中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (06): 704-710.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0581
李家青1, 杨晴1, 袁敦禄1, 黄晶晶2, 常青1, 聂静雯1, 周竹1, 李青1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-07-21
修回日期:2022-10-11
出版日期:2023-02-20
发布日期:2022-10-20
通讯作者:
李青
基金资助:
LI Jiaqing1, YANG Qing1, YUAN Dunlu1, HUANG Jingjing2, CHANG Qing1, NIE Jingwen1, ZHOU Zhu1, LI Qing1,*( )
)
Received:2022-07-21
Revised:2022-10-11
Published:2023-02-20
Online:2022-10-20
Contact:
LI Qing
About author:摘要: 背景 贫血是慢性肾脏病患者最常见的临床表现,也是肾脏疾病的主要并发症,影响患者的生命质量、加速疾病进展并增加患者死亡风险,纠正贫血和监测改善肾性贫血药物的疗效及安全性意义重大。 目的 比较罗沙司他与红细胞生成刺激剂在治疗维持性血液透析患者肾性贫血中的疗效和安全性。 方法 计算机检索PubMed、FMRS、万方数据知识服务平台以及ClinicalTrials.gov,检索时间为建库至2022-01-19。筛选维持性血液透析患者透析龄≥3个月的随机对照试验,其中试验组口服罗沙司他,对照组注射红细胞生成刺激剂。由2名研究者独立完成文献筛选和资料提取,对文献进行质量评价后采用Review Manager 5.3软件进行Meta分析。 结果 共纳入5篇文献,包括6项随机对照研究、901例患者。其中试验组549例,对照组352例。Meta分析结果显示,罗沙司他在提高血液透析患者的血清铁〔MD=2.49,95%CI(0.82,4.16),P=0.004〕、转铁蛋白〔MD=0.31,95%CI(0.17,0.44),P<0.000 01〕、总铁结合力〔MD=7.51,95%CI(5.01,10.01),P<0.000 01〕水平方面均优于红细胞生成刺激剂。两组总的不良事件发生率比较,差异无统计学意义〔RR=1.10,95%CI(0.99,1.22),P=0.07〕。 结论 罗沙司他在升高血清铁、转铁蛋白、总铁结合力方面较红细胞生成刺激剂效果更好;短期内使用罗沙司他未增加血液透析患者不良事件风险。
| 第一作者 | 发表年份(年) | 国家 | NCT | 单中心/多中心 | 临床研究阶段 | 样本量(例) | 男性〔n(%)〕 | 年龄(岁) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | ||||||
| AKIZAWA[ | 2020 | 日本 | NCT02952092 | 多中心 | Ⅲ期 | 150 | 151 | 101(67.3) | 107(70.9) | 64.6±11.7 | 64.9±10.1 |
| AKIZAWA[ | 2019 | 日本 | NCT01964196 | 多中心 | Ⅲ期 | 13 | 43 | 10(76.9) | 26(60.5) | 64.4±8.7 | 61.9±10.6 |
| CHEN[ | 2019 | 中国 | NCT02652806 | 多中心 | Ⅲ期 | 204 | 100 | 126(61.8) | 58(58.0) | 47.6±11.7 | 51.0±11.8 |
| CHEN[ | 2017 | 中国 | NCT01596855 | 多中心 | Ⅱ期 | 74 | 22 | 45(60.4) | 13(59.1) | 50.0±12.8 | 53.8±10.0 |
