中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (11): 1330-1339.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0721
黄鹏飞1, 张云静1, 马冬1,2,*( ), 吴云艳3, 赵永波3,*(
), 吴云艳3, 赵永波3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-09-23
修回日期:2023-01-11
出版日期:2023-04-15
发布日期:2023-01-31
通讯作者:
马冬, 赵永波
基金资助:
HUANG Pengfei1, ZHANG Yunjing1, MA Dong1,2,*( ), WU Yunyan3, ZHAO Yongbo3,*(
), WU Yunyan3, ZHAO Yongbo3,*( )
)
Received:2022-09-23
Revised:2023-01-11
Published:2023-04-15
Online:2023-01-31
Contact:
MA Dong, ZHAO Yongbo
About author:摘要: 背景 急性A型主动脉夹层(ATAAD)是一种致命性疾病,快速、有效地识别ATAAD患者术后预后指标对其预后分层具有重要意义。血氯离子(Cl-)是人体重要的阴离子,影响多种疾病的发生、发展,但其与ATAAD的关系尚未完全明确。目的 探讨ATAAD患者入院血Cl-水平与术后30 d内全因死亡之间的关系,并分析ATAAD患者血Cl-水平与血钠离子(Na+)水平之间的相关性。方法 采用回顾性队列研究方法,连续纳入2016年2月至2019年12月河北医科大学第四医院经孙氏手术治疗的ATAAD患者206例,随访患者术后30 d内全因死亡及术后不良结局发生情况。根据入院血Cl-水平三分位数将患者分为三组:T1组(血Cl-≤102 mmol/L,n=69)、T2组(102 mmol/L<血Cl-≤106 mmol/L,n=70)、T3组(血Cl->106 mmol/L,n=67),比较不同组间的临床基线资料、实验室检查结果、术中资料和术后30 d内的预后结局。绘制入院时血Cl-、血Na+水平对ATAAD患者术后30 d内死亡预测价值的受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线,计算ROC曲线下面积(AUC)、约登指数、灵敏度、特异度、最佳截断值。采用多因素Logistic回归分析探讨ATAAD患者术后30 d内全因死亡的影响因素。为了分析血Cl-与血Na+的关系,根据血Cl-与血Na+预测ATAAD患者术后30 d内全因死亡的最佳截断值(107 mmol/L和139 mmol/L)将ATAAD患者分为四组:高血Cl-高血Na+组(血Cl->107 mmol/L+血Na+>139 mmol/L组,n=35),高血Cl-低血Na+组(血Cl->107 mmol/L+血Na+≤139 mmol/L组,n=21),低血Cl-高血Na+组(血Cl-≤107 mmol/L+血Na+>139 mmol/L组,n=41),低血Cl-低血Na+组(血Cl-≤107 mmol/L+血Na+≤139 mmol/L组,n=109),比较各组间的全因死亡率和累积生存率。采用Kaplan-Meier法绘制不同血Cl-水平,不同血Cl-+血Na+水平组ATAAD患者累积生存率的生存曲线,生存曲线比较采用Log-rank检验。采用Pearson相关性分析探讨血Cl-和血Na+的相关性;按年龄≥50岁(是/否)、性别(男/女)、高血压(是/否)、吸烟(是/否)、饮酒(是/否),血Na+>139 mmol/L(是/否)水平分组进行亚组分析,并利用相乘交互作用模型评价血Cl-与上述亚组之间的交互作用。结果 ROC曲线结果显示,入院时血Cl-水平预测ATAAD患者术后30 d内全因死亡的AUC为0.695〔95%CI(0.595,0.795),P<0.01〕,约登指数、灵敏度及特异度分别为0.331,54.5%、78.6%,最佳截断值为107 mmol/L;血Na+水平预测ATAAD患者术后30 d内全因死亡的AUC为0.648〔95%CI(0.544,0.752),P<0.01〕,约登指数、灵敏度及特异度分别为0.282,60.6%、67.6%,最佳截断值为139 mmol/L。多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,高血Cl-、高血Na+和术前发生灌注不足是ATAAD患者术后30 d内全因死亡的独立危险因素〔OR=1.168,95%CI(1.058,1.289),P=0.002;OR=1.098,95%CI(1.012,1.191),P=0.024;OR=5.837,95%CI(2.395,14.226),P<0.001〕;T3组是T1组ATAAD患者术后30 d内全因死亡风险的3.785倍〔95%CI(1.121,12.782),P=0.032〕,血Cl->107 mmol/L是血Cl-≤107 mmol/L ATAAD患者术后30 d内死亡风险的3.367倍〔95%CI(1.469,9.186),P=0.005〕。Kaplan-Meier生存曲线分析显示,T3组患者术后30 d累积生存率低于T1组、T2组(χ2=8.711,P=0.003;χ2=9.079,P=0.011);血Cl->107 mmol/L组患者30 d累积生存率低于血Cl-≤107 mmol/L组(χ2=13.326,P<0.001)。Pearson相关性分析结果显示,血Cl-水平和血Na+水平呈低度正相关(r=0.401,P<0.001);不同血Cl-+血Na+水平组的全因死亡率相比,差异有统计学意义(χ2=20.89,P<0.001);高血Cl-高血Na+组的30 d累积生存率低于其余三组(χ2=16.398,P<0.001;χ2=13.719,P<0.001;χ2=9.225,P=0.002)。亚组分析结果显示,血Cl-与年龄、性别、高血压、吸烟及饮酒无交互作用(P交互>0.05),ATAAD患者的血Cl-水平与血Na+(Na+>139 mmol/L)水平存在一定交互作用(P交互=0.012)。结论 ATAAD患者入院时血Cl-水平和血Na+水平具有相关性,入院时高血Cl-水平是ATAAD患者术后30 d内全因死亡的独立危险因素。
