中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (15): 1892-1901.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0574
所属专题: 内分泌代谢性疾病最新文章合辑; 老年问题最新文章合辑
收稿日期:2022-08-15
修回日期:2022-10-12
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2022-11-14
通讯作者:
程康耀
基金资助:
YANG Bei, HAN Lin, WANG Yin, CHENG Kangyao*( )
)
Received:2022-08-15
Revised:2022-10-12
Published:2023-05-20
Online:2022-11-14
Contact:
CHENG Kangyao
摘要: 背景 胰岛素在糖尿病患者的治疗中起着重要作用,可以进行每日多次皮下注射胰岛素(MDI),也可以通过胰岛素泵实现持续皮下胰岛素注射(CSII),目前对两种注射方法在老年2型糖尿病(T2DM)人群中的治疗效果仍存在争议。 目的 应用Meta分析方法评价CSII对老年T2DM患者的治疗效果,并用试验序贯分析(TSA)检验Meta分析结果的有效性。 方法 计算机检索Cochrane Library、PubMed、Embase、Medline、Scopus、Web of Science、中国知网(CNKI)、万方数据知识服务平台(Wanfang Data)、维普期刊资源整合服务平台(CQVIP)和中国生物医学文献数据库(SinoMed)从建库至2021年12月公开发表的关于CSII治疗老年T2DM的随机对照试验(RCT)。试验组通过胰岛素泵实施CSII治疗,对照组采取MDI治疗。主要结局指标:空腹血糖(FPG)、餐后2 h血糖(2 hPG)、糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)、低血糖发生率;次要结局指标:平均血糖波动幅度(MAGE)、胰岛素日用量、血糖达标时间。两名研究者独立筛选文献、评价文献质量并提取资料。采用Review Manager 5.3软件对符合质量标准的文献进行Meta分析,使用哥本哈根临床试验中心研发的TSA v0.9完成试验序贯分析。 结果 共纳入16篇RCT。Meta分析结果显示,试验组改善老年T2DM患者的FPG〔MD=-0.82,95%CI(-1.09,-0.54),P<0.05〕、2 hPG〔MD=-0.76,95%CI(-1.39,-0.14),P<0.05〕、HbA1c〔SMD=-1.23,95%CI(-2.23,-0.23),P<0.05〕、严重低血糖发生率〔RD=-0.10,95%CI(-0.17,-0.03),P<0.05〕、胰岛素日用量〔MD=-9.63,95%CI(-12.35,-6.92),P<0.05〕、MAGE〔MD=-1.19,95%CI(-1.40,-0.97),P<0.05〕效果优于对照组。对主要结局指标进行试验序贯分析发现,CSII治疗能降低老年T2DM患者的FPG、2 hPG、HbA1c水平和严重低血糖发生率。 结论 相对于MDI,CSII能进一步改善老年T2DM患者的血糖控制水平、降低低血糖发生率和平均血糖波动幅度。
| 步骤 | 检索策略 |
|---|---|
| 1 | Mesh descriptor:[Diabetes Mellitus,Type 2] explode all trees |
| 2 | (diabetes mellitus,non-insulin dependent OR diabetes mellitus,ketosis resistant OR diabetes mellitus,type II OR type 2 diabetes mellitus OR diabetes,type 2 OR NIDDM):ti,ab,kw |
| 3 | #1 OR #2 |
| 4 | Mesh descriptor:[Insulin Infusion System] explode all trees |
| 5 | (continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion OR insulin pump OR artificial endocrine pancreas OR artificial beta cell OR CSII):ti,ab,kw |