| PROVENZANO[ | 2016 | 美国 | NCT01147666 | 多中心 | Ⅱ期 | 41 | 13 | 27(66.0) | 9(69.0) | 55.8±13.4 | 59.5±10.1 |
| PROVENZANO[ | 2016 | 美国 | NCT01147666 | 多中心 | Ⅱ期 | 67 | 23 | 45(67.0) | 14(61.0) | 56.9±12.1 | 57.0±11.6 |
| 第一作者 | 基线血红蛋白(g/dl) | 干预措施 | 罗沙司他剂量 | 干预时间(周) | 结局指标 | ||||||
| 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | ||||||||
| AKIZAWA[ | 11.00±0.56 | 11.00±0.60 | 罗沙司他 | ESAs | 70 mg、100 mg,TIW | 24 | ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧ | ||||
| AKIZAWA[ | 9.35±0.75 | 10.85±0.54 | 罗沙司他 | ESAs | 50 mg、70 mg,TIW;70 mg、100 mg,TIW | 24 | ①②③④⑤⑦⑧ | ||||
| CHEN[ | 10.40±0.70 | 10.50±0.70 | 罗沙司他 | ESAs | 100 mg(体质量45~<60 kg)、120 mg(体质量≥60 kg) | 26 | ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧ | ||||
| CHEN[ | 10.80±0.70 | 10.60±1.00 | 罗沙司他 | ESAs | 1.1~1.8 mg/kg、1.5~3.0 mg/kg、1.7~2.3 mg/kg,TIW | 6 | ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧ | ||||
| PROVENZANO[ | 11.30±0.60 | 11.50±0.60 | 罗沙司他 | ESAs | 1.0 mg/kg、1.5 mg/kg、1.8 mg/kg、2.0 mg/kg,TIW | 6 | ①②③⑤⑥⑦⑧ | ||||
| PROVENZANO[ | 11.20±0.70 | 11.20±1.00 | 罗沙司他 | ESAs | 1.0 mg/kg、1.5 mg/kg、1.8 mg/kg、2.0 mg/kg,TIW | 19 | ①②③⑤⑥⑦⑧ | ||||
表1 纳入研究的基本情况
Table 1 Characteristics of studies included in meta-analysis
| 第一作者 | 发表年份(年) | 国家 | NCT | 单中心/多中心 | 临床研究阶段 | 样本量(例) | 男性〔n(%)〕 | 年龄(岁) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | ||||||
| AKIZAWA[ | 2020 | 日本 | NCT02952092 | 多中心 | Ⅲ期 | 150 | 151 | 101(67.3) | 107(70.9) | 64.6±11.7 | 64.9±10.1 |
| AKIZAWA[ | 2019 | 日本 | NCT01964196 | 多中心 | Ⅲ期 | 13 | 43 | 10(76.9) | 26(60.5) | 64.4±8.7 | 61.9±10.6 |
| CHEN[ | 2019 | 中国 | NCT02652806 | 多中心 | Ⅲ期 | 204 | 100 | 126(61.8) | 58(58.0) | 47.6±11.7 | 51.0±11.8 |
