中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (15): 1847-1856.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0851
所属专题: 内分泌代谢性疾病最新文章合辑; 数智医疗最新文章合辑
收稿日期:2022-12-16
修回日期:2023-01-24
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2022-12-20
通讯作者:
段俊国
基金资助:
LIU Chun1, JIAN Wenyuan2, DUAN Junguo2,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-12-16
Revised:2023-01-24
Published:2023-05-20
Online:2022-12-20
Contact:
DUAN Junguo
摘要: 背景 近年来,人工智能(AI)在医学领域发展迅速,在糖尿病视网膜病变(DR)中的应用范围不断扩展。 目的 通过文献计量分析总结AI在DR领域的应用情况,阐明AI在DR领域相关研究的现状、热点和新兴趋势,以期为未来的研究提供思路。 方法 以Web of Science数据库为来源,检索建库至2022-11-04的AI应用于DR领域的相关文献,运用CiteSpace软件对纳入文献进行发文量、国家、机构、作者、共被引和关键词的文献计量学分析。 结果 共获得1 770篇文献,2011年1月至2022年11月发文量总体呈上升趋势,2021年发文量达峰值(402篇)。中国是发文量(440篇)位居第1的国家,英国为中心性(0.26)最高的国家。机构合作网络图谱共纳入436家机构,以中山大学和首都医科大学为代表。作者合作网络图谱共纳入601位作者,以JIA Y L和HWANG T为代表。GULSHAN V、ABRàMOFF M D与TING D W 3位高被引作者对该领域做出了重要贡献。Ophthalmology、Invest Ophth Vis Sci和Ieee T Med Imaging是AI应用于DR领域的相关研究最具影响力的3大期刊。AI应用于DR研究的热点领域主要集中在病灶分割和DR诊断方面。对DR并发症糖尿病性黄斑水肿的疗效预测、DR病程管理以及AI算法性能提高可能是未来的研究趋势。 结论 研究者可参考本研究所示的研究热点及趋势,重点关注AI在DR诊断、病程管理与AI算法性能提高方面的相关问题。
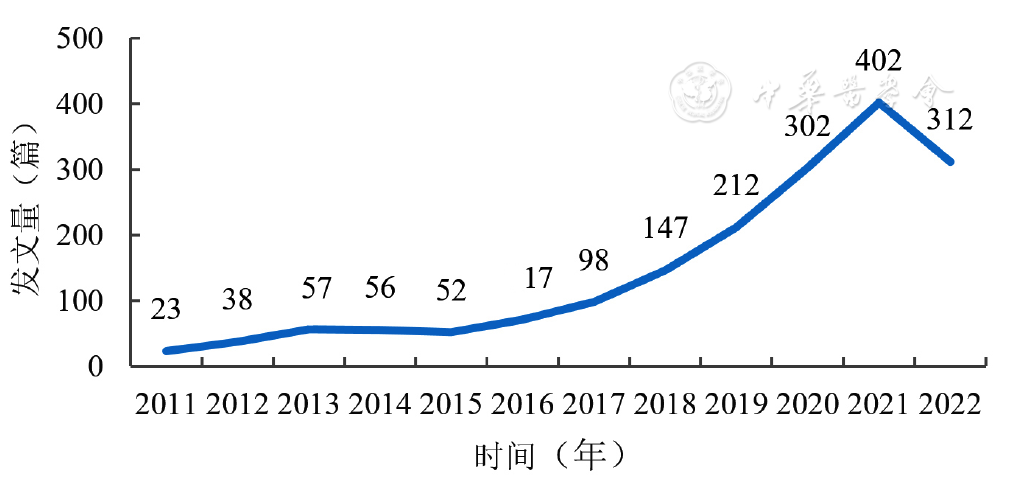
图1 2011年1月至2022年11月AI应用于DR研究的年发文量趋势
Figure 1 Number of annual studies regarding artificial intelligence in diabetic retinopathy from January 2011 to November 2022
| 序号 | 被引作者 | 被引频次(次) | 中介中心性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GULSHAN V | 412 | 0.03 |
| 2 | ABRÀMOFF M D | 363 | 0.17 |
| 3 | TING D W | 285 | 0.04 |
| 4 | NIEMEIJER M | 240 | 0.02 |
| 5 | HE K | 201 | 0.04 |
| 6 | QUELLEC G | 179 | 0.04 |
| 7 | GARGEYA R | 176 | 0.02 |
| 8 | SZEGEDY C | 172 | 0.03 |
| 9 | DECENCIERE E | 164 | 0.04 |
| 10 | KRIZHEVSKY A | 153 | 0.03 |
表1 AI应用于DR研究被引频次排名前10的作者
Table 1 The top 10 authors of cited frequency for studies regarding artificial intelligence in diabetic retinopathy
