中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (04): 504-511.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0497
所属专题: 内分泌代谢性疾病最新文章合辑; 骨健康最新文章合辑; 骨质疏松最新文章合辑
嵇星辰1, 王明欣2, 陈少华3, 高改1, 吴小婉1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-07-15
修回日期:2022-11-28
出版日期:2023-02-05
发布日期:2022-12-19
通讯作者:
吴小婉
基金资助:
JI Xingchen1, WANG Mingxin2, CHEN Shaohua3, GAO Gai1, WU Xiaowan1,*( )
)
Received:2022-07-15
Revised:2022-11-28
Published:2023-02-05
Online:2022-12-19
Contact:
WU Xiaowan
About author:摘要: 背景 糖尿病和骨质疏松均是中老年人的常见病,且糖尿病可导致多种急/慢性并发症,但糖尿病性骨骼改变常被忽略。女性绝经后患骨质疏松较为普遍,绝经后2型糖尿病患者更是具有多种合并骨质疏松的危险因素,因此早期识别这些因素并开展针对性干预十分必要。 目的 探讨我国绝经后2型糖尿病患者骨质疏松的影响因素。 方法 于2021年7月,计算机检索中国知网、维普网、万方数据知识服务平台、中国生物医学文献数据库、PubMed、EmBase、the Cochrane Library数据库,获取与我国绝经后2型糖尿病患者骨质疏松影响因素相关的文献,检索时间设定为从建库至2021年7月。由2名研究员独自进行文献筛选及数据提取,采用RevMan 5.4软件及Stata 15.0统计软件对数据结果进行Meta分析。 结果 最终纳入21篇研究,提取出11个影响因素。Meta分析结果显示:年龄〔MD(95%CI)=6.56(5.24,7.88)〕、绝经年限〔MD(95%CI)=5.93(4.23,7.62)〕、糖尿病病程〔MD(95%CI)=1.94(0.89,2.98)〕、体质指数〔MD(95%CI)=-1.99(-2.63,-1.36)〕、血清钙〔MD(95%CI)=0.03(0.01,0.06)〕、空腹血糖〔MD(95%CI)=0.49(0.09,0.90)〕、糖化血红蛋白〔MD(95%CI)=0.37(0.02,0.71)〕、空腹胰岛素〔MD(95%CI)=3.65(1.24,6.06)〕是我国绝经后2型糖尿病患者合并骨质疏松的影响因素(P<0.05);血肌酐〔MD(95%CI)=4.02(0.00,8.04)〕、血清磷〔MD(95%CI)=0.00(-0.05,0.05)〕、碱性磷酸酶〔MD(95%CI)=1.26(-0.06,2.57)〕对我国绝经后2型糖尿病患者合并骨质疏松的影响无统计学意义(P>0.05)。敏感性分析结果显示:除血肌酐外,其他因素的结果均较稳定。 结论 年龄、绝经年限、糖尿病病程、BMI、血清钙、空腹胰岛素、空腹血糖、糖化血红蛋白是我国2型糖尿病患者合并骨质疏松的影响因素,而血肌酐、血清磷、碱性磷酸酶对我国绝经后2型糖尿病患者合并骨质疏松的影响还需进一步论证。
| 作者 | 年份(年) | 地区 | 研究类型 | 年龄(岁) | 绝经年限(年) | 研究时段 | 样本量 | 影响因素 | 检测部位 | 质量评价(分) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 周友俊等[ | 2010 | 昆明市 | 病例对照研究 | 病例组:65±10 对照组:57±10 | ≥1a | — | 病例组:72 对照组:70 | ①④⑥⑦ ⑧⑨⑩⑪ | L1~4、股骨颈、Wards三角、大转子、髋部 | 6 |
| 征海华等[ | 2010 | 上海市 | 病例对照研究 | 病例组:72.3±7.9 对照组:65.8±10.9 | ≥5a | — | 病例组:136 对照组:152 | ①②④⑤ ⑥⑧⑦⑩ | L1~4 | 6 |
| 张建民[ | 2014 | 马鞍山市 | 病例对照研究 | 57.3±6.2a | 8.4±4.2a | — | 病例组:23 对照组:18 | ④⑥⑧⑩ | L1~4、左侧股骨 | 6 |
| 应蓉等[ | 2017 | 上海市 | 病例对照研究 | 70.81±10.95a | 病例组:27.41±9.18 对照组:16.65±11.38 | 2015年1月至2016年8月 | 病例组:43 对照组:47 | ①②③④⑤ ⑥⑦⑧⑩ | 右髋关节 | 6 |