| CHEN[ | 2017 | 中国 | NCT01596855 | 多中心 | Ⅱ期 | 74 | 22 | 45(60.4) | 13(59.1) | 50.0±12.8 | 53.8±10.0 |
| PROVENZANO[ | 2016 | 美国 | NCT01147666 | 多中心 | Ⅱ期 | 41 | 13 | 27(66.0) | 9(69.0) | 55.8±13.4 | 59.5±10.1 |
| PROVENZANO[ | 2016 | 美国 | NCT01147666 | 多中心 | Ⅱ期 | 67 | 23 | 45(67.0) | 14(61.0) | 56.9±12.1 | 57.0±11.6 |
| 第一作者 | 基线血红蛋白(g/dl) | 干预措施 | 罗沙司他剂量 | 干预时间(周) | 结局指标 | ||||||
| 试验组 | 对照组 | 试验组 | 对照组 | ||||||||
| AKIZAWA[ | 11.00±0.56 | 11.00±0.60 | 罗沙司他 | ESAs | 70 mg、100 mg,TIW | 24 | ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧ | ||||
| AKIZAWA[ | 9.35±0.75 | 10.85±0.54 | 罗沙司他 | ESAs | 50 mg、70 mg,TIW;70 mg、100 mg,TIW | 24 | ①②③④⑤⑦⑧ | ||||
| CHEN[ | 10.40±0.70 | 10.50±0.70 | 罗沙司他 | ESAs | 100 mg(体质量45~<60 kg)、120 mg(体质量≥60 kg) | 26 | ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧ | ||||
| CHEN[ | 10.80±0.70 | 10.60±1.00 | 罗沙司他 | ESAs | 1.1~1.8 mg/kg、1.5~3.0 mg/kg、1.7~2.3 mg/kg,TIW | 6 | ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧ | ||||
| PROVENZANO[ | 11.30±0.60 | 11.50±0.60 | 罗沙司他 | ESAs | 1.0 mg/kg、1.5 mg/kg、1.8 mg/kg、2.0 mg/kg,TIW | 6 | ①②③⑤⑥⑦⑧ | ||||
| PROVENZANO[ | 11.20±0.70 | 11.20±1.00 | 罗沙司他 | ESAs | 1.0 mg/kg、1.5 mg/kg、1.8 mg/kg、2.0 mg/kg,TIW | 19 | ①②③⑤⑥⑦⑧ | ||||
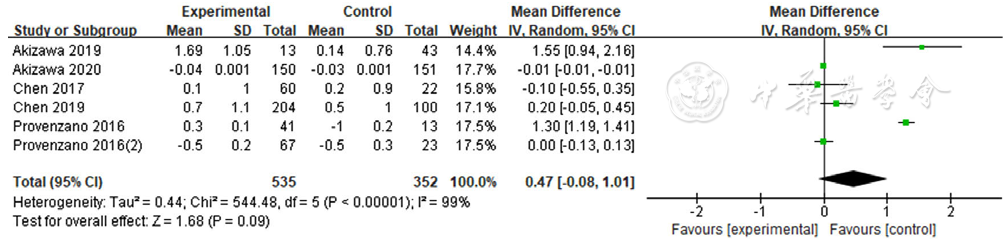
图3 罗沙司他与ESAs对血红蛋白影响的森林图
Figure 3 Forest plot for comparison the efficacy between roxadustat and erythropoiesis stimulating agents on improving hemoglobin level
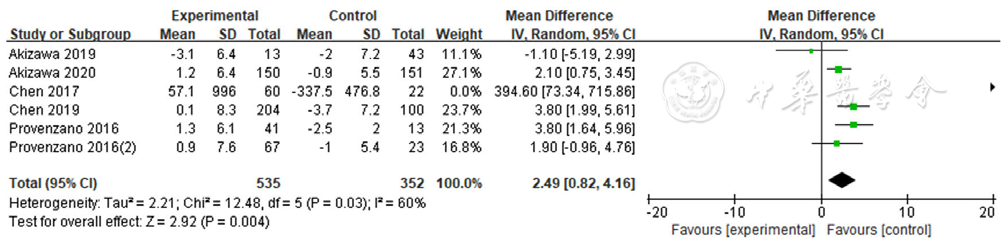
图4 罗沙司他与ESAs对血清铁影响的森林图
Figure 4 Forest plot for comparison the efficacy between roxadustat and erythropoiesis stimulating agents on improving serum iron level

图5 罗沙司他与ESAs对铁蛋白影响的森林图