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄( | 性别(男/女) | 高血压〔n(%)〕 | 冠心病〔n(%)〕 | 吸烟〔n(%)〕 | 饮酒〔n(%)〕 | 体温( | 心率( | 收缩压( | 舒张压( | 住院时长〔M(P25,P75),d〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总患者 | 206 | 51.6±11.5 | 139/67 | 150(72.8) | 9(4.4) | 96(46.6) | 111(53.9) | 36.6±0.5 | 79±18 | 135±27 | 75±18 | 18.0(12.8,26.0) |
| T1组 | 69 | 50.8±11.9 | 48/21 | 54(78.3) | 5(7.2) | 39(56.5) | 43(62.3) | 36.7±0.5 | 79±19 | 138±24 | 78±17 | 19.0(14.0,28.0) |
| T2组 | 70 | 51.9±10.9 | 46/24 | 45(64.3) | 2(2.9) | 28(40.0) | 34(48.6) | 36.5±0.5 | 79±18 | 134±27d | 72±19 | 17.0(11.5,23.0) |
| T3组 | 67 | 52.3±11.7 | 45/22 | 51(76.1) | 2(3.0) | 67(43.3) | 34(50.7) | 36.8±0.5e | 79±16 | 132±27de | 74±17 | 19.0(11.0,28.3) |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.309a | 0.239b | 3.946b | 2.057b | 4.251b | 3.036b | 3.713a | 0.011a | 3.108a | 1.946a | 1.985c | |
| P值 | 0.735 | 0.887 | 0.137 | 0.357 | 0.119 | 0.219 | 0.026 | 0.989 | 0.047 | 0.146 | 0.371 | |
| 组别 | 丙氨酸氨基转移酶〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | 肌酐〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | 尿素氮〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 血糖〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 血小板计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/L〕 | 白细胞计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/L〕 | 红细胞计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/L〕 | 血红蛋白〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | |||
| 总患者 | 21.8(15.5,33.2) | 35.6(19.9,66.9) | 80.0(63.0,110.0) | 6.2(4.7,7.7) | 7.2(6.2,8.6) | 165.0(134.0,202.5) | 11.3(9.2,14.1) | 4.1(3.8,4.5) | 127.1(115.5,136.4) | |||
| T1组 | 20.0(15.4,29.1) | 36.1(18.6,67.3) | 87.0(66.5,118.5) | 6.5(4.7,8.9) | 7.7(6.2,9.5) | 168.0(131.0,209.0) | 11.5(9.0,13.5) | 4.1(3.8,4.4) | 125.9(113.9,133.8) | |||
| T2组 | 22.0(16.2,32.7) | 32.9(18.4,59.7) | 81.0(63.0,108.5) | 5.4(4.6,7.7) | 7.2(6.2,7.9) | 167.0(142.0,167.0) | 11.7(9.4,14.5) | 4.2(3.7,4.5) | 128.1(113.5,136.3) | |||
| T3组 | 22.1(14.6,36.9) | 40.7(22.5,67.2) | 77.0(63.0,103.3) | 6.2(5.3,7.6) | 7.0(6.3,8.6) | 158.0(127.0,194.2) | 10.8(9.1,14.3) | 4.1(3.8,4.6) | 126.9(116.7,139.3) | |||
| 检验统计量值 | 0.409c | 1.756c | 2.788c | 2.831c | 3.418c | 3.135c | 2.087c | 0.311c | 0.734c | |||
| P值 | 0.815 | 0.416 | 0.248 | 0.243 | 0.181 | 0.209 | 0.352 | 0.856 | 0.693 | |||
