 47 | 0.35 |
| 8 | 防护装备 | 11 | 0.00 | mortality | 46 | 0.09 |
| 9 | 皮肤病 | 11 | 0.00 | management | 43 | 0.19 |
| 10 | 焦虑 | 11 | 0.05 | outcome | 40 | 0.07 |
| 11 | 医护人员 | 9 | 0.06 | prevalence | 39 | 0.12 |
| 12 | 抑郁 | 8 | 0.11 | outbreak | 36 | 0.11 |
| 13 | 影响因素 | 8 | 0.15 | health care | 35 | 0.14 |
| 14 | 心理健康 | 8 | 0.11 | primary care | 34 | 0.00 |
| 15 | 防控工作 | 7 | 0.10 | anxiety | 33 | 0.05 |
| 16 | 医疗队 | 7 | 0.04 | sar | 33 | 0.00 |
| 17 | 发热门诊 | 6 | 0.10 | disease | 33 | 0.14 |
| 18 | 疫情 | 6 | 0.02 | burnout | 31 | 0.10 |
| 19 | 心理状态 | 6 | 0.08 | disorder | 29 | 0.11 |
| 20 | 社区 | 6 | 0.08 | telemedicine | 28 | 0.07 |
表1 国内、国际文献关键词频次排名
Table 1 Top 20 keywords with the highest frequency of use in China's and international studies
| 序号 | 国内文献 | 国际文献 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 关键词 | 词频(次) | 中心度 | 关键词 | 词频(次) | 中心度 | |
| 1 | 疫情防控 | 62 | 0.55 | impact | 124 | 0.12 |
| 2 | 医务人员 | 55 | 0.31 | covid 19 | 80 | 0.11 |
| 3 | 新冠疫情 | 54 | 0.39 | care | 77 | 0.10 |
| 4 | 基层医院 | 18 | 0.29 | health | 66 | 0.13 |
| 5 | 全科医生 | 17 | 0.09 | risk | 58 | 0.17 |
| 6 | 防治原则 | 11 | 0.00 | mental health | 52 | 0.15 |
| 7 | 皮肤问题 | 11 | 0.00 | depression | 47 | 0.35 |
| 8 | 防护装备 | 11 | 0.00 | mortality | 46 | 0.09 |
| 9 | 皮肤病 | 11 | 0.00 | management | 43 | 0.19 |
| 10 | 焦虑 | 11 | 0.05 | outcome | 40 | 0.07 |
| 11 | 医护人员 | 9 | 0.06 | prevalence | 39 | 0.12 |
| 12 | 抑郁 | 8 | 0.11 | outbreak | 36 | 0.11 |
| 13 | 影响因素 | 8 | 0.15 | health care | 35 | 0.14 |
| 14 | 心理健康 | 8 | 0.11 | primary care | 34 | 0.00 |
| 15 | 防控工作 | 7 | 0.10 | anxiety | 33 | 0.05 |
| 16 | 医疗队 | 7 | 0.04 | sar | 33 | 0.00 |
| 17 | 发热门诊 | 6 | 0.10 | disease | 33 | 0.14 |
| 18 | 疫情 | 6 | 0.02 | burnout | 31 | 0.10 |
| 19 | 心理状态 | 6 | 0.08 | disorder | 29 | 0.11 |
| 20 | 社区 | 6 | 0.08 | telemedicine | 28 | 0.07 |
| 聚类ID | 聚类标签 | 聚类规模 | 轮廓值 | 年份(年) | 研究标签 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 核酸检测 | 26 | 0.861 | 2020 | 核酸检测;防控措施;新冠感染;防控工作;新型冠状病毒 |
| 1 | 疫情防控 | 25 | 0.999 | 2021 | 疫情防控;紧密型医联体;卫生院;消费券;健康扶贫 |
| 2 | 新冠疫情 | 23 | 0.986 | 2021 | 新冠感染疫情;心理健康;医联体;人文关怀;新型冠状病毒 |
| 3 | 医务人员 | 21 | 0.984 | 2021 | 医务人员;心理状态;医疗队;疫情防控;新型冠状病毒 |