| 6 | #4 OR #5 |
| 7 | (multiple daily injections OR MDI OR flexible multiple daily insulin OR FMDI OR multiple subcutaneous injections OR MSI OR intensive insulin therapy OR multiple injection regimens):ti,ab,kw |
| 8 | #6 AND #7 |
| 9 | Mesh descriptor:[Aged] explode all trees |
| 10 | (old* OR elderly OR senile OR aging OR senior citizen OR geriatric OR seniors OR older adult):ti,ab,kw |
| 11 | #9 OR #10 |
| 12 | Mesh descriptor:[Randomized Controlled Trial (Publication Type)] explode all trees |
| 13 | ("randomized controlled trial" ):pt |
| 14 | (randomised OR randomized OR controlled OR RCT OR randomly):ti,ab,kw |
| 15 | #12 OR #13 OR #14 |
| 16 | #3 AND #8 AND #11 AND #15 |
表1 Cochrane Library检索策略
Table 1 Strategy for searching RCTs in the Cochrane Library
| 步骤 | 检索策略 |
|---|---|
| 1 | Mesh descriptor:[Diabetes Mellitus,Type 2] explode all trees |
| 2 | (diabetes mellitus,non-insulin dependent OR diabetes mellitus,ketosis resistant OR diabetes mellitus,type II OR type 2 diabetes mellitus OR diabetes,type 2 OR NIDDM):ti,ab,kw |
| 3 | #1 OR #2 |
| 4 | Mesh descriptor:[Insulin Infusion System] explode all trees |
| 5 | (continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion OR insulin pump OR artificial endocrine pancreas OR artificial beta cell OR CSII):ti,ab,kw |
| 6 | #4 OR #5 |
| 7 | (multiple daily injections OR MDI OR flexible multiple daily insulin OR FMDI OR multiple subcutaneous injections OR MSI OR intensive insulin therapy OR multiple injection regimens):ti,ab,kw |
| 8 | #6 AND #7 |
| 9 | Mesh descriptor:[Aged] explode all trees |
| 10 | (old* OR elderly OR senile OR aging OR senior citizen OR geriatric OR seniors OR older adult):ti,ab,kw |
| 11 | #9 OR #10 |
| 12 | Mesh descriptor:[Randomized Controlled Trial (Publication Type)] explode all trees |
| 13 | ("randomized controlled trial" ):pt |
| 14 | (randomised OR randomized OR controlled OR RCT OR randomly):ti,ab,kw |