| 组别 | 中性粒细胞计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/L〕 | 淋巴细胞计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/L〕 | 单核细胞计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/L〕 | 体外循环时间>4 h〔n(%)〕 | 主动脉阻断时间( | 术前发生灌注不足〔n(%)〕 | 阴离子间隙( | 血K+ 〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 血Na+ 〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 血Ca2+〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | ||
| 总患者 | 9.7(7.5,12.4) | 0.9(0.6,1.2) | 0.7(0.5,0.9) | 74(35.9) | 119.9±20.6 | 53(25.7) | 15.2±3.9 | 4.0(3.4,4.0) | 139.0(136.0,141.0) | 2.2(2.1,2.3) | ||
| T1组 | 9.8(7.1,11.8) | 0.9(0.6,1.4) | 0.7(0.5,1.0) | 23(33.3) | 125.6±27.6 | 22(31.9) | 16.1±3.2 | 3.8(3.2,4.0) | 136.0(134.0,139.0) | 2.1(2.0,2.3) | ||
| T2组 | 10.1(7.4,12.8) | 0.9(0.6,1.3) | 0.7(0.6,0.9) | 27(38.6) | 119.8±24.3 | 17(24.3) | 15.4±3.9 | 4.0(3.6,4.1) | 139.0(137.0,140.0)d | 2.2(2.1,2.3) | ||
| T3组 | 9.6(7.9,12.8) | 0.8(0.6,0.9) | 0.6(0.5,0.9) | 24(35.8) | 121.4±21.1 | 14(20.9) | 14.1±4.4d | 4.0(3.4,4.1) | 140.0(139.0,143.0)d | 2.1(2.0,2.3) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | 2.350c | 4.241c | 2.441c | 0.415b | 2.601a | 2.263b | 4.387a | 4.383c | 57.384c | 5.782c | ||
| P值 | 0.309 | 0.120 | 0.295 | 0.813 | 0.310 | 0.322 | 0.014 | 0.112 | 0.001 | 0.056 |
表1 三组ATAAD患者临床基线资料比较
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of three groups of acute Stanford type A aortic dissection patients
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄( | 性别(男/女) | 高血压〔n(%)〕 | 冠心病〔n(%)〕 | 吸烟〔n(%)〕 | 饮酒〔n(%)〕 | 体温( | 心率( | 收缩压( | 舒张压( | 住院时长〔M(P25,P75),d〕 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总患者 | 206 | 51.6±11.5 | 139/67 | 150(72.8) | 9(4.4) | 96(46.6) | 111(53.9) | 36.6±0.5 | 79±18 | 135±27 | 75±18 | 18.0(12.8,26.0) |
| T1组 | 69 | 50.8±11.9 | 48/21 | 54(78.3) | 5(7.2) | 39(56.5) | 43(62.3) | 36.7±0.5 | 79±19 | 138±24 | 78±17 | 19.0(14.0,28.0) |
| T2组 | 70 | 51.9±10.9 | 46/24 | 45(64.3) | 2(2.9) | 28(40.0) | 34(48.6) | 36.5±0.5 | 79±18 | 134±27d | 72±19 | 17.0(11.5,23.0) |
| T3组 | 67 | 52.3±11.7 | 45/22 | 51(76.1) | 2(3.0) | 67(43.3) | 34(50.7) | 36.8±0.5e | 79±16 | 132±27de | 74±17 | 19.0(11.0,28.3) |
| 检验统计量值 | 0.309a | 0.239b | 3.946b | 2.057b | 4.251b | 3.036b | 3.713a | 0.011a | 3.108a | 1.946a | 1.985c | |
| P值 | 0.735 | 0.887 | 0.137 | 0.357 | 0.119 | 0.219 | 0.026 | 0.989 | 0.047 | 0.146 | 0.371 | |
| 组别 | 丙氨酸氨基转移酶〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶〔M(P25,P75),U/L〕 | 肌酐〔M(P25,P75),μmol/L〕 | 尿素氮〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 血糖〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 血小板计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/L〕 | 白细胞计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/L〕 | 红细胞计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/L〕 | 血红蛋白〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | |||