| 序号 | 被引作者 | 被引频次(次) | 中介中心性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GULSHAN V | 412 | 0.03 |
| 2 | ABRÀMOFF M D | 363 | 0.17 |
| 3 | TING D W | 285 | 0.04 |
| 4 | NIEMEIJER M | 240 | 0.02 |
| 5 | HE K | 201 | 0.04 |
| 6 | QUELLEC G | 179 | 0.04 |
| 7 | GARGEYA R | 176 | 0.02 |
| 8 | SZEGEDY C | 172 | 0.03 |
| 9 | DECENCIERE E | 164 | 0.04 |
| 10 | KRIZHEVSKY A | 153 | 0.03 |
| 序号 | 被引期刊 | JCR分区 | IF | 被引频次 | 中介中心性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ophthalmology | Q1 | 14.28 | 791 | 0.02 |
| 2 | Invest Ophth Vis Sci | Q1 | 4.93 | 711 | 0.01 |
| 3 | Ieee T Med Imaging | Q1 | 11.04 | 628 | 0.01 |
| 4 | Brit J Ophthalmol | Q1 | 5.91 | 576 | 0.01 |
| 5 | Jama-J Am Med Assoc | Q1 | 157.38 | 526 | 0.03 |
| 6 | Med Image Anal | Q1 | 13.83 | 432 | 0.01 |
| 7 | Diabetes Care | Q1 | 17.16 | 431 | 0.01 |
| 8 | Plos One | Q2 | 3.75 | 413 | 0.02 |
| 9 | Am J Ophthalmol | Q1 | 5.49 | 403 | 0.01 |
| 10 | Lect Notes Comput Sc | 未查到 | — | 391 | 0.03 |
表2 AI应用于DR研究被引频次排名前10的发表期刊
Table 2 The top 10 journals of cited frequency for studies regarding artificial intelligence in diabetic retinopathy
| 序号 | 被引期刊 | JCR分区 | IF | 被引频次 | 中介中心性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ophthalmology | Q1 | 14.28 | 791 | 0.02 |
| 2 | Invest Ophth Vis Sci | Q1 | 4.93 | 711 | 0.01 |
| 3 | Ieee T Med Imaging | Q1 | 11.04 | 628 | 0.01 |
| 4 | Brit J Ophthalmol | Q1 | 5.91 | 576 | 0.01 |
| 5 | Jama-J Am Med Assoc | Q1 | 157.38 | 526 | 0.03 |
| 6 | Med Image Anal | Q1 | 13.83 | 432 | 0.01 |
| 7 | Diabetes Care | Q1 | 17.16 | 431 | 0.01 |
| 8 | Plos One | Q2 | 3.75 | 413 | 0.02 |
| 9 | Am J Ophthalmol | Q1 | 5.49 | 403 | 0.01 |
| 10 | Lect Notes Comput Sc | 未查到 | — | 391 | 0.03 |
| 序号 | 文章标题 | 第一作者 | 发表年份(年) | 共被引频次(次) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Algorithm for Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy in Retinal Fundus Photographs[ | GULSHAN V | 2016 | 354 |