| 4 | 发热门诊 | 21 | 0.934 | 2020 | 发热门诊;基层医院;疫情;调查;发热患者 |
| 5 | 影响因素 | 18 | 0.938 | 2020 | 影响因素;家庭医生;认知;护理人员;防范路径 |
| 6 | 联防联控 | 16 | 0.966 | 2020 | 联防联控;卫生健康;封闭管理;社区;习近平 |
| 7 | 全科医生 | 15 | 0.933 | 2020 | 全科医生;健康教育;糖尿病;健康管理;全科医生培训 |
| 8 | 抑郁 | 13 | 0.918 | 2020 | 抑郁;焦虑;心理韧性;中老年人;心理应对 |
| 9 | 家庭医生签约 | 12 | 0.975 | 2021 | 家庭医生签约服务;医疗机构;方舱医院;公立医院改革;中医院 |
表2 新冠感染背景下国内基层卫生相关研究关键词聚类
Table 2 Cluster details of keywords in China's studies on primary ealthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic
| 聚类ID | 聚类标签 | 聚类规模 | 轮廓值 | 年份(年) | 研究标签 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 核酸检测 | 26 | 0.861 | 2020 | 核酸检测;防控措施;新冠感染;防控工作;新型冠状病毒 |
| 1 | 疫情防控 | 25 | 0.999 | 2021 | 疫情防控;紧密型医联体;卫生院;消费券;健康扶贫 |
| 2 | 新冠疫情 | 23 | 0.986 | 2021 | 新冠感染疫情;心理健康;医联体;人文关怀;新型冠状病毒 |
| 3 | 医务人员 | 21 | 0.984 | 2021 | 医务人员;心理状态;医疗队;疫情防控;新型冠状病毒 |
| 4 | 发热门诊 | 21 | 0.934 | 2020 | 发热门诊;基层医院;疫情;调查;发热患者 |
| 5 | 影响因素 | 18 | 0.938 | 2020 | 影响因素;家庭医生;认知;护理人员;防范路径 |
| 6 | 联防联控 | 16 | 0.966 | 2020 | 联防联控;卫生健康;封闭管理;社区;习近平 |
| 7 | 全科医生 | 15 | 0.933 | 2020 | 全科医生;健康教育;糖尿病;健康管理;全科医生培训 |
| 8 | 抑郁 | 13 | 0.918 | 2020 | 抑郁;焦虑;心理韧性;中老年人;心理应对 |
| 9 | 家庭医生签约 | 12 | 0.975 | 2021 | 家庭医生签约服务;医疗机构;方舱医院;公立医院改革;中医院 |
| 聚类ID | 聚类标签 | 聚类规模 | 轮廓值 | 年份(年) | 研究标签 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | telemedicine | 20 | 0.796 | 2020 | public health perspective;autonomy power dynamics;antibiotic use;comparing medication;clinical pharmacist visit transition |
| 1 | care | 20 | 0.809 | 2020 | covid-19 pandemic;covid-19 infection;cov-2 infection;nursing home;ethnic disparities in covid-19 infection |
| 2 | infection | 16 | 0.681 | 2020 | other high-risk group;severe asthma;cov-2 transmission fear;knowledge attitude developing country |
| 3 | stress | 15 | 0.756 | 2020 | surgical breast cancer care;multicenter retrospective cohort study;nursing student;young individual;cascading pathologies |
| 4 | topic areas | 13 | 0.822 | 2020 | rapid evidence synthesis;users perception;urgent need;living kidney donation;kidney transplantation |