| 总患者 | 21.8(15.5,33.2) | 35.6(19.9,66.9) | 80.0(63.0,110.0) | 6.2(4.7,7.7) | 7.2(6.2,8.6) | 165.0(134.0,202.5) | 11.3(9.2,14.1) | 4.1(3.8,4.5) | 127.1(115.5,136.4) | |||
| T1组 | 20.0(15.4,29.1) | 36.1(18.6,67.3) | 87.0(66.5,118.5) | 6.5(4.7,8.9) | 7.7(6.2,9.5) | 168.0(131.0,209.0) | 11.5(9.0,13.5) | 4.1(3.8,4.4) | 125.9(113.9,133.8) | |||
| T2组 | 22.0(16.2,32.7) | 32.9(18.4,59.7) | 81.0(63.0,108.5) | 5.4(4.6,7.7) | 7.2(6.2,7.9) | 167.0(142.0,167.0) | 11.7(9.4,14.5) | 4.2(3.7,4.5) | 128.1(113.5,136.3) | |||
| T3组 | 22.1(14.6,36.9) | 40.7(22.5,67.2) | 77.0(63.0,103.3) | 6.2(5.3,7.6) | 7.0(6.3,8.6) | 158.0(127.0,194.2) | 10.8(9.1,14.3) | 4.1(3.8,4.6) | 126.9(116.7,139.3) | |||
| 检验统计量值 | 0.409c | 1.756c | 2.788c | 2.831c | 3.418c | 3.135c | 2.087c | 0.311c | 0.734c | |||
| P值 | 0.815 | 0.416 | 0.248 | 0.243 | 0.181 | 0.209 | 0.352 | 0.856 | 0.693 | |||
| 组别 | 中性粒细胞计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/L〕 | 淋巴细胞计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/L〕 | 单核细胞计数〔M(P25,P75),×109/L〕 | 体外循环时间>4 h〔n(%)〕 | 主动脉阻断时间( | 术前发生灌注不足〔n(%)〕 | 阴离子间隙( | 血K+ 〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 血Na+ 〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | 血Ca2+〔M(P25,P75),mmol/L〕 | ||
| 总患者 | 9.7(7.5,12.4) | 0.9(0.6,1.2) | 0.7(0.5,0.9) | 74(35.9) | 119.9±20.6 | 53(25.7) | 15.2±3.9 | 4.0(3.4,4.0) | 139.0(136.0,141.0) | 2.2(2.1,2.3) | ||
| T1组 | 9.8(7.1,11.8) | 0.9(0.6,1.4) | 0.7(0.5,1.0) | 23(33.3) | 125.6±27.6 | 22(31.9) | 16.1±3.2 | 3.8(3.2,4.0) | 136.0(134.0,139.0) | 2.1(2.0,2.3) | ||
| T2组 | 10.1(7.4,12.8) | 0.9(0.6,1.3) | 0.7(0.6,0.9) | 27(38.6) | 119.8±24.3 | 17(24.3) | 15.4±3.9 | 4.0(3.6,4.1) | 139.0(137.0,140.0)d | 2.2(2.1,2.3) | ||
| T3组 | 9.6(7.9,12.8) | 0.8(0.6,0.9) | 0.6(0.5,0.9) | 24(35.8) | 121.4±21.1 | 14(20.9) | 14.1±4.4d | 4.0(3.4,4.1) | 140.0(139.0,143.0)d | 2.1(2.0,2.3) | ||
| 检验统计量值 | 2.350c | 4.241c | 2.441c | 0.415b | 2.601a | 2.263b | 4.387a | 4.383c | 57.384c | 5.782c | ||
| P值 | 0.309 | 0.120 | 0.295 | 0.813 | 0.310 | 0.322 | 0.014 | 0.112 | 0.001 | 0.056 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 30 d内全因死亡率 | 急性肾损伤发生率 | 谵妄发生率 | 急性脑卒中发生率 | 术后二次出血发生率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1组 | 69 | 5(7.2) | 8(11.6) | 4(5.8) | 2(2.9) | 2(2.9) |
| T2组 | 70 | 10(14.3)a | 10(14.3) | 8(11.4) | 3(4.3) | 4(5.7) |
| T3组 | 67 | 18(26.9)ab | 19(28.4)ab | 5(7.5) | 9(13.4)ab | 4(6.0) |
| χ2值 | 9.963 | 7.455 | 1.537 | 7.011 | 0.843 | |
| P值 | 0.007 | 0.024 | 0.464 | 0.031 | 0.656 |
表2 三组患者术后30 d内预后结局比较〔n(%)〕