| 2 | Development and Validation of a Deep Learning System for Diabetic Retinopathy and Related Eye Diseases Using Retinal Images from Multiethnic Populations with Diabetes[ | TING D W | 2017 | 218 |
| 3 | Automated Identification of Diabetic Retinopathy Using Deep Learning[ | GARGEYA R | 2017 | 175 |
| 4 | Improved Automated Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy on a Publicly Available Dataset Through Integration of Deep Learning[ | ABRÀMOFF M D | 2016 | 127 |
| 5 | Pivotal trial of an autonomous AI-based diagnostic system for detection of diabetic retinopathy in primary care offices[ | ABRÀMOFF M D | 2018 | 74 |
| 6 | Deep learning[ | LECUN Y | 2015 | 69 |
| 7 | Identifying Medical Diagnoses and Treatable Diseases by Image-Based Deep Learning[ | KERMANY D S | 2018 | 61 |
| 8 | Prediction of cardiovascular risk factors from retinal fundus photographs via deep learning[ | POPLIN R | 2018 | 61 |
| 9 | Clinically applicable deep learning for diagnosis and referral in retinal disease[ | DE F | 2018 | 59 |
| 10 | Grader Variability and the Importance of Reference Standards for Evaluating Machine Learning Models for Diabetic Retinopathy[ | KRAUSE J | 2018 | 58 |
表3 AI应用于DR研究共被引频次排名前10的文献
Table 3 The top 10 most-cited articles for studies regarding artificial intelligence in diabetic retinopathy
| 序号 | 文章标题 | 第一作者 | 发表年份(年) | 共被引频次(次) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Algorithm for Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy in Retinal Fundus Photographs[ | GULSHAN V | 2016 | 354 |
| 2 | Development and Validation of a Deep Learning System for Diabetic Retinopathy and Related Eye Diseases Using Retinal Images from Multiethnic Populations with Diabetes[ | TING D W | 2017 | 218 |