| 5 | depression | 11 | 0.902 | 2020 | psychological distress;healthcare professional;depression anxiety;high level;australian frontline healthcare worker |
| 6 | vas | 9 | 0.873 | 2020 | containment sheet-a;frugal innovation;total knee arthroplasty;correct personal protective equipment use;mastery learning |
| 7 | diagnosis | 9 | 0.972 | 2020 | covid-19 policy intervention;equity harm;racial disparity;stroke patient;scoping review |
| 8 | acute myocardial infection | 5 | 0.954 | 2020 | acute coronary syndrome;era;breast cancer management pathway;map-c study;study protocol |
| 9 | health economics | 5 | 0.932 | 2021 | metropolitan health care worker;home-dwelling people;covid-19 restriction;psychological symptom;self-directed e-learning intervention |
表3 新冠感染背景下国际基层卫生相关研究关键词聚类
Table 3 Cluster details of keywords in international studies on primary healthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic
| 聚类ID | 聚类标签 | 聚类规模 | 轮廓值 | 年份(年) | 研究标签 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | telemedicine | 20 | 0.796 | 2020 | public health perspective;autonomy power dynamics;antibiotic use;comparing medication;clinical pharmacist visit transition |
| 1 | care | 20 | 0.809 | 2020 | covid-19 pandemic;covid-19 infection;cov-2 infection;nursing home;ethnic disparities in covid-19 infection |
| 2 | infection | 16 | 0.681 | 2020 | other high-risk group;severe asthma;cov-2 transmission fear;knowledge attitude developing country |
| 3 | stress | 15 | 0.756 | 2020 | surgical breast cancer care;multicenter retrospective cohort study;nursing student;young individual;cascading pathologies |
| 4 | topic areas | 13 | 0.822 | 2020 | rapid evidence synthesis;users perception;urgent need;living kidney donation;kidney transplantation |
| 5 | depression | 11 | 0.902 | 2020 | psychological distress;healthcare professional;depression anxiety;high level;australian frontline healthcare worker |
| 6 | vas | 9 | 0.873 | 2020 | containment sheet-a;frugal innovation;total knee arthroplasty;correct personal protective equipment use;mastery learning |
| 7 | diagnosis | 9 | 0.972 | 2020 | covid-19 policy intervention;equity harm;racial disparity;stroke patient;scoping review |