| 王瑜等[ | 2021 | 台州市 | 病例对照研究 | 67.77±7.14a | 49.60±3.31a | 2017年1月至2019年11月 | 病例组:147 对照组:202 | ①②③④ ⑥⑦⑧ | 股骨颈、大转子、腰椎 | 7 |
| 王燕等[ | 2011 | 河北省 | 病例对照研究 | 62.5±13.6a | 1~14a | — | 病例组:81 对照组:33 | ①②③④ ⑦⑨⑩ | L2~4、股骨颈、大转子、粗隆间 | 7 |
| 王小华等[ | 2014 | 河北省 | 病例对照研究 | 54±5a | 6±3a | 2011—2013年 | 病例组:58 对照组:62 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | 腰椎正位、左侧股骨颈、Wards三角、股骨粗隆 | 6 |
| 林珊珊等[ | 2019 | 北京市 | 病例对照研究 | 病例组:57.32±2.04 对照组:49.27±1.87 | — | 2016年2月至2018年2月 | 病例组:50 对照组:50 | ①⑧ | L1~4,双侧股骨 | 6 |
| 黄银琼等[ | 2019 | 福建省 | 病例对照研究 | 61.8±7.5a | >1a | 2016年8月至2018年12月 | 病例组:31 对照组:22 | ① | 髋部、股骨颈 | 6 |
| 何丽等[ | 2019 | 郑州市 | 横断面研究 | 64.35±8.56a | — | 2016年8月至2017年8月 | 病例组:544 对照组:138 | ①③④ ⑤⑦⑪ | 腰椎、股骨颈、全髋 | 6b |
| 马剑侠等[ | 2016 | 河北省 | 病例对照研究 | 病例组:64.3±10.1 对照组:62.1±9.5 | — | 2012年1月至2014年10月 | 病例组:60 对照组:68 | ①③④⑦⑧ | L1~4、双侧股骨 | 7 |
| 巩伟伟等[ | 2018 | 上海市 | 病例对照研究 | 55.3±4.51a | 5.46±3.16a | 2016年6月至2017年5月 | 病例组:43 对照组:40 | ①②③④⑤⑧⑪ | L1~4,股骨颈 | 7 |
| 陈雪等[ | 2018 | 温州市 | 病例对照研究 | 病例组:68.09±9.62 对照组:61.06±10.88 | 病例组:18.22±11.44 对照组:11.22±9.07 | 2015年10月至2016年11月 | 病例组:100 对照组:51 | ①②③ ④⑤ | L1~4、股骨颈、股骨转子、股骨内部、股骨Wards三角 | 6 |
| 征海华等[ | 2011 | 上海市 | 病例对照研究 | 病例组:72.59±8.83 对照组:65.65±11.42 | ≥5a | 2008年6月至2010年6月 | 病例组:147 对照组:153 | ①②④ ⑤⑦⑧ | — | 7 |
| 李琪等[ | 2018 | 遵义市 | 病例对照研究 | 50~75a | 2~14a | 2016年12月至2017年11月 | 病例组:45 对照组:40 | ①②③ ④⑧ | L1~4、股骨颈、Wards三角、大转子 | 7 |
| 吕晓双等[ | 2021 | 无锡市 | 病例对照研究 | 47~85a | 2~30a | 2018年8月至2019年12月 | 病例组:90 对照组:88 | ①④⑥⑧ | 腰椎、股骨颈、全髋 | 6 |
| 赖春红[ | 2020 | 江西省 | 病例对照研究 | 67.55±7.36a | 18(14,22)a | 2018年12月至2019年12月 | 病例组:114 对照组:25 | ①④ | L1~4、全髋、股骨颈 | 7 |
| 姜璐[ | 2017 | 山东省 | 病例对照研究 | 病例组:68.23±7.79 对照组:56.92±6.85 | 病例组:19.69±8.75 对照组:7.64±6.85 | 2014年10月至2016年12月 | 病例组:159 对照组:75 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | L1~4、全髋、股骨颈、Wards三角、大转子 | 7 |
| ZHAO等[ | 2020 | 北京市 | 横断面研究 | 63.65±7.9a | — | 2017年1月至2019年12月 | 病例组:99 对照组:41 | ①②③④ ⑥⑦⑧ | 髋部、腰椎 | 7b |