Figure 5 Forest plot for comparison the efficacy between roxadustat and erythropoiesis stimulating agents on improving ferritin level
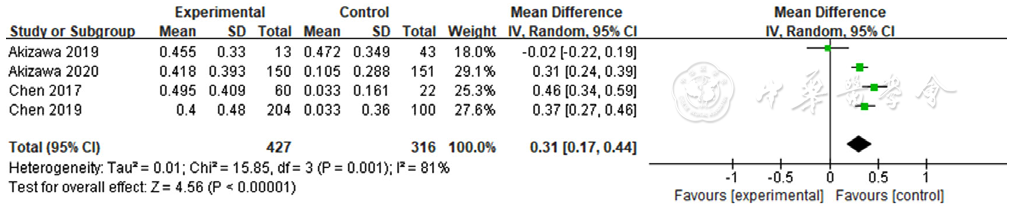
图6 罗沙司他与ESAs对转铁蛋白影响的森林图
Figure 6 Forest plot for comparison the efficacy between roxadustat and erythropoiesis stimulating agents on improving transferrin level
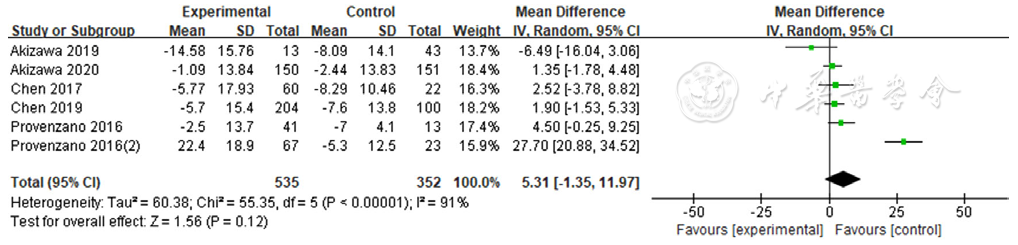
图7 罗沙司他与ESAs对转铁蛋白饱和度影响的森林图
Figure 7 Forest plot for comparison the efficacy between roxadustat and erythropoiesis stimulating agents on improving transferrin saturation
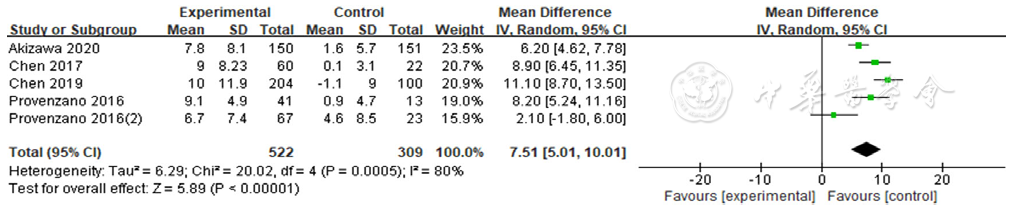
图8 罗沙司他与ESAs对总铁结合力影响的森林图
Figure 8 Forest plot for comparison the efficacy between roxadustat and erythropoiesis stimulating agents on improving total iron-binding capacity
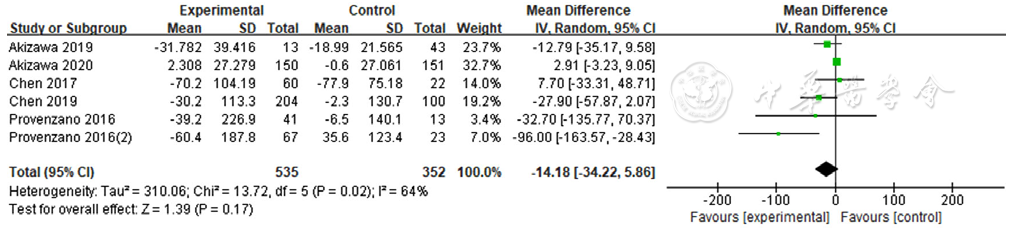
图9 罗沙司他与ESAs对铁调素影响的森林图
Figure 9 Forest plot for comparison the efficacy between roxadustat and erythropoiesis stimulating agents on improving hepcidin

图10 罗沙司他与ESAs总的不良事件发生率比较森林图
Figure 10 Forest plot for comparison the overall incidence of adverse events related to roxadustat and erythropoiesis stimulating agents
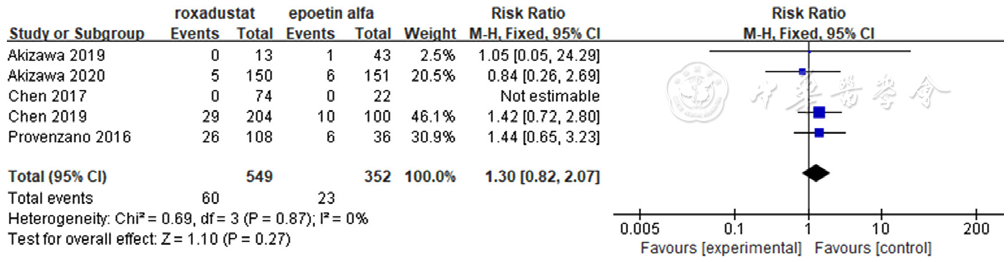
图11 罗沙司他与ESAs药物相关严重不良事件发生率比较森林图
Figure 11 Forest plot for comparison of incidence of serious adverse events related to roxadustat and erythropoiesis stimulating agents
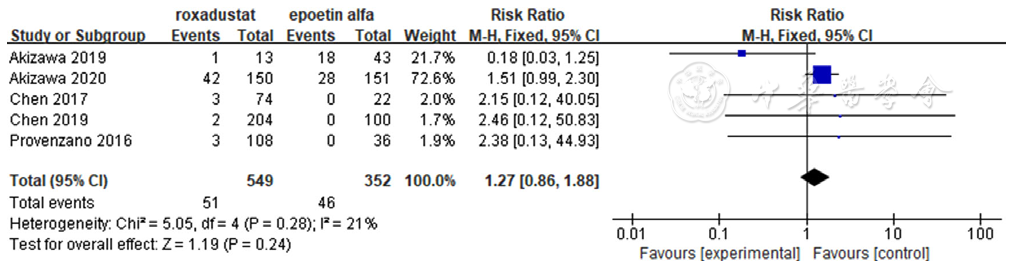
图12 罗沙司他与ESAs胃肠道不良事件发生率比较森林图
Figure 12 Forest plot for comparison the incidence of gastrointestinal disorders related to roxadustat and erythropoiesis stimulating agents
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
孟松,朱晶晶,李少华,等. 授权教育结合思维导图对维持性血液透析重度肾性贫血患者的影响[J]. 国际移植与血液净化杂志,2021,19(6):43-45. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn115399-20210421-06012.