Table 2 Comparison of outcomes of three groups within 30 days after operation
| 组别 | 例数 | 30 d内全因死亡率 | 急性肾损伤发生率 | 谵妄发生率 | 急性脑卒中发生率 | 术后二次出血发生率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1组 | 69 | 5(7.2) | 8(11.6) | 4(5.8) | 2(2.9) | 2(2.9) |
| T2组 | 70 | 10(14.3)a | 10(14.3) | 8(11.4) | 3(4.3) | 4(5.7) |
| T3组 | 67 | 18(26.9)ab | 19(28.4)ab | 5(7.5) | 9(13.4)ab | 4(6.0) |
| χ2值 | 9.963 | 7.455 | 1.537 | 7.011 | 0.843 | |
| P值 | 0.007 | 0.024 | 0.464 | 0.031 | 0.656 |
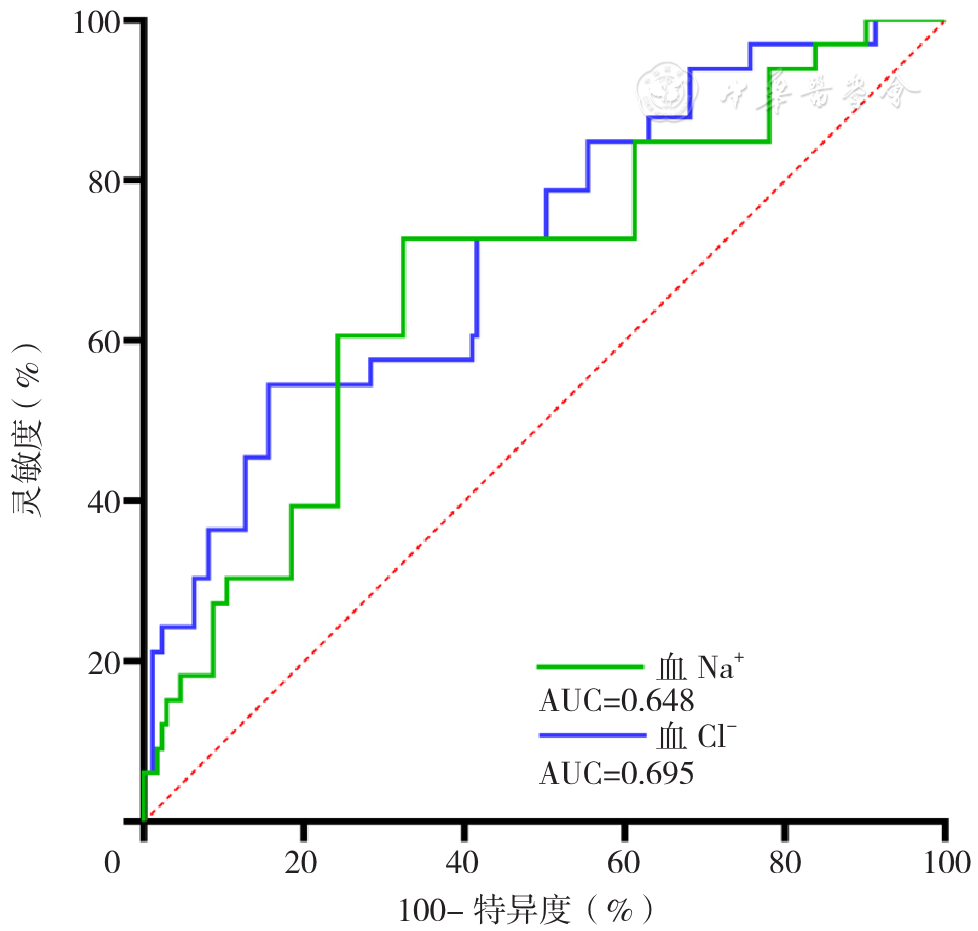
图1 入院时血Cl-、血Na+水平预测ATAAD患者术后30 d内全因死亡的ROC曲线注:ROC曲线=受试者工作特征曲线,Na+=钠离子,Cl-=氯离子,AUC=ROC曲线下面积
Figure 1 ROC curve analysis of admission serum Cl- and Na+ for predicting postoperative 30-dayall-cause mortality in acute Stanford type A aortic dissection patients
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.013 | 0.017 | 0.652 | 0.419 | 1.013(0.981,1.047) |
| 男性 | 0.204 | 0.397 | 0.263 | 0.608 | 1.226(0.563,2.669) |
| 高血压 | 0.182 | 0.440 | 0.171 | 0.679 | 1.200(0.506,2.884) |
| 冠心病 | 0.425 | 0.825 | 0.265 | 0.606 | 1.530(0.304,7.712) |
| 吸烟 | -3.500 | 0.387 | 0.815 | 0.367 | 0.705(0.330,1.506) |
| 饮酒 | -0.113 | 0.380 | 0.089 | 0.766 | 0.893(0.424,1.882) |
| 体温 | -0.258 | 0.371 | 0.485 | 0.486 | 0.772(0.373,4.589) |
| 心率 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.058 | 0.810 | 1.003(0.982,1.024) |
| 收缩压 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.116 | 0.733 | 1.002(0.989,1.016) |
| 舒张压 | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0.996 | 0.318 | 1.011(0.990,1.032) |
| 丙氨酸氨基转移酶 | -0.001 | 0.001 | 0.209 | 0.648 | 0.999(0.997,1.002) |
| 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.129 | 0.719 | 1.000(0.998,1.001) |
| 肌酐 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.028 | 0.866 | 1.000(0.995,1.004) |
| 尿素氮 | -0.010 | 0.052 | 0.034 | 0.853 | 0.990(0.894,1.097) |
| 血糖 | 0.041 | 0.044 | 0.872 | 0.350 | 1.042(0.956,1.134) |
| 血小板计数 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.029 | 0.865 | 1.000(0.995,1.006) |
| 白细胞计数 | -0.006 | 0.050 | 0.013 | 0.994 | 0.994(0.901,1.097) |
| 红细胞计数 | 0.074 | 0.350 | 0.045 | 0.833 | 1.077(0.542,2.140) |
| 血红蛋白 | -0.003 | 0.012 | 0.048 | 0.827 | 0.997(0.975,1.021) |
| 中性粒细胞计数 | -0.011 | 0.051 | 0.043 | 0.836 | 0.989(0.895,1.094) |
| 淋巴细胞计数 | -0.164 | 0.336 | 0.238 | 0.626 | 0.849(0.439,1.641) |
| 单核细胞计数 | 0.041 | 0.539 | 0.006 | 0.939 | 1.042(0.362,2.995) |
| 体外循环时间>4 h | 0.476 | 0.385 | 1.534 | 0.216 | 1.610(0.758,3.422) |
| 术前发生灌注不足 | 1.241 | 0.395 | 9.893 | 0.002 | 3.459(1.596,7.497) |
| 阴离子间隙 | -0.023 | 0.050 | 0.213 | 0.645 | 0.977(0.886,1.077) |
| 血Na+ | 0.105 | 0.036 | 8.609 | 0.003 | 1.111(1.036,1.192) |