| 15 | #12 OR #13 OR #14 |
| 16 | #3 AND #8 AND #11 AND #15 |
| 第一作者 | 年份(年) | 国家 | 样本量(试验组/对照组) | 患者年龄(试验组/对照组,岁) | 干预方法 | 干预时间 | 评价指标 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 对照组 | |||||||
| HERMAN[ | 2005 | 美国 | 48/50 | 66.6±5.9/66.2±4.5 | A | B | 12个月 | ①④ |
| 裴泂[ | 2007 | 中国 | 30/28 | 72.3±8.6/72.3±7.6 | A | D | 3个月 | ①②③④⑦ |
| 谢国庆[ | 2007 | 中国 | 16/15 | 71.0±6.0/72.0±8.0 | A | B | 3个月 | ①②③⑦ |
| 毛春谱[ | 2010 | 中国 | 17/19 | 71.4±8.9/70.8±9.8 | A | B | 1个月 | ①⑥⑦ |
| 杨秋伟[ | 2011 | 中国 | 28/28 | 71.8±8.1/69.1±8.5 | A | D | 2周 | ②③④⑥ |
| 傅明捷[ | 2013 | 中国 | 40/40 | 65.2±3.2/64.5±3.7 | A | B | 2周 | ①②③④⑥⑦ |
| 李思瓯[ | 2013 | 中国 | 25/23 | 71.8±8.3/71.4±8.1 | A | B | 3个月 | ①②③ |
| 张琦[ | 2013 | 中国 | 30/30 | 68±6/68±6 | A | B | 2周 | ②③⑥⑦ |
| 徐育良[ | 2014 | 中国 | 35/35 | 68.2±6.4/69.4±6.8 | A | B | 7 d | ②③ |
| 马丽辉[ | 2015 | 中国 | 40/40 | 65.7±5.5/66.6±6.3 | A | B | 2周 | ⑤ |
| 张雪云[ | 2016 | 中国 | 39/33 | 73.62±2.84/73.88±2.96 | A | B | 10~14 d | ⑤ |
| 孙世萌[ | 2017 | 中国 | 48/47 | 68.8±6.1/70.1±6.3 | A | B | 2周 | ②③ |
| 崔小伟[ | 2017 | 中国 | 35/35 | 67.8±3.6/69.1±2.8 | A | B | 10~14 d | ⑤ |
| 冯兰超[ | 2019 | 中国 | 42/42 | 67.34±5.26/66.40±5.32 | A | C | 30 d | ②③⑥ |
| 郎名丽[ | 2019 | 中国 | 45/45 | 70.5±2.7/71.3±2.3 | A | B | 2周 | ②③④⑥⑦ |
| 邱金梅[ | 2019 | 中国 | 50/50 | 71.85±10.29/72.13±10.34 | A | C | 4周 | ②③ |
表2 纳入研究的基本特征
Table 2 Basic characteristics of included RCTs
| 第一作者 | 年份(年) | 国家 | 样本量(试验组/对照组) | 患者年龄(试验组/对照组,岁) | 干预方法 | 干预时间 | 评价指标 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 对照组 | |||||||
| HERMAN[ | 2005 | 美国 | 48/50 | 66.6±5.9/66.2±4.5 | A | B | 12个月 | ①④ |
| 裴泂[ | 2007 | 中国 | 30/28 | 72.3±8.6/72.3±7.6 | A | D | 3个月 | ①②③④⑦ |
| 谢国庆[ | 2007 | 中国 | 16/15 | 71.0±6.0/72.0±8.0 | A | B | 3个月 | ①②③⑦ |
| 毛春谱[ | 2010 | 中国 | 17/19 | 71.4±8.9/70.8±9.8 | A | B | 1个月 | ①⑥⑦ |
| 杨秋伟[ | 2011 | 中国 | 28/28 | 71.8±8.1/69.1±8.5 | A | D | 2周 | ②③④⑥ |
| 傅明捷[ | 2013 | 中国 | 40/40 | 65.2±3.2/64.5±3.7 | A | B | 2周 | ①②③④⑥⑦ |