| ZHOU等[ | 2017 | 西藏自治区 | 病例对照研究 | 61±8a | >1a | — | 病例组:27 对照组:30 | ①④⑧ | 脊柱、股骨颈、髋部 | 6 |
| CHEN等[ | 2018 | 台湾地区 | 病例对照研究 | 60.7±6.9a | — | 2014年9月至2015年8月 | 病例组:37 对照组:105 | ①③④⑧ | 髋部、腰椎 | 7 |
表1 纳入文献的基本特征及质量评价
Table 1 Essential information and quality evaluation of included literature
| 作者 | 年份(年) | 地区 | 研究类型 | 年龄(岁) | 绝经年限(年) | 研究时段 | 样本量 | 影响因素 | 检测部位 | 质量评价(分) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 周友俊等[ | 2010 | 昆明市 | 病例对照研究 | 病例组:65±10 对照组:57±10 | ≥1a | — | 病例组:72 对照组:70 | ①④⑥⑦ ⑧⑨⑩⑪ | L1~4、股骨颈、Wards三角、大转子、髋部 | 6 |
| 征海华等[ | 2010 | 上海市 | 病例对照研究 | 病例组:72.3±7.9 对照组:65.8±10.9 | ≥5a | — | 病例组:136 对照组:152 | ①②④⑤ ⑥⑧⑦⑩ | L1~4 | 6 |
| 张建民[ | 2014 | 马鞍山市 | 病例对照研究 | 57.3±6.2a | 8.4±4.2a | — | 病例组:23 对照组:18 | ④⑥⑧⑩ | L1~4、左侧股骨 | 6 |
| 应蓉等[ | 2017 | 上海市 | 病例对照研究 | 70.81±10.95a | 病例组:27.41±9.18 对照组:16.65±11.38 | 2015年1月至2016年8月 | 病例组:43 对照组:47 | ①②③④⑤ ⑥⑦⑧⑩ | 右髋关节 | 6 |
| 王瑜等[ | 2021 | 台州市 | 病例对照研究 | 67.77±7.14a | 49.60±3.31a | 2017年1月至2019年11月 | 病例组:147 对照组:202 | ①②③④ ⑥⑦⑧ | 股骨颈、大转子、腰椎 | 7 |
| 王燕等[ | 2011 | 河北省 | 病例对照研究 | 62.5±13.6a | 1~14a | — | 病例组:81 对照组:33 | ①②③④ ⑦⑨⑩ | L2~4、股骨颈、大转子、粗隆间 | 7 |
| 王小华等[ | 2014 | 河北省 | 病例对照研究 | 54±5a | 6±3a | 2011—2013年 | 病例组:58 对照组:62 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | 腰椎正位、左侧股骨颈、Wards三角、股骨粗隆 | 6 |
| 林珊珊等[ | 2019 | 北京市 | 病例对照研究 | 病例组:57.32±2.04 对照组:49.27±1.87 | — | 2016年2月至2018年2月 | 病例组:50 对照组:50 | ①⑧ | L1~4,双侧股骨 | 6 |
| 黄银琼等[ | 2019 | 福建省 | 病例对照研究 | 61.8±7.5a | >1a | 2016年8月至2018年12月 | 病例组:31 对照组:22 | ① | 髋部、股骨颈 | 6 |
| 何丽等[ | 2019 | 郑州市 | 横断面研究 | 64.35±8.56a | — | 2016年8月至2017年8月 | 病例组:544 对照组:138 | ①③④ ⑤⑦⑪ | 腰椎、股骨颈、全髋 | 6b |
| 马剑侠等[ | 2016 | 河北省 | 病例对照研究 | 病例组:64.3±10.1 对照组:62.1±9.5 | — | 2012年1月至2014年10月 | 病例组:60 对照组:68 | ①③④⑦⑧ | L1~4、双侧股骨 | 7 |
| 巩伟伟等[ | 2018 | 上海市 | 病例对照研究 | 55.3±4.51a | 5.46±3.16a | 2016年6月至2017年5月 | 病例组:43 对照组:40 | ①②③④⑤⑧⑪ | L1~4,股骨颈 | 7 |
| 陈雪等[ | 2018 | 温州市 | 病例对照研究 | 病例组:68.09±9.62 对照组:61.06±10.88 | 病例组:18.22±11.44 对照组:11.22±9.07 | 2015年10月至2016年11月 | 病例组:100 对照组:51 | ①②③ ④⑤ | L1~4、股骨颈、股骨转子、股骨内部、股骨Wards三角 | 6 |