| 血K+ | -0.002 | 0.301 | 0.001 | 0.995 | 0.998(0.553,1.801) |
| 血Ca2+ | -1.508 | 0.968 | 2.425 | 0.119 | 0.221(0.033,1.477) |
| 血Cl- | 0.151 | 0.041 | 13.544 | <0.001 | 1.163(1.073,1.261) |
表3 ATAAD患者30 d内术后全因死亡的单因素Logistic回归分析
Table 3 Univariate Logistic regression analysis of factors associated with postoperative 30-day all-cause mortality in acute Stanford type A aortic dissection patients
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.013 | 0.017 | 0.652 | 0.419 | 1.013(0.981,1.047) |
| 男性 | 0.204 | 0.397 | 0.263 | 0.608 | 1.226(0.563,2.669) |
| 高血压 | 0.182 | 0.440 | 0.171 | 0.679 | 1.200(0.506,2.884) |
| 冠心病 | 0.425 | 0.825 | 0.265 | 0.606 | 1.530(0.304,7.712) |
| 吸烟 | -3.500 | 0.387 | 0.815 | 0.367 | 0.705(0.330,1.506) |
| 饮酒 | -0.113 | 0.380 | 0.089 | 0.766 | 0.893(0.424,1.882) |
| 体温 | -0.258 | 0.371 | 0.485 | 0.486 | 0.772(0.373,4.589) |
| 心率 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.058 | 0.810 | 1.003(0.982,1.024) |
| 收缩压 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.116 | 0.733 | 1.002(0.989,1.016) |
| 舒张压 | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0.996 | 0.318 | 1.011(0.990,1.032) |
| 丙氨酸氨基转移酶 | -0.001 | 0.001 | 0.209 | 0.648 | 0.999(0.997,1.002) |
| 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.129 | 0.719 | 1.000(0.998,1.001) |
| 肌酐 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.028 | 0.866 | 1.000(0.995,1.004) |
| 尿素氮 | -0.010 | 0.052 | 0.034 | 0.853 | 0.990(0.894,1.097) |
| 血糖 | 0.041 | 0.044 | 0.872 | 0.350 | 1.042(0.956,1.134) |
| 血小板计数 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.029 | 0.865 | 1.000(0.995,1.006) |
| 白细胞计数 | -0.006 | 0.050 | 0.013 | 0.994 | 0.994(0.901,1.097) |
| 红细胞计数 | 0.074 | 0.350 | 0.045 | 0.833 | 1.077(0.542,2.140) |
| 血红蛋白 | -0.003 | 0.012 | 0.048 | 0.827 | 0.997(0.975,1.021) |
| 中性粒细胞计数 | -0.011 | 0.051 | 0.043 | 0.836 | 0.989(0.895,1.094) |
| 淋巴细胞计数 | -0.164 | 0.336 | 0.238 | 0.626 | 0.849(0.439,1.641) |
| 单核细胞计数 | 0.041 | 0.539 | 0.006 | 0.939 | 1.042(0.362,2.995) |
| 体外循环时间>4 h | 0.476 | 0.385 | 1.534 | 0.216 | 1.610(0.758,3.422) |
| 术前发生灌注不足 | 1.241 | 0.395 | 9.893 | 0.002 | 3.459(1.596,7.497) |
| 阴离子间隙 | -0.023 | 0.050 | 0.213 | 0.645 | 0.977(0.886,1.077) |
| 血Na+ | 0.105 | 0.036 | 8.609 | 0.003 | 1.111(1.036,1.192) |
| 血K+ | -0.002 | 0.301 | 0.001 | 0.995 | 0.998(0.553,1.801) |
| 血Ca2+ | -1.508 | 0.968 | 2.425 | 0.119 | 0.221(0.033,1.477) |
| 血Cl- | 0.151 | 0.041 | 13.544 | <0.001 | 1.163(1.073,1.261) |
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.003 | 0.019 | 0.018 | 0.893 | 1.003(0.966,1.041) | |
| 男性 | 0.018 | 0.466 | 0.002 | 0.969 | 1.019(0.409,2.539) | |