| 3 | Automated Identification of Diabetic Retinopathy Using Deep Learning[ | GARGEYA R | 2017 | 175 |
| 4 | Improved Automated Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy on a Publicly Available Dataset Through Integration of Deep Learning[ | ABRÀMOFF M D | 2016 | 127 |
| 5 | Pivotal trial of an autonomous AI-based diagnostic system for detection of diabetic retinopathy in primary care offices[ | ABRÀMOFF M D | 2018 | 74 |
| 6 | Deep learning[ | LECUN Y | 2015 | 69 |
| 7 | Identifying Medical Diagnoses and Treatable Diseases by Image-Based Deep Learning[ | KERMANY D S | 2018 | 61 |
| 8 | Prediction of cardiovascular risk factors from retinal fundus photographs via deep learning[ | POPLIN R | 2018 | 61 |
| 9 | Clinically applicable deep learning for diagnosis and referral in retinal disease[ | DE F | 2018 | 59 |
| 10 | Grader Variability and the Importance of Reference Standards for Evaluating Machine Learning Models for Diabetic Retinopathy[ | KRAUSE J | 2018 | 58 |
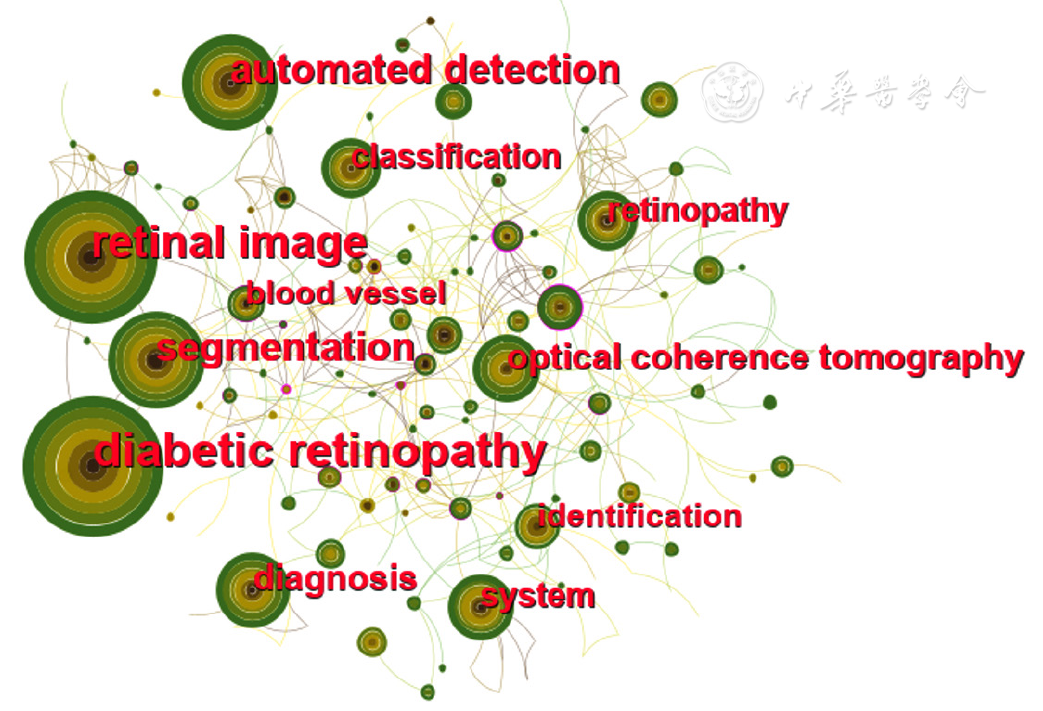
图5 2011—2017年AI应用于DR研究的关键词共现图谱
Figure 5 Co-occurrence map of keywords for studies regarding artificial intelligence in diabetic retinopathy from 2011 to 2017
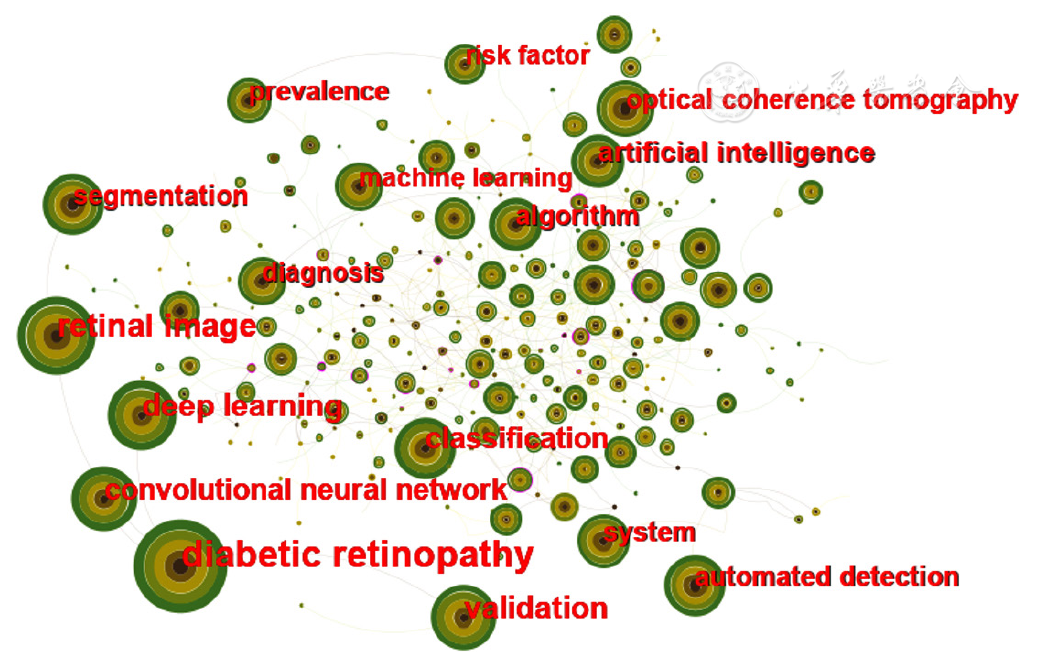

图6 2018—2022年AI应用于DR研究的关键词共现图谱
Figure 6 Co-occurrence map of keywords for studies regarding artificial intelligence in diabetic retinopathy from 2018 to 2022
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] | |
| [8] |
陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等. CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J]. 科学学研究,2015,33(2):242-253. DOI:10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.2015.02.009.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
李科科,于文兵,李硕奇,等. 基于CiteSpace的大学生社交焦虑研究的热点与前沿趋势分析[J]. 中国全科医学,2022,25(33):4217-4226. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0390.