| 征海华等[ | 2011 | 上海市 | 病例对照研究 | 病例组:72.59±8.83 对照组:65.65±11.42 | ≥5a | 2008年6月至2010年6月 | 病例组:147 对照组:153 | ①②④ ⑤⑦⑧ | — | 7 |
| 李琪等[ | 2018 | 遵义市 | 病例对照研究 | 50~75a | 2~14a | 2016年12月至2017年11月 | 病例组:45 对照组:40 | ①②③ ④⑧ | L1~4、股骨颈、Wards三角、大转子 | 7 |
| 吕晓双等[ | 2021 | 无锡市 | 病例对照研究 | 47~85a | 2~30a | 2018年8月至2019年12月 | 病例组:90 对照组:88 | ①④⑥⑧ | 腰椎、股骨颈、全髋 | 6 |
| 赖春红[ | 2020 | 江西省 | 病例对照研究 | 67.55±7.36a | 18(14,22)a | 2018年12月至2019年12月 | 病例组:114 对照组:25 | ①④ | L1~4、全髋、股骨颈 | 7 |
| 姜璐[ | 2017 | 山东省 | 病例对照研究 | 病例组:68.23±7.79 对照组:56.92±6.85 | 病例组:19.69±8.75 对照组:7.64±6.85 | 2014年10月至2016年12月 | 病例组:159 对照组:75 | ①②③ ④⑦⑧ | L1~4、全髋、股骨颈、Wards三角、大转子 | 7 |
| ZHAO等[ | 2020 | 北京市 | 横断面研究 | 63.65±7.9a | — | 2017年1月至2019年12月 | 病例组:99 对照组:41 | ①②③④ ⑥⑦⑧ | 髋部、腰椎 | 7b |
| ZHOU等[ | 2017 | 西藏自治区 | 病例对照研究 | 61±8a | >1a | — | 病例组:27 对照组:30 | ①④⑧ | 脊柱、股骨颈、髋部 | 6 |
| CHEN等[ | 2018 | 台湾地区 | 病例对照研究 | 60.7±6.9a | — | 2014年9月至2015年8月 | 病例组:37 对照组:105 | ①③④⑧ | 髋部、腰椎 | 7 |
| 影响因素 | 纳入文献(篇) | 异质性检验 | 效应模型 | Meta分析结果〔MD(95%CI)〕 | Z值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2(%) | P值 | ||||||
| 年龄 | 20[ | 85 | <0.01 | 随机 | 6.56(5.24,7.88) | 9.74 | <0.01 |
| 绝经年限 | 11[ | 90 | <0.01 | 随机 | 5.93(4.23,7.62) | 6.84 | <0.01 |
| 糖尿病病程 | 12[ | 75 | <0.01 | 随机 | 1.94(0.89,2.98) | 3.64 | <0.01 |
| BMI | 19[ | 88 | <0.01 | 随机 | -1.99(-2.63,-1.36) | 6.20 | <0.01 |
| 血清钙 | 7[ | 41 | 0.12 | 固定 | 0.03(0.01,0.07) | 2.98 | <0.01 |
| 血肌酐 | 6[ | 77 | <0.01 | 随机 | 4.02(0.00,8.04) | 1.96 | 0.05 |
| 空腹血糖 | 11[ | 60 | <0.01 | 随机 | 0.49(0.09,0.90) | 2.37 | 0.02 |
| 糖化血红蛋白 | 16[ | 73 | <0.01 | 随机 | 0.37(0.02,0.71) | 2.08 | 0.04 |
| 空腹胰岛素 | 2[ | 48 | 0.16 | 固定 | 3.65(1.24,6.06) | 2.97 | <0.01 |
| 血清磷 | 4[ | 54 | 0.09 | 随机 | 0.00(-0.05,0.05) | 0.05 | 0.96 |
| 碱性磷酸酶 | 3[ | 38 | 0.20 | 固定 | 1.26(-0.06,2.57) | 1.88 | 0.06 |
表2 我国绝经后2型糖尿病患者骨质疏松影响因素的Meta分析结果
Table 2 Meta-analysis of associated factors for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes in China