| 术前发生灌注不足 | 1.764 | 0.455 | 15.067 | <0.001 | 5.837(2.395,14.226) | |
| 血Na+ | 0.094 | 0.041 | 5.092 | 0.024 | 1.098(1.012,1.191) | |
| 血Cl- | 0.155 | 0.050 | 9.498 | 0.002 | 1.168(1.058,1.289) | |
| 血Cl-水平 | ||||||
| T1 | — | — | — | — | 1.000 | |
| T2 | 0.629 | 0.618 | 1.033 | 0.309 | 1.875(0.558,6.301) | |
| T3 | 1.712 | 0.446 | 14.699 | 0.032 | 3.785(1.121,12.782) | |
| 血Cl-水平最佳截断值 | ||||||
| ≤107 mmol/L | — | — | — | — | 1.000 | |
| >107 mmol/L | 1.301 | 0.468 | 7.742 | 0.005 | 3.367(1.469,9.186) | |
表4 ATAAD患者术后30 d内术后全因死亡的多因素Logistic回归分析
Table 4 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of factors associated with postoperative 30-day all-cause mortality in acute Stanford type A aortic dissection patients
| 变量 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR(95%CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.003 | 0.019 | 0.018 | 0.893 | 1.003(0.966,1.041) | |
| 男性 | 0.018 | 0.466 | 0.002 | 0.969 | 1.019(0.409,2.539) | |
| 术前发生灌注不足 | 1.764 | 0.455 | 15.067 | <0.001 | 5.837(2.395,14.226) | |
| 血Na+ | 0.094 | 0.041 | 5.092 | 0.024 | 1.098(1.012,1.191) | |
| 血Cl- | 0.155 | 0.050 | 9.498 | 0.002 | 1.168(1.058,1.289) | |
| 血Cl-水平 | ||||||
| T1 | — | — | — | — | 1.000 | |
| T2 | 0.629 | 0.618 | 1.033 | 0.309 | 1.875(0.558,6.301) | |
| T3 | 1.712 | 0.446 | 14.699 | 0.032 | 3.785(1.121,12.782) | |
| 血Cl-水平最佳截断值 | ||||||
| ≤107 mmol/L | — | — | — | — | 1.000 | |
| >107 mmol/L | 1.301 | 0.468 | 7.742 | 0.005 | 3.367(1.469,9.186) | |
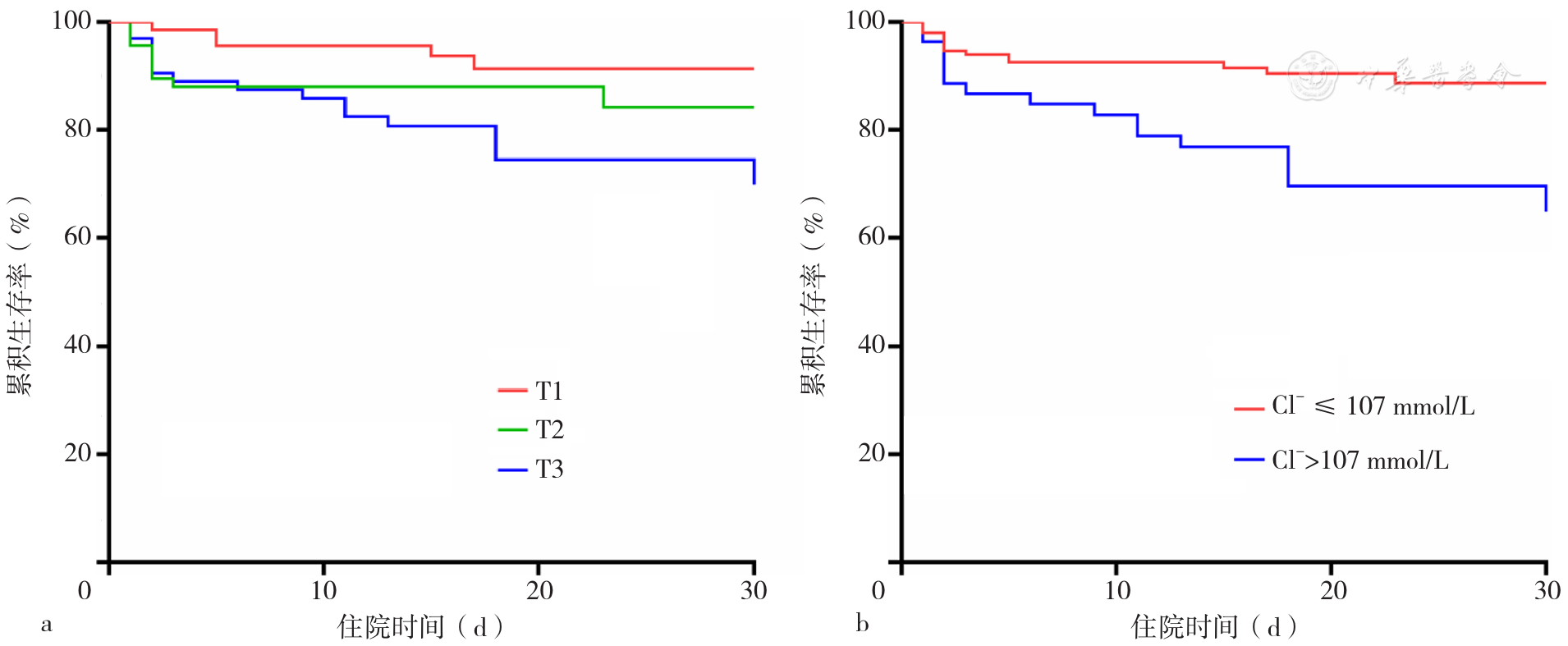
图2 不同Cl-水平ATAAD患者术后30 d内累积生存率的生存曲线注:T1=血Cl-≤102 mmol/L,T2=102<血Cl-≤106 mmol/L,T3=血Cl->106 mmol/L
Figure 2 Cumulative survivalcurves within 30 days after surgery for acute Stanford type A aortic dissection patients with different admission serum Cl- levels
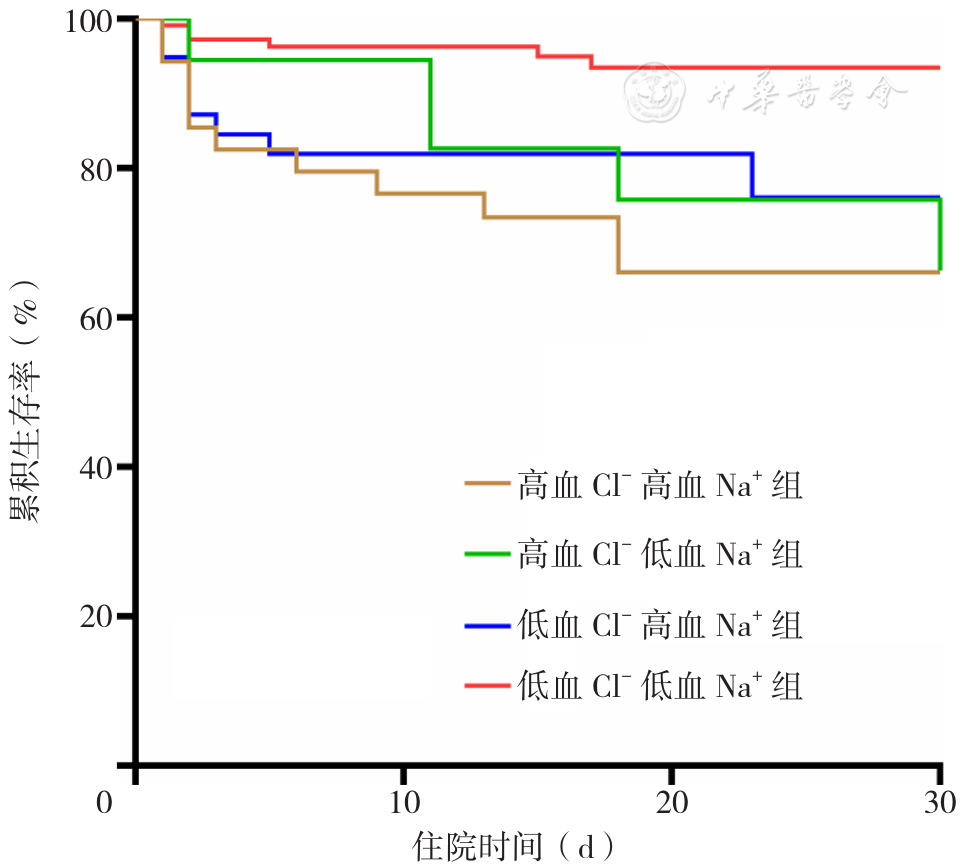
图4 不同血Cl-、血Na+水平组ATAAD患者术后30 d内累积生存率的生存曲线
Figure 4 Cumulative survival curves within 30 days after surgery for acute Stanford type A aortic dissection patients with different admission serum Cl- and Na+ levels
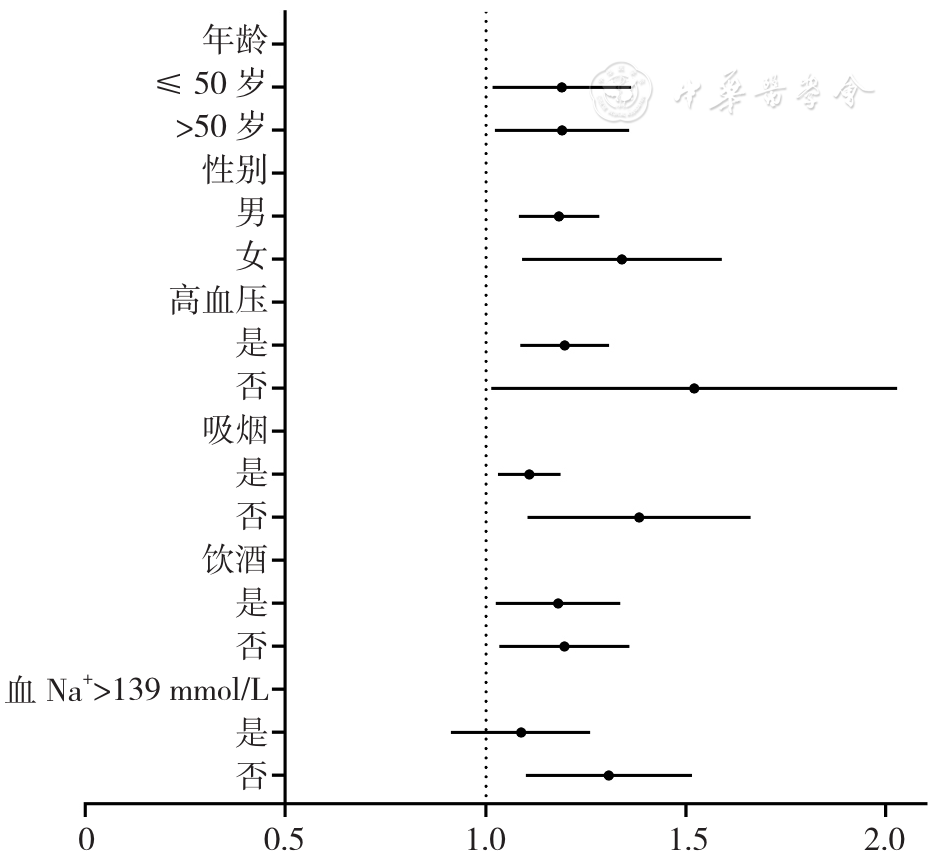
图5 血Cl-与ATAAD患者30 d内全因死亡的亚组分析
Figure 5 Subgroup analysis for the association of admission serum Cl- and postoperative 30-day all-cause mortality in acute Stanford type A aortic dissection patients
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
盛颖. 临床高危特征及疼痛程度预判急性主动脉夹层的作用[J]. 临床急诊杂志,2017,18(5):392-394. DOI:10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2017.05.020.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
黄毕,田力,樊晓寒,等. A型急性主动脉夹层患者入院时血小板计数与住院死亡率的相关性研究[J]. 中国循环杂志,2014,29(10):814-818. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2014.10.014.