| 李思瓯[ | 2013 | 中国 | 25/23 | 71.8±8.3/71.4±8.1 | A | B | 3个月 | ①②③ |
| 张琦[ | 2013 | 中国 | 30/30 | 68±6/68±6 | A | B | 2周 | ②③⑥⑦ |
| 徐育良[ | 2014 | 中国 | 35/35 | 68.2±6.4/69.4±6.8 | A | B | 7 d | ②③ |
| 马丽辉[ | 2015 | 中国 | 40/40 | 65.7±5.5/66.6±6.3 | A | B | 2周 | ⑤ |
| 张雪云[ | 2016 | 中国 | 39/33 | 73.62±2.84/73.88±2.96 | A | B | 10~14 d | ⑤ |
| 孙世萌[ | 2017 | 中国 | 48/47 | 68.8±6.1/70.1±6.3 | A | B | 2周 | ②③ |
| 崔小伟[ | 2017 | 中国 | 35/35 | 67.8±3.6/69.1±2.8 | A | B | 10~14 d | ⑤ |
| 冯兰超[ | 2019 | 中国 | 42/42 | 67.34±5.26/66.40±5.32 | A | C | 30 d | ②③⑥ |
| 郎名丽[ | 2019 | 中国 | 45/45 | 70.5±2.7/71.3±2.3 | A | B | 2周 | ②③④⑥⑦ |
| 邱金梅[ | 2019 | 中国 | 50/50 | 71.85±10.29/72.13±10.34 | A | C | 4周 | ②③ |
| 第一作者 | 选择偏倚 | 分配隐藏 | 实施偏倚 | 测量偏倚 | 随访偏倚 | 报告偏倚 | 其他偏倚 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HERMAN[ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| 裴泂[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 谢国庆[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 毛春谱[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 杨秋伟[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 傅明捷[ | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 李思瓯[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 张琦[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| 徐育良[ | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 马丽辉[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| 张雪云[ | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 孙世萌[ | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| 崔小伟[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 冯兰超[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 郎名丽[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 邱金梅[ | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
表3 纳入文献的偏倚风险评估结果
Table 3 Risk of bias assessment for included RCTs