| 8 | acute myocardial infection | 5 | 0.954 | 2020 | acute coronary syndrome;era;breast cancer management pathway;map-c study;study protocol |
| 9 | health economics | 5 | 0.932 | 2021 | metropolitan health care worker;home-dwelling people;covid-19 restriction;psychological symptom;self-directed e-learning intervention |
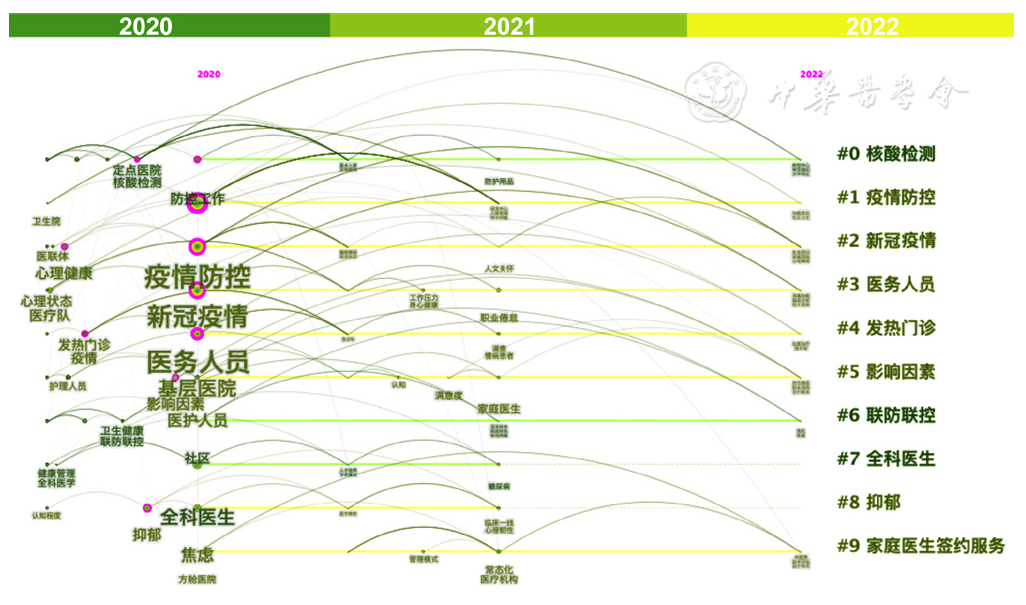
图10 新冠感染背景下国内基层卫生相关研究关键词聚类时间线分布图谱
Figure 10 Timeline view of clusters of keywords in China's studies on primary healthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic
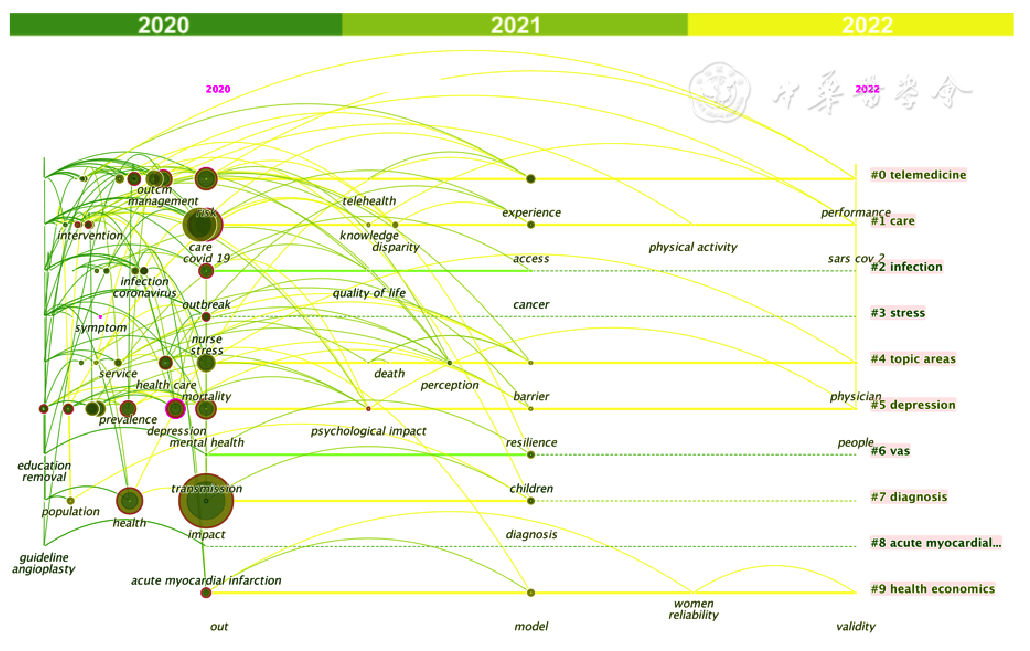
图11 新冠感染背景下国际基层卫生相关研究关键词聚类时间线分布图谱
Figure 11 Timeline view of clusters of keywords in international studies on primary healthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic
| [1] |
人民日报. 习近平:健全国家公共卫生应急管理体系[EB/OL].(2020-02-29)[2022-08-14].
|
| [2] |
刘梦林. 公共危机事件中基层社区治理的局限性及对策探析:以我国此次新冠肺炎疫情应对为例[J]. 行政科学论坛,2020,7(8):18-22.
|
| [3] |
吴莹,葛道顺. 特大城市公共卫生安全风险与基层治理应对:基于新冠肺炎疫情下北京、上海、武汉的社区防疫经验[J]. 学习与实践,2020,37(9):75-84. DOI:10.19624/j.cnki.cn42-1005/c.2020.09.009.
|
| [4] |
卢祖洵,徐鸿彬,李丽清,等. 关于加强基层医疗卫生服务建设的建议:兼论推进疫情防控关口前移[J]. 行政管理改革,2020,12(3):23-29. DOI:10.14150/j.cnki.1674-7453.2020.03.003.
|
| [5] |
刘则渊,陈悦,侯海燕. 科学知识图谱:方法与应用[M]. 北京:人民出版社,2008:3-5.
|
| [6] |
陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等. CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J]. 科学学研究,2015,33(2):242-253. DOI:10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.2015.02.009.
|
| [7] |
吴晓秋,吕娜. 基于关键词共现频率的热点分析方法研究[J]. 情报理论与实践,2012,35(8):115-119. DOI:10.16353/j.cnki.1000-7490.2012.08.026.
|
| [8] |
刘军. 整体网分析:UCINET软件实用指南[M]. 2版.上海:格致出版社,2014.
|
| [9] |
蔡建东,马婧,袁媛. 国外CSCL理论的演进与前沿热点问题:基于Citespace的可视化分析[J]. 现代教育技术,2012,22(5):10-16. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-8097.2012.05.002.
|
| [10] |
陈超美. CiteSpace中的Burst Detection[EB/OL].(2012-05-03)[2022-08-14].
|
| [11] |
秦晓楠,卢小丽,武春友. 国内生态安全研究知识图谱:基于Citespace的计量分析[J]. 生态学报,2014,34(13):3693-3703. DOI:10.5846/stxb201211081566.
|
| [12] |
WHO. Timeline:WHO's COVID-19 response[EB/OL].(2022-03-28)[2022-08-14].
|
| [13] |
人民日报. 关于疫情防控工作,总书记的最新指示来了![EB/OL].(2020-02-14)[2022-08-14].