|
| [10] |
田力,樊晓寒,朱俊,等. A型急性主动脉夹层患者血浆D-二聚体浓度和住院死亡的关系[J]. 中华高血压杂志,2014,22(2):200. DOI:10.16439/j.cnki.1673-7245.2014.02.030.
|
| [11] |
柳叶,李倩,吴小文. 急性Stanford A型主动脉夹层患者术后死亡危险因素分析[J]. 护理实践与研究,2021,18(13):1969-1972. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-9676.2021.13.020.
|
| [12] |
顾嘉玺,邵永丰,倪布清,等. 急性Stanford A型主动脉夹层孙氏手术后院内死亡危险因素分析[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2020,40(8):1194-1197. DOI:10.7655/NYDXBNS20200820.
|
| [13] |
曾文新,红科,柳学,等. C反应蛋白与白蛋白比值在急性A型主动脉夹层手术患者预后预测中的价值[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志,2016,25(6):764-768. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2016.06.016.
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
谭莉. 血酮测定评估急性胃肠炎患儿脱水和代谢性酸中毒的价值[J]. 西南国防医药,2018,28(12):1204-1207. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-0188.2018.12.025.
|
| [22] |
中国医师协会心血管外科分会大血管外科专业委员会. 主动脉夹层诊断与治疗规范中国专家共识[J]. 中华胸心血管外科杂志,2017,33(11):641-654. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-4497.2017.11.001.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
Standards of medical care in diabetes-2016: summary of revisions[J]. Diabetes Care,2016,39(Suppl 1):S4-5. DOI:10.2337/dc16-S003.
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
赵宏亮,徐子良,郑敏文. 急性Stanford A型主动脉夹层术后新发脑梗死的危险因素分析[J]. 影像诊断与介入放射学,2020,29(4):243-246. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-8001.2020.04.001.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
湛镇伊,杨建安,刘银河. 微小RNA在主动脉夹层中差异性表达与发病机制的研究进展[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志,2019,27(10):910-914. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-3949.2019.10.015.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [1] | 薛崇祥, 鲁星妤, 刘哲宁, 董慧静, 郑玉敏, 崔慧娟. 动态监测肺癌患者基因变化规律及其预后意义[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(36): 4527-4534. |
| [2] | 崔晓娜, 冯瑞霞, 韩雨澎, 周瑶瑶, 刘小军, 李建朝. 静脉-动脉体外膜肺氧合和主动脉内球囊反搏联合辅助顺序对急性心肌梗死合并心源性休克患者的临床效果比较研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(35): 4439-4445. |
| [3] | 彰金, 丁治国, 祁烁, 李颖, 李伟强, 张媛媛, 周通. 血清甲状腺激素水平与心力衰竭患者住院期间预后的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4125-4129. |
| [4] | 张思宇, 周郁秋, 杜晓慧, 王正君. 精神病未治期及其早期干预的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(33): 4110-4117. |
| [5] | 孟江涛, 杨思宇, 孙蕾, 雷瑞宁, 赵晓霞. 弥散张量成像联合运动诱发电位评估脑梗死偏瘫患者运动功能预后价值的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4098-4102. |
| [6] | 陈希, 章娟, 李霖, 张佳琪, 吴耀丽, 郭慧, 王超群. 中国中老年人体力活动与全因死亡风险的关系:前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(31): 3890-3895. |
| [7] | 施晓琦, 罗南都, 黄娇娇, 杜作晨, 黄佩, 曹秀丽, 陈艳, 何志旭. 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶/丙氨酸氨基转移酶与儿童噬血细胞性淋巴组织细胞增生症预后的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(30): 3801-3808. |
| [8] | 闫可, 魏菀怡, 李曙光, 么伟楠, 董静, 王晓斌, 张雪原, 杨洁, 沈文斌, 祝淑钗. 巩固化疗对接受根治性同步放化疗的临床Ⅱ~Ⅲ期食管鳞状细胞癌患者预后的影响分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(30): 3772-3779. |
| [9] | 闫可, 魏菀怡, 邓文钊, 沈文斌, 李曙光, 杜星语, 张雪原, 杨洁, 祝淑钗. 颈胸上段食管鳞癌根治性同步放化疗远期预后分析及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(30): 3785-3790. |
| [10] | 徐哲, 张金霞, 张秀红, 谢开红. 中老年人睡眠时间与全因死亡风险关系的队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(28): 3507-3512. |
| [11] | 汤时蓝, 谢可欣, 刘玲谕, 齐甜甜, 杨燕绥. 慢性意识障碍患者康复预后及照护研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(27): 3342-3348. |
| [12] | 孙帅刚, 盛晓笑, 张文惠, 田慧娟, 翟亚玲. 免疫球蛋白G4合并其他不同免疫球蛋白G亚型沉积的特发性膜性肾病患者的临床病理及短期预后分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(21): 2632-2638. |
| [13] | 赵泽玮, 康宁, 郭丰丽, 王钟玉, 郑向前. 极光激酶A表达对甲状腺髓样癌切除术后患者生化治愈的影响作用研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(20): 2508-2512. |
| [14] | 张康, 姬文帅, 孔欣欣, 杜琛, 谢凯, 王海峰. 序贯性脏器功能衰竭评分和CURB-65评分及肺炎严重指数评分对重症肺炎患者28天死亡的预测效能比较研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(18): 2217-2222. |
| [15] | 王珺, 吴佳霏, 王依景, 郑博月, 王宇, 江川艳, 李慧. 以达雷妥尤单抗为基础的化疗方案对多发性骨髓瘤疗效和预后影响的真实世界研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(18): 2256-2262. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