| 第一作者 | 选择偏倚 | 分配隐藏 | 实施偏倚 | 测量偏倚 | 随访偏倚 | 报告偏倚 | 其他偏倚 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HERMAN[ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| 裴泂[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 谢国庆[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 毛春谱[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 杨秋伟[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 傅明捷[ | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 李思瓯[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 张琦[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| 徐育良[ | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 马丽辉[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| 张雪云[ | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 孙世萌[ | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| 崔小伟[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 冯兰超[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 郎名丽[ | 不清楚 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
| 邱金梅[ | 低风险 | 不清楚 | 高风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不清楚 |
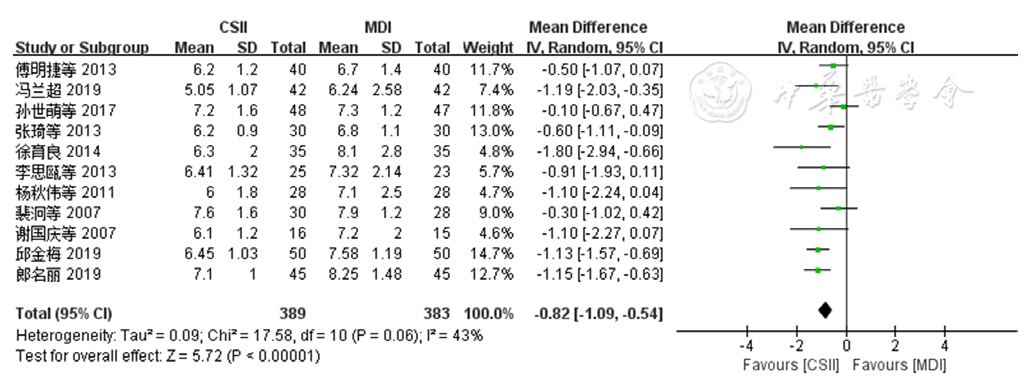
图2 两种胰岛素注射方法对老年T2DM患者FPG影响的森林图注:T2DM=2型糖尿病,MDI=每日多次皮下注射胰岛素,CSII=持续皮下胰岛素注射
Figure 2 Forest plot comparing the effectiveness of insulin administered by two methods on fasting plasma glucose among older adults with T2DM
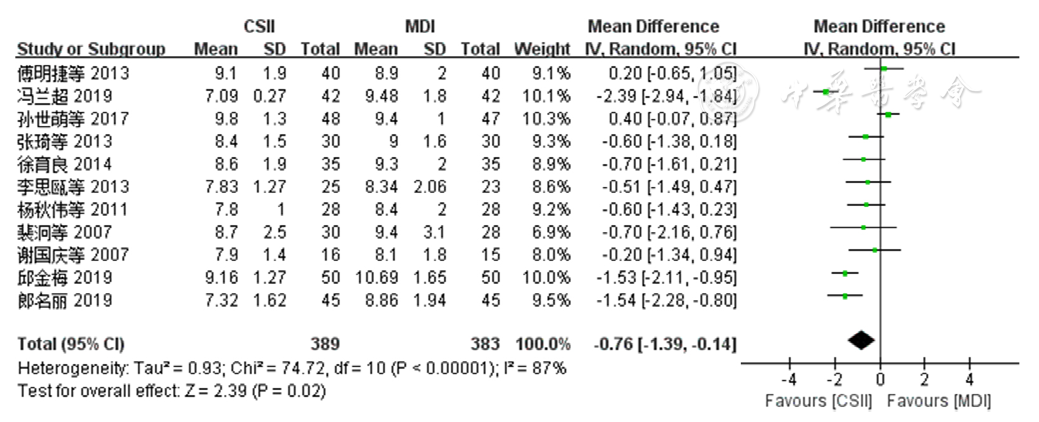
图3 两种胰岛素注射方法对老年T2DM患者2 hPG影响的森林图
Figure 3 Forest plot comparing the effectiveness of insulin administered by two methods on 2-hour postprandial plasma glucose among older adults with T2DM
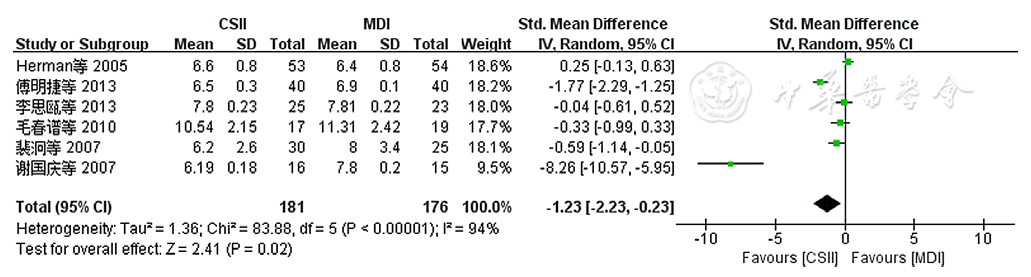
图4 两种胰岛素注射方法对老年T2DM患者HbA1c影响的森林图
Figure 4 Forest plot comparing the effectiveness of insulin administered by two methods on HbA1c among older adults with T2DM
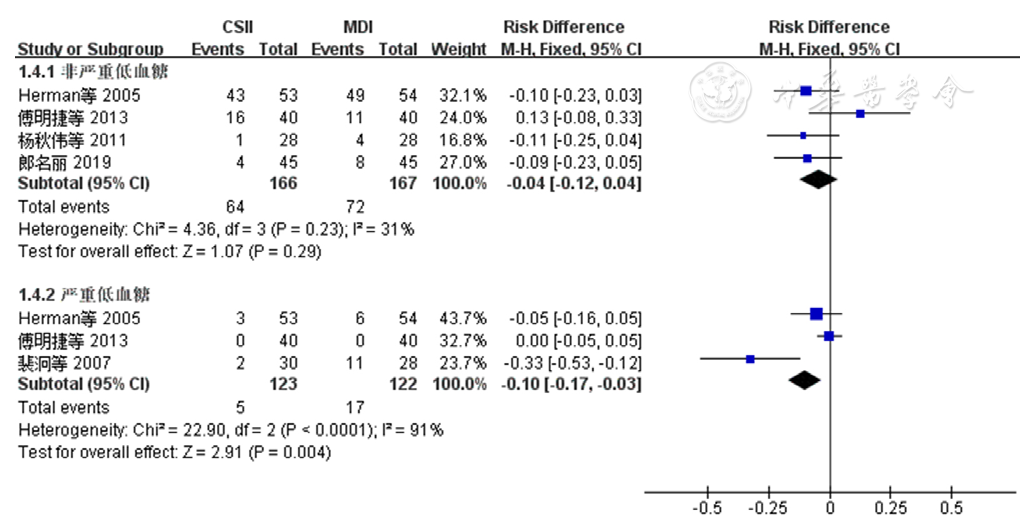
图5 两种胰岛素注射方法对老年T2DM患者低血糖发生率影响的森林图
Figure 5 Forest plot comparing the effectiveness of insulin administered by two methods on the incidence of hypoglycaemia among older adults with T2DM
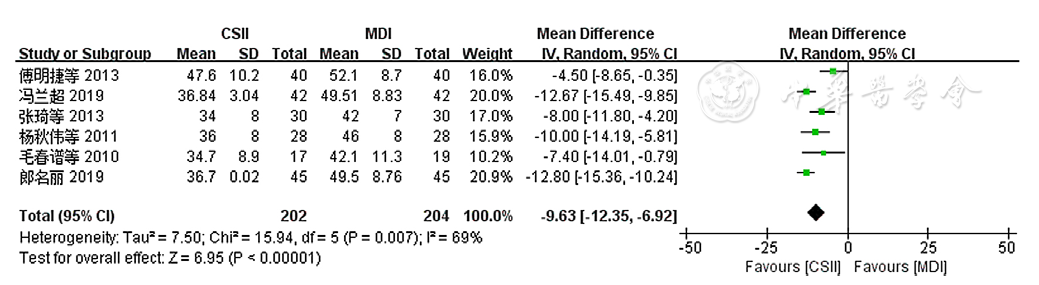
图6 两种注射方法对老年T2DM患者胰岛素日用量影响的森林图
Figure 6 Forest plot comparing the total daily dose of insulin administered by two methods among older adults with T2DM