|
| [14] |
唐燕. 新冠肺炎疫情防控中的社区治理挑战应对:基于城乡规划与公共卫生视角[J]. 南京社会科学,2020,31(3):8-14,27. DOI:10.15937/j.cnki.issn1001-8263.2020.03.002.
|
| [15] |
陈迎春,常静肼,张全红,等. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情下湖北省基层卫生机构联防联控协作机制分析[J]. 医学与社会,2020,33(9):10-14. DOI:10.13723/j.yxysh.2020.09.003.
|
| [16] |
牟岚,金新政. 远程医疗发展现状综述[J]. 卫生软科学,2012,26(6):506-509.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
苏斌原,叶苑秀,张卫,等. 新冠肺炎疫情不同时间进程下民众的心理应激反应特征[J]. 华南师范大学学报(社会科学版),2020,65(3):79-94.
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] | |
| [29] |
张宴萍,褚连芳,庄开岑,等. 新冠肺炎疫情下医务人员压力、焦虑、抑郁状况及影响因素研究[J]. 现代预防医学,2021,48(1):38-43.
|
| [30] |
|
| [1] | 余娜, 柏晓玲, 逄锦, 牛雨田, 胡庆, 王远芳, 杨容泽. 贵阳市≥18岁抗疫一线人员对吸入用新型冠状病毒疫苗接种体验的质性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(36): 4575-4580. |
| [2] | 王世越, 董晨, 常楚迪, 南月敏. 中国原发性肝癌基层筛查的机遇与挑战[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(36): 4498-4504. |
| [3] | 钟萍萍, 南亚昀, 彭琳琳, 周宇婷, 陈琼. 2003—2022年老年人多重用药文献计量学分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(35): 4404-4411. |
| [4] | 李殿江, 潘恩春, 孙中明, 文进博, 王苗苗, 武鸣, 沈冲. 社区2型糖尿病患者临床惰性现状及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4296-4301. |
| [5] | 徐健, 戴芳芳, 潘文雷, 黄倩, 陆萍, 王剑峰, 贾环, 杨宇琪, 黄蛟灵. "健康中国"背景下我国社区中医药服务研究热点和前沿趋势的可视化分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4343-4350. |
| [6] | 王婕, 李仕明, 魏士飞, 王宁利. 重视基层卫生服务在儿童近视防控行为干预中的作用[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4213-4217. |
| [7] | 王敏, 郭文军, 陈永真, 凤心雨, 汤忠泉, 赵晓敏, 欧婷, 戴昕妤, 李云涛. 基于Web of Science数据库的未分化疾病文献计量学和可视化分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(31): 3930-3938. |
| [8] | 田美玲, 马国娟, 杜立燕, 肖远革, 张赛, 张翠, 唐增军. 2014—2021年河北省妊娠期糖尿病患病率及流行病学研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(26): 3320-3324. |
| [9] | 赵世超, 平静, 朱虹, 纪婉婷, 王雨燕, 王颖. 工作特征模型视角下基层卫生人员内在激励机制研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(25): 3118-3126. |
| [10] | 李梦宇, 连隽, 廖子锐, 昝子晴, 刘璐, 尤莉莉, 刘远立. 国家基本公共卫生服务老年人健康体检的异常检出率分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(22): 2756-2762. |
| [11] | 吴建, 于丞丞, 杨银梅, 夏青云, 李泉漫, 付晓丽. 中国四地区老年人新型冠状病毒疫苗接种行为及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(22): 2763-2770. |
| [12] | 郑晓, 田峰, 陈一鸣, 薛本立, 石磊, 张持晨. 2002—2022年我国多重慢病领域研究热点及演进趋势分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(21): 2567-2573. |
| [13] | 何梅, 李荟, 母立峰, 杨明. 阿兹夫定对新型冠状病毒感染患者肝肾功能影响的研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(20): 2476-2481. |
| [14] | 欧欣, 杨佳. 基于政策文本分析的我国基层公共卫生治理体系研究:以公共卫生委员会为例[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(19): 2346-2354. |
| [15] | 周敏, 郑子光, 游宏宇, 郭淼, 喻伟, 杨旭. 减少室内空气颗粒物对老年人心血管和呼吸系统生理指标的影响:一项随机双盲交叉试验[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(17): 2114-2119. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||