| 影响因素 | 纳入文献(篇) | 异质性检验 | 效应模型 | Meta分析结果〔MD(95%CI)〕 | Z值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2(%) | P值 | ||||||
| 年龄 | 20[ | 85 | <0.01 | 随机 | 6.56(5.24,7.88) | 9.74 | <0.01 |
| 绝经年限 | 11[ | 90 | <0.01 | 随机 | 5.93(4.23,7.62) | 6.84 | <0.01 |
| 糖尿病病程 | 12[ | 75 | <0.01 | 随机 | 1.94(0.89,2.98) | 3.64 | <0.01 |
| BMI | 19[ | 88 | <0.01 | 随机 | -1.99(-2.63,-1.36) | 6.20 | <0.01 |
| 血清钙 | 7[ | 41 | 0.12 | 固定 | 0.03(0.01,0.07) | 2.98 | <0.01 |
| 血肌酐 | 6[ | 77 | <0.01 | 随机 | 4.02(0.00,8.04) | 1.96 | 0.05 |
| 空腹血糖 | 11[ | 60 | <0.01 | 随机 | 0.49(0.09,0.90) | 2.37 | 0.02 |
| 糖化血红蛋白 | 16[ | 73 | <0.01 | 随机 | 0.37(0.02,0.71) | 2.08 | 0.04 |
| 空腹胰岛素 | 2[ | 48 | 0.16 | 固定 | 3.65(1.24,6.06) | 2.97 | <0.01 |
| 血清磷 | 4[ | 54 | 0.09 | 随机 | 0.00(-0.05,0.05) | 0.05 | 0.96 |
| 碱性磷酸酶 | 3[ | 38 | 0.20 | 固定 | 1.26(-0.06,2.57) | 1.88 | 0.06 |
| 影响因素 | 合并分析结果 | 改变模型分析结果 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 效应模型 | MD(95%CI) | P值 | 效应模型 | MD(95%CI) | P值 | |
| 年龄 | 随机 | 6.56(5.24,7.88) | <0.01 | 固定 | 7.15(6.69,7.60) | <0.01 |
| 绝经年限 | 随机 | 5.93(4.23,7.62) | <0.01 | 固定 | 4.96(4.46,5.46) | <0.01 |
| 糖尿病病程 | 随机 | 1.94(0.89,2.98) | <0.01 | 固定 | 2.11(1.64,2.59) | <0.01 |
| BMI | 随机 | -1.99(-2.63,-1.36) | <0.01 | 固定 | -2.24(-2.45,-2.04) | <0.01 |
| 血清钙 | 固定 | 0.03(0.01,0.06) | <0.01 | 随机 | 0.04(0.00,0.07) | 0.03 |
| 血肌酐 | 随机 | 4.02(0.00,8.04) | 0.05 | 固定 | 1.47(0.91,2.04) | <0.01 |
| 空腹血糖 | 随机 | 0.49(0.09,0.90) | 0.02 | 固定 | 0.38(0.15,0.61) | <0.01 |
| 糖化血红蛋白 | 随机 | 0.37(0.02,0.71) | 0.04 | 固定 | 0.35(0.19,0.52) | <0.01 |
| 空腹胰岛素 | 固定 | 3.65(1.24,6.06) | <0.01 | 随机 | 3.68(0.33,7.03) | 0.03 |
| 血清磷 | 随机 | 0.00(-0.05,0.05) | 0.96 | 固定 | 0.00(-0.03,0.03) | 0.97 |
| 碱性磷酸酶 | 固定 | 1.26(-0.06,2.57) | 0.06 | 固定 | 2.89(-1.25,7.04) | 0.17 |
表3 我国绝经后2型糖尿病患者骨质疏松影响因素的敏感性分析结果
Table 3 Sensitivity analysis of the effects of associated factors on osteoporosis in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes in China
| 影响因素 | 合并分析结果 | 改变模型分析结果 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 效应模型 | MD(95%CI) | P值 | 效应模型 | MD(95%CI) | P值 | |