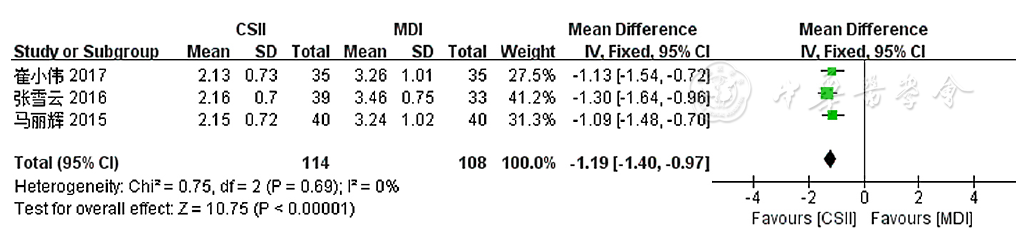
图7 两种注射方法对老年T2DM患者MAGE影响的森林图
Figure 7 Forest plot comparing the effectiveness of insulin administered by two methods on the mean amplitude of glycemic excursions among older adults with T2DM
| 血糖控制标准 | 研究数量 | MD(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 空腹血糖<7.8 mmol/L;餐后2 h血糖<11.1 mmol/L | 2[ | -4.99(-8.80,-1.18) | 0.010 |
| 空腹血糖<7 mmol/L;餐后2 h血糖<11.1 mmol/L | 1[ | -2.20(-3.14,-1.26) | <0.001 |
| 空腹血糖<7 mmoL/L;餐后2 h血糖<10.0 mmol/L | 3[ | -3.79(-5.94,-1.65) | 0.000 5 |
表4 两种注射方法对老年T2DM患者血糖达标时间的影响
Table 4 Effect of insulin administered by two methods on the time to reach the glycemic target among older adults with T2DM
| 血糖控制标准 | 研究数量 | MD(95%CI) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 空腹血糖<7.8 mmol/L;餐后2 h血糖<11.1 mmol/L | 2[ | -4.99(-8.80,-1.18) | 0.010 |
| 空腹血糖<7 mmol/L;餐后2 h血糖<11.1 mmol/L | 1[ | -2.20(-3.14,-1.26) | <0.001 |
| 空腹血糖<7 mmoL/L;餐后2 h血糖<10.0 mmol/L | 3[ | -3.79(-5.94,-1.65) | 0.000 5 |
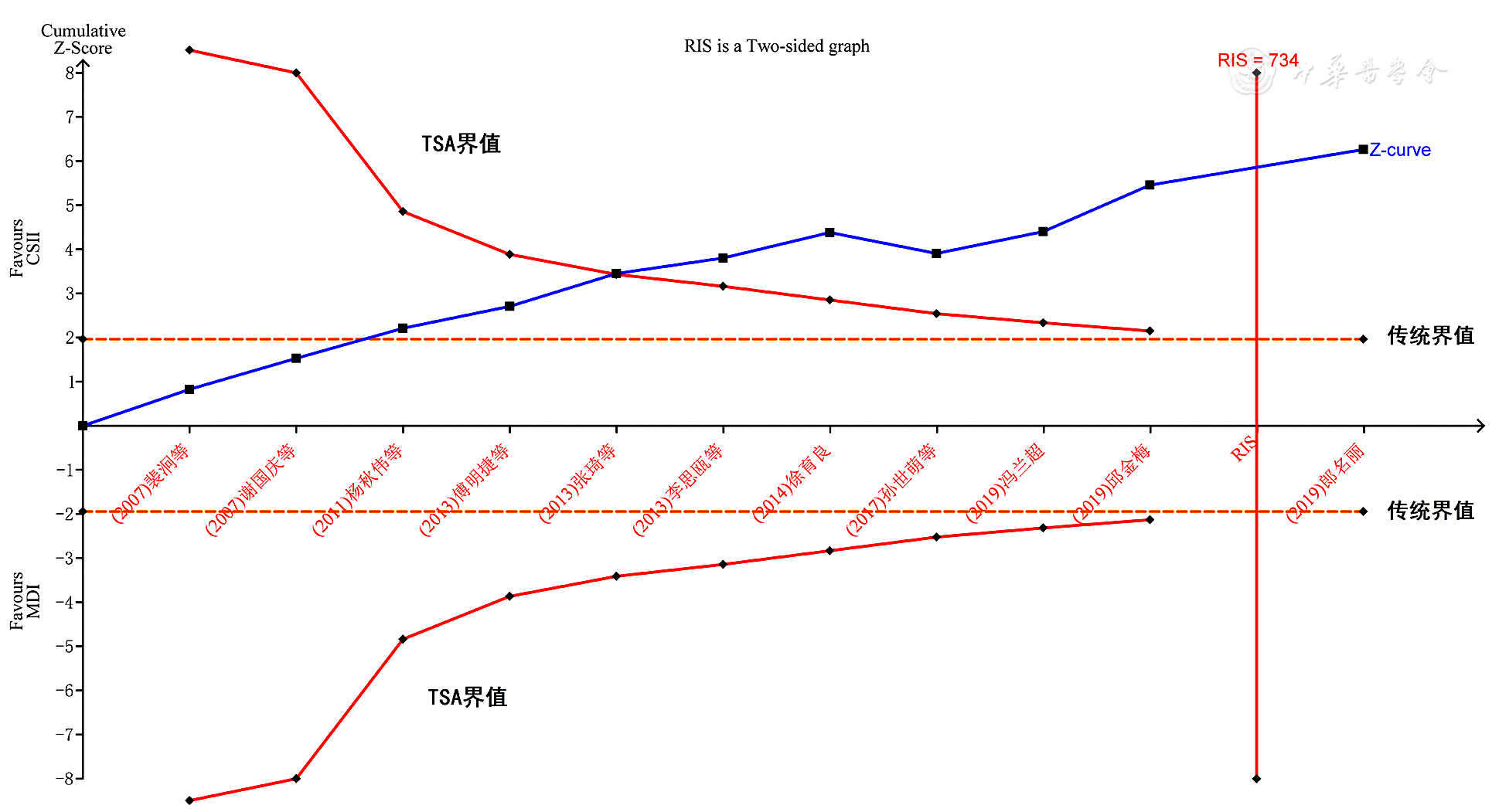
图8 两种注射方法对老年T2DM患者FPG影响的序贯分析
Figure 8 The trial sequential analysis of the effect of insulin administered by two methods on fasting plasma glucose among older adults with T2DM
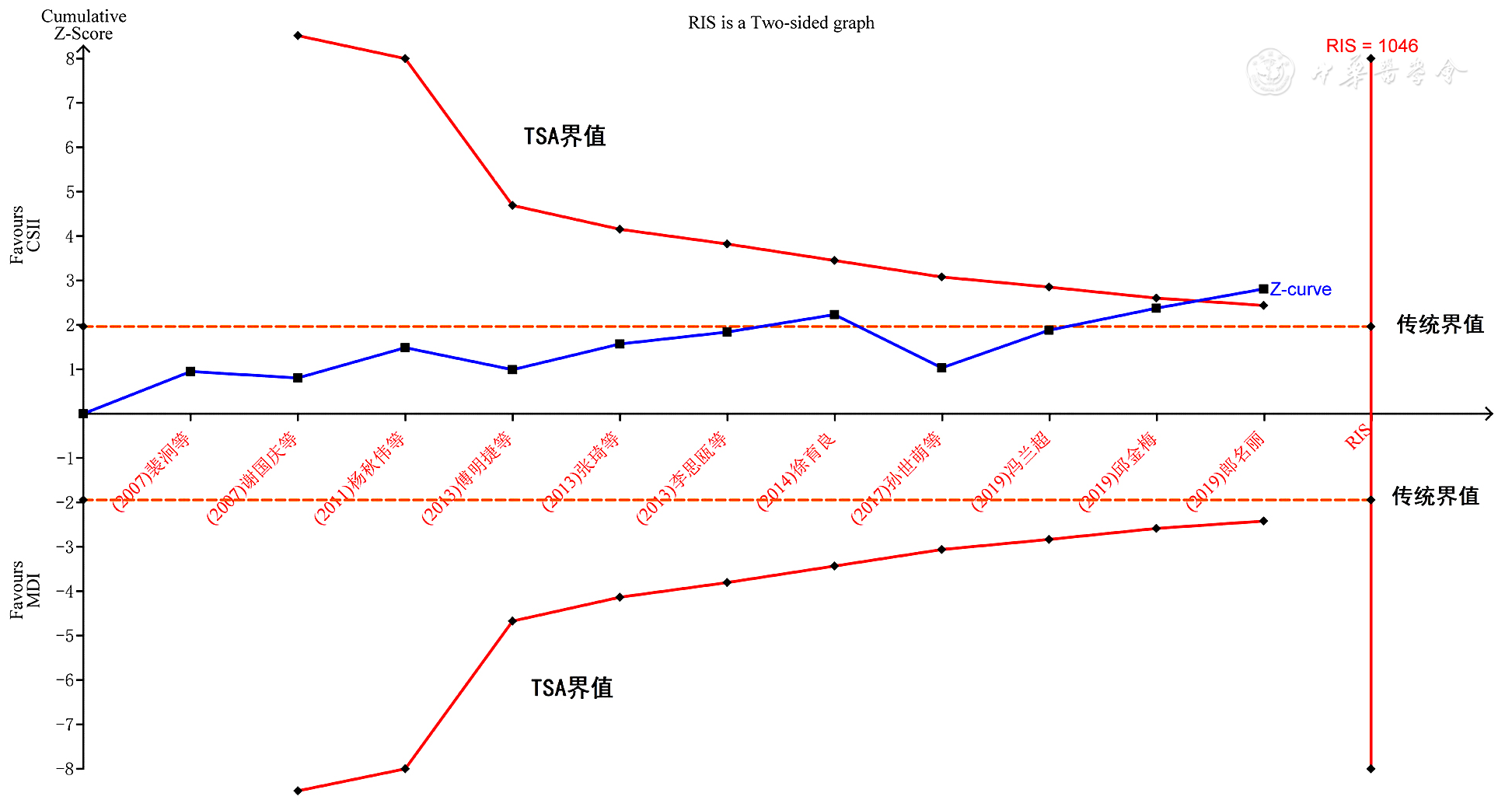
图9 两种注射方法对老年T2DM患者2 hPG影响的序贯分析
Figure 9 The trial sequential analysis of the effect of insulin administered by two methods on 2-hour postprandial plasma glucose among older adults with T2DM
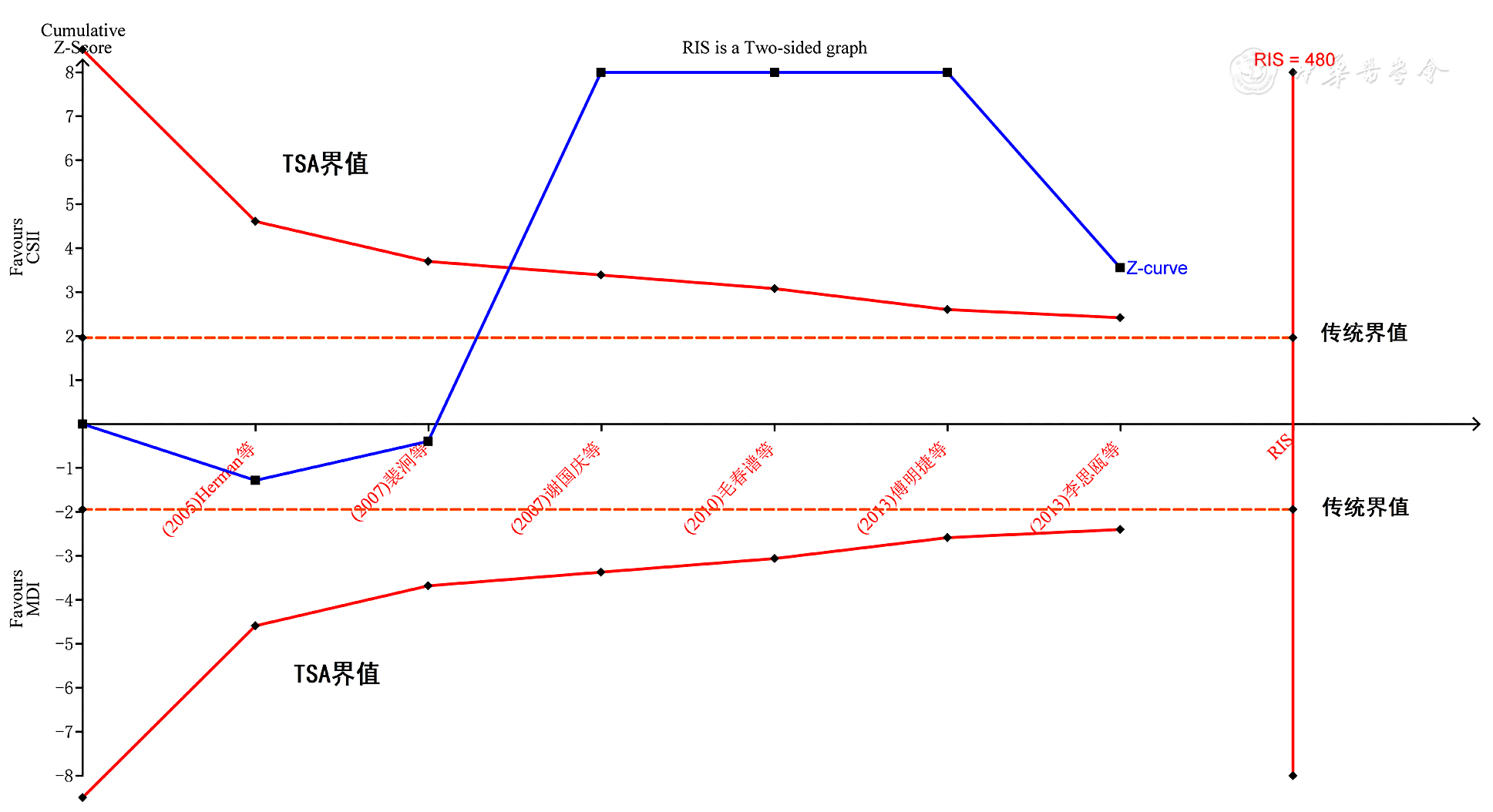
图10 两种注射方法对老年T2DM患者HbA1c影响的序贯分析
Figure 10 The trial sequential analysis of the effectiveness of insulin administered by two methods on HbA1c among older adults with T2DM
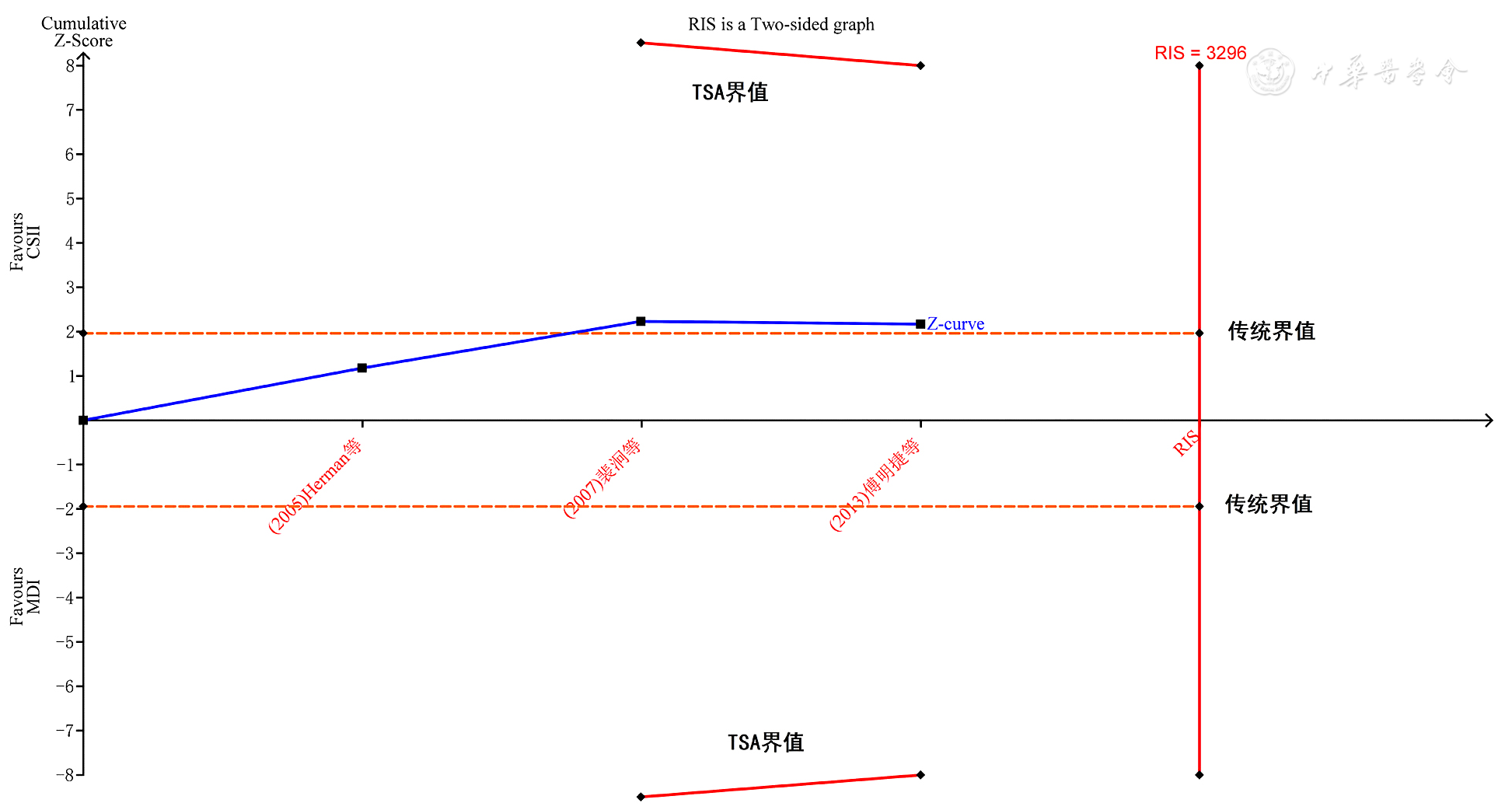
图11 两种注射方法对老年T2DM患者严重低血糖发生率影响序贯分析
Figure 11 The trial sequential analysis of the effectiveness of insulin administered by two methods on the incidence of severe hypoglycaemia among older adults with T2DM