|
| [15] | |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
KDOQI, NATIONAL KIDNEY FOUNDATION. KDOQI clinical practice guidelines and clinical practice recommendations for anemia in chronic kidney disease[J]. Am J Kidney Dis,2006,47(5 Suppl 3):S11-145. DOI:10.1053/j.ajkd.2006.03.010.
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
李辉锋,毛永炎. 罗沙司他治疗慢性肾脏病透析患者合并肾性贫血的效果和安全性[J]. 中国实用医刊,2021,48(22):99-102. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn115689-20210820-02744.
|
| [1] | 谢雪梅, 高静, 柏丁兮, 卢贤英, 何佳丽, 李月. 老年人多重用药依从性现状及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(35): 4394-4403. |
| [2] | 王越, 陈晴, 刘鲁蓉. 中国老年人抑郁检出率及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4329-4335. |
| [3] | 王喆, 董志浩, 郑好, 孔文程, 张玉宽, 张秋月, 韩晶. 针刺干预偏头痛优势方案构建研究:基于熵权TOPSIS法[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4336-4342. |
| [4] | 蹇秋枫, 徐荣华, 姚倩, 周媛媛. 中国老年脑卒中患者认知障碍患病率和影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4070-4079. |
| [5] | 贾钰, 周紫彤, 曹学华, 胡婉琴, 向凤, 熊浪宇, 王晓霞. 中国40~65岁女性围绝经期综合征发生率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4080-4088. |
| [6] | 李纪新, 邱林杰, 任燕, 王文茹, 李美洁, 张晋. 膳食炎症指数与超重和肥胖及腹型肥胖关系的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4089-4097. |
| [7] | 何静漪, 王芳, 税晓玲, 李玲, 梁倩. 非药物干预改善围绝经期失眠症状疗效的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(31): 3963-3974. |
| [8] | 朱琳, 郭闫葵, 高琛, 陈学志, 王法帅. 单纯西药、中成药及其联合治疗卒中后失眠疗效的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(30): 3823-3832. |
| [9] | 张懂理, 沈冲, 张卫川, 陈海滨, 赵建军. 程序性死亡因子1/程序性死亡因子1配体抑制剂治疗肾细胞癌有效性及安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(30): 3815-3822. |
| [10] | 何莉, 张逸凡, 沈雪纯, 孙燕, 赵洋. 中国大陆地区居民慢性病共病的流行趋势:一项Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(29): 3599-3607. |
| [11] | 胡婧伊, 洪景, 郭晓冬, 张晓红, 莫宁, 周小翠, 余钦, 周敏华, 孙艳, 倪柳, 石晓丽, 苏小青, 李玉倩. 社区参与安宁疗护对临终期肿瘤患者干预效果的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(28): 3573-3584. |
| [12] | 林洋, 王芳, 王寒, 武蓉, 王瑶, 徐子尧, 王旭, 王彦丁. 老年共病患者衰弱患病率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(25): 3185-3193. |
| [13] | 段玉霞, 李珍, 张斯齐, 房志学, 秦月兰. 结直肠癌诊疗中患者决策辅助工具应用效果的系统评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(25): 3194-3201. |
| [14] | 郭银宁, 缪雪怡, 蒋小曼, 徐婷, 许勤. 蛋白质补充对衰弱/衰弱前期老年人肌肉质量和肌肉力量以及身体功能影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(23): 2854-2863. |
| [15] | 韩知浩, 马小琴. 癌症晚期患者代理决策者预立医疗照护计划参与度影响因素的混合方法系统评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(22): 2785-2792. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