|
| [11] |
陈冉,杨皓然,史会连,等. 1991—2021年肝硬化营养研究热点及趋势可视化分析[J]. 中国全科医学,2022(32):4091-4098. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0247.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] | |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
尹义龙,袭肖明. 眼科疾病智能诊断方法最新进展[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版),2020,58(11):33-38. DOI:10.6040/j.issn.1671-7554.0.2020.1136.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
药品监督管理局,国家药监局关于批准注册96个医疗器械产品公告[EB/OL]. (2020-09-16)[2023-01-08].
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [1] | 牛奔, 朱晓倩, 杨辰, 梁万年, 刘珏. 基于CiteSpace的国内外医疗大语言模型研究热点演进及趋势分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3200-3208. |
| [2] | 王慧, 胡银环, 冯显东, 刘莎, 汪洋帆. 人工智能在心理干预中的应用:效果、挑战与前景[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3209-3216. |
| [3] | 潘琦, 任菁菁, 马方晖, 胡梦杰. 全科医师对AI辅助诊疗系统的认知与需求调查[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3127-3136. |
| [4] | 赵亚利, 路孝琴, 刘珏, 张艺帆, 朱祖懿, 陈开元, 刘民, 梁万年. 智能全科医生评估指标体系构建[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2705-2711. |
| [5] | 王爽, 吴树法, 令垚, 谭茜蔚, 曹汝岱, 曾慧婷, 孔丹莉, 丁元林, 于海兵. 基于代谢组学探究非脂质代谢物在肥胖与糖尿病视网膜病变间的中介作用:孟德尔随机化研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2625-2634. |
| [6] | 王松柱, 姚易, 周伊恒, 赵茄茜, 杨荣, 赵茜, 张瑞, 代华, 李东泽, 廖晓阳, 杨辉. 近五年全科医学研究热点及发展趋势分析:基于CiteSpace的可视化分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(19): 2330-2337. |
| [7] | 闫温馨, 刘珏, 梁万年. DeepSeek赋能全科医学:潜在应用与展望[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2065-2069. |
| [8] | 李伊婷, 徒文静, 尹婷婷, 梅紫琦, 张苏闽, 王萌, 徐桂华. 人工智能在炎症性肠病患者营养管理中应用的范围综述[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1709-1716. |
| [9] | 戈琼, 胡佳康, 俞玉琪, 赖文文, 罗时文, 卢曲琴. RNA测序技术应用于肝癌的文献计量学分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(12): 1473-1478. |
| [10] | 王甘红, 张子豪, 奚美娟, 夏开建, 周燕婷, 陈健. 基于卷积神经网络建立中药材自动识别的人工智能模型及应用程序[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(09): 1128-1136. |
| [11] | 程琦, 于文兵, 李科科, 左右, 焦乾鑫, 刘新浩, 高丽丽. 基于CiteSpace的中学生心理健康研究的热点与前沿趋势分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(07): 853-862. |
| [12] | 清华大学万科公共卫生与健康学院, 北京大学公共卫生学院, 中国医师协会全科医师分会. 智能全科医生中国专家共识[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(02): 135-142. |
| [13] | 张璇, 张飞, 李铭麟, 王佳贺. 智能机器人在基层慢性病管理中的应用与挑战[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(01): 7-12. |
| [14] | 王舒云, 梁夏, 李霞, 林琳, 冯启明, 黄照权. 中国县域医共体研究热点与前沿分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(01): 83-88. |
| [15] | 王珍妮, 须月萍, 夏开建, 徐晓丹, 顾丽华. 基于YOLO神经网络构建压力性损伤自动检测和分期的人工智能模型[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(36): 4582-4590. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