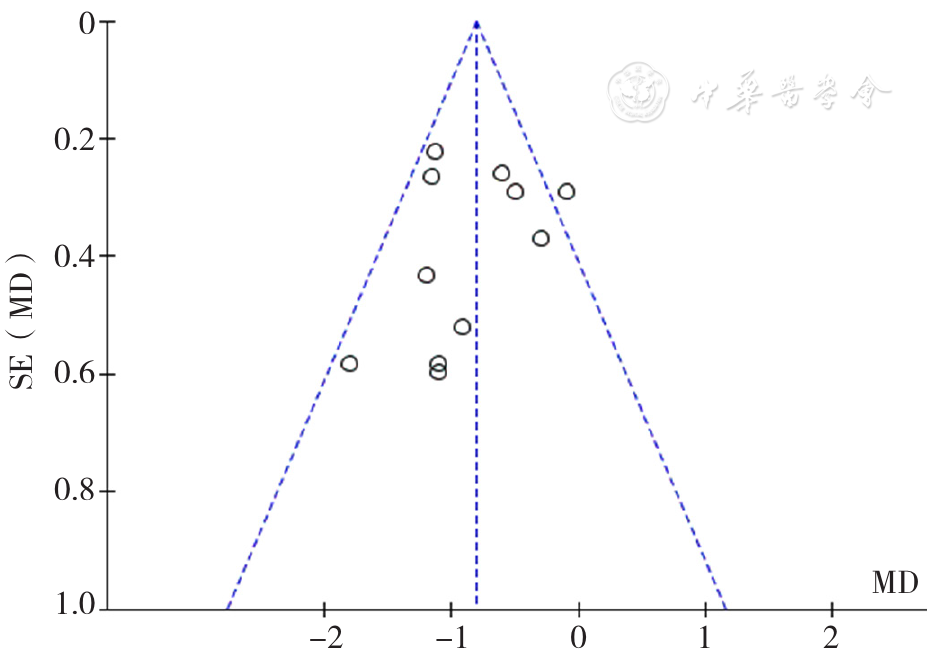
图12 FPG相关漏斗图
Figure 12 Funnel plot assessing potential publication bias in effectiveness of insulin administered by two methods on fasting plasma glucose among older adults with T2DM
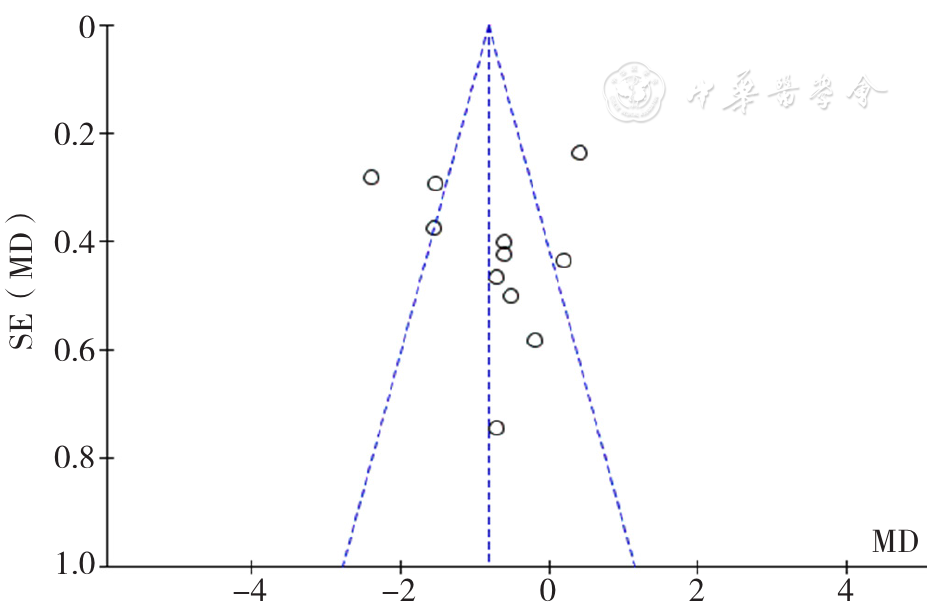
图13 2 hPG相关漏斗图
Figure 13 Funnel plot assessing potential publication bias in effectiveness of insulin administered by two methods on 2-hour postprandial plasma glucose among older adults with T2DM
| [1] |
International Diabetes Federation. About diabetes -Type 2 diabetes [EB/OL]. (2020-10-16) [2021-12-25].
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
NHS Digital. National diabetes audit report 1 care processes and treatment targets 2017-18[EB/OL].[2021-12-25].
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
《中国老年型糖尿病防治临床指南》编写组. 中国老年2型糖尿病防治临床指南(2022年版)[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志,2022,30(1):2-51. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6187.2022.01.002.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
中华医学会内分泌学分会,中华医学会糖尿病学分会,中国医师协会内分泌代谢科医师分会. 中国胰岛素泵治疗指南(2021年版)[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志,2021,37(8):679-701. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn311282-20210428-00265.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
国家老年医学中心,中华医学会老年医学分会,中国老年保健协会糖尿病专业委员会. 中国老年糖尿病诊疗指南(2021年版). 中华糖尿病杂志,2021,13(1):14-46. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn115791-20201209-00707.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
裴泂,陈正方,缪韦韦. 胰岛素泵治疗老年2型糖尿病的疗效观察[J]. 实用老年医学,2007,21(6):417-418. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-9198.2007.06.023.
|
| [16] |
谢国庆,孙梅芳,崔卫利,等.胰岛素泵治疗老年2型糖尿病的临床观察[J].中原医刊,2007,34(10):42-43. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-4756.2007.10.020.
|
| [17] |
毛春谱,李小毅,张红梅,等. 短期应用胰岛素泵治疗老年2型糖尿病19例临床分析[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2010,30(2):253-254. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2010.02.050.
|
| [18] |
杨秋伟,谢红伟,马明娟,等. 持续皮下输注赖脯胰岛素治疗老年非初诊2型糖尿病患者临床观察[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2011,11(18):3469-3471. DOI:10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2011.18.029.
|
| [19] |
傅明捷,黄萍,廖淑金,等.动态血糖监测系统联合胰岛素泵在老年2型糖尿病患者中的应用效果[J].广东医学,2013,34(20):3170-3172. DOI:10.13820/j.cnki.gdyx.2013.20.033.
|
| [20] |
李思瓯,梁爽,张忠敏. 采用胰岛素泵治疗老年2型糖尿病效果观察[J]. 中国药物经济学,2013,8(4):214-215. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5846.2013.04.109.
|
| [21] |
张琦,马红.胰岛素泵治疗老年2型糖尿病的临床观察[J].山西医药杂志(下半月刊),2013,42(8):904-905.
|
| [22] |
徐育良. 胰岛素泵和多次胰岛素皮下注射治疗老年2型糖尿病的疗效比较[J]. 中国处方药,2014,12(4):43-44.
|
| [23] |
马丽辉. 胰岛素泵强化治疗对老年2型糖尿病足患者血糖波动、氧化应激损伤的影响[J]. 解放军医药杂志,2015,27(4):48-52. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-140X.2015.04.013.
|
| [24] |
张雪云. 胰岛素泵强化治疗对老年2型糖尿病足患者血糖、氧化应激及溃疡愈合的影响[J]. 河南医学研究,2016,25(10):1844-1845.
|
| [25] |
孙世萌,汪艳芳,丁乐,等. 不同途径短期解除高糖毒性对老年2型糖尿病患者平衡功能的影响[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2017,27(27):59-63. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2017.27.011.
|
| [26] |
崔小伟. 胰岛素泵治疗对老年2型糖尿病足患者血糖波动及氧化应激损伤的影响[J]. 中国医疗器械信息,2017,23(18):75-76. DOI:10.15971/j.cnki.cmdi.2017.18.036.
|
| [27] |
冯兰超,孟丹丹. 胰岛素泵治疗老年糖尿病患者效果分析[J]. 全科口腔医学电子杂志,2019,6(21):174-175. DOI:10.16269/j.cnki.cn11-9337/r.2019.21.130.
|
| [28] |
郎名丽. 胰岛素泵在老年2型糖尿病患者中的临床疗效观察[J]. 中国现代药物应用,2019,13(12):87-89. DOI:10.14164/j.cnki.cn11-5581/r.2019.12.046.
|
| [29] |
邱金梅. 胰岛素泵强化治疗对老年2型糖尿病足患者氧化应激反应的影响[J]. 双足与保健,2019,28(20):79-80. DOI:10.19589/j.cnki.issn1004-6569.2019.20.079.
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
都汶妮. 糖尿病患者胰岛素笔注射后漏液相关因素及其护理的研究[D]. 芜湖:皖南医学院,2017.
|
| [32] | |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
中华医学会内分泌学分会. 糖尿病患者血糖波动管理专家共识[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志,2017,33(8):633-636. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.2017.08.002.
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
陈志军,高文远,王颖. 胰岛素泵治疗2型糖尿病的药物经济学评价[J]. 中国现代应用药学,2012,29(4):367-370. DOI:10.13748/j.cnki.issn1007-7693.2012.04.018.
|
| [46] |
|
| [1] | 许佳兰, 阎红, 文君, 周紫彤, 王思宇. 老年癌症患者潜在不适当用药发生率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3815-3822. |
| [2] | 李玲, 李雅萍, 钱时兴, 聂婧, 陆春华, 李霞. 社区中老年人认知功能影响因素及风险预测研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3773-3778. |
| [3] | 张天宇, 于海搏, 陈飞, 李新, 张佳佳, 詹晓凯, 申曼, 汤然, 范斯斌, 赵凤仪, 黄仲夏. POEMS综合征全身系统性治疗疗效和安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3447-3455. |
| [4] | 全家霖, 朱琳, 苏煜, 陈泽恺, 陈梓淇, 张卓凡. 运动方式对超重或肥胖儿童青少年执行功能改善效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3422-3431. |
| [5] | 张睿敏, 董哲毅, 李爽, 王倩, 陈香美. 基于肾活检病理诊断的糖尿病肾病中医相关因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3307-3313. |
| [6] | 崔宇阳, 程桂荣, 曾燕, 黄招兰, 谭伟. 社区老年人婚姻状况和社会支持及生活习惯与认知障碍的关联:基于湖北老年记忆队列基线调查[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3240-3247. |
| [7] | 燕芳红, 彭国恬, 张国莉, 孙瑞仪, 马玉霞, 韩琳. 医联体内老年慢性病管理内容的匹配分析:基于"指南-实践-需求"视角[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3119-3126. |
| [8] | 于文华, 李建国, 段文燕, 高旭妍, 李夏夏, 张子龙, 张丽, 马丽娜. 老年人功能受损评估量表在社区老年人中的信效度检验[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3000-3004. |
| [9] | 杨晨, 陈瞳, 张利方, 张洪旭, 李鹏飞, 张雪娟. 达格列净对老年乳腺癌幸存者射血分数保留的心力衰竭合并2型糖尿病患者的预后影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3053-3058. |
| [10] | 李嘉欣, 刘钟桧, 谢硕, 付志方, 孙丹, 焦红梅. 分解代谢及炎症状态的生物标志物变化趋势对老年患者慢性危重症的早期预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2993-2999. |
| [11] | 蒋世华, 朱政, 任盈盈, 朱垚磊, 王越, 高希彬. 中国儿童青少年近视患病率及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3043-3052. |
| [12] | 李浩, 李江涛, 刘丹, 王建军. 贝利尤单抗和阿尼鲁单抗及泰它西普治疗系统性红斑狼疮疗效和安全性的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2924-2933. |
| [13] | 王笑林, 李秋月, 周彦君, 张金辉, 梁涛. 转移性结直肠癌患者呋喹替尼治疗相关心血管毒性发生率和风险的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2934-2940. |
| [14] | 吴莎, 张代义, 李晋, 宣勤考, 钱晓东, 朱传武, 浦剑虹, 朱莉. 基于体检队列的代谢相关脂肪性肝病与高血糖关联及联合预测模型构建研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2861-2869. |
| [15] | 刘月影, 王雪丽, 刘雨秋, 魏立民. 空腹C肽与糖尿病病程比值与2型糖尿病发生代谢相关脂肪性肝病的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2852-2860. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