| 年龄 | 随机 | 6.56(5.24,7.88) | <0.01 | 固定 | 7.15(6.69,7.60) | <0.01 |
| 绝经年限 | 随机 | 5.93(4.23,7.62) | <0.01 | 固定 | 4.96(4.46,5.46) | <0.01 |
| 糖尿病病程 | 随机 | 1.94(0.89,2.98) | <0.01 | 固定 | 2.11(1.64,2.59) | <0.01 |
| BMI | 随机 | -1.99(-2.63,-1.36) | <0.01 | 固定 | -2.24(-2.45,-2.04) | <0.01 |
| 血清钙 | 固定 | 0.03(0.01,0.06) | <0.01 | 随机 | 0.04(0.00,0.07) | 0.03 |
| 血肌酐 | 随机 | 4.02(0.00,8.04) | 0.05 | 固定 | 1.47(0.91,2.04) | <0.01 |
| 空腹血糖 | 随机 | 0.49(0.09,0.90) | 0.02 | 固定 | 0.38(0.15,0.61) | <0.01 |
| 糖化血红蛋白 | 随机 | 0.37(0.02,0.71) | 0.04 | 固定 | 0.35(0.19,0.52) | <0.01 |
| 空腹胰岛素 | 固定 | 3.65(1.24,6.06) | <0.01 | 随机 | 3.68(0.33,7.03) | 0.03 |
| 血清磷 | 随机 | 0.00(-0.05,0.05) | 0.96 | 固定 | 0.00(-0.03,0.03) | 0.97 |
| 碱性磷酸酶 | 固定 | 1.26(-0.06,2.57) | 0.06 | 固定 | 2.89(-1.25,7.04) | 0.17 |
| 影响因素 | 排除文献 | 排除前 | 排除后 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 效应模型 | MD(95%CI) | P值 | 效应模型 | MD(95%CI) | P值 | ||
| 年龄 | [ | 随机 | 6.56(5.24,7.88) | <0.01 | 随机 | 6.17(5.05,7.30) | <0.01 |
| 绝经年限 | [ | 随机 | 5.93(4.23,7.62) | <0.01 | 随机 | 5.64(4.41,6.87) | <0.01 |
| 糖尿病病程 | [ | 随机 | 1.94(0.89,2.98) | <0.01 | 随机 | 2.36(1.56,3.15) | <0.01 |
| BMI | [ | 随机 | -1.99(-2.63,-1.36) | <0.01 | 随机 | -1.84(-2.24,-1.45) | <0.01 |
| 空腹血糖 | [ | 随机 | 0.49(0.09,0.90) | 0.02 | 固定 | 0.48(0.24,0.73) | <0.01 |
| 糖化血红蛋白 | [ | 随机 | 0.37(0.02,0.71) | 0.04 | 随机 | 0.44(0.10,0.79) | 0.01 |
表4 我国绝经后2型糖尿病患者骨质疏松影响因素的排除分析结果
Table 4 Exclusion analysis of associated factors for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes in China
| 影响因素 | 排除文献 | 排除前 | 排除后 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 效应模型 | MD(95%CI) | P值 | 效应模型 | MD(95%CI) | P值 | ||
| 年龄 | [ | 随机 | 6.56(5.24,7.88) | <0.01 | 随机 | 6.17(5.05,7.30) | <0.01 |
| 绝经年限 | [ | 随机 | 5.93(4.23,7.62) | <0.01 | 随机 | 5.64(4.41,6.87) | <0.01 |
| 糖尿病病程 | [ | 随机 | 1.94(0.89,2.98) | <0.01 | 随机 | 2.36(1.56,3.15) | <0.01 |
| BMI | [ | 随机 | -1.99(-2.63,-1.36) | <0.01 | 随机 | -1.84(-2.24,-1.45) | <0.01 |
| 空腹血糖 | [ | 随机 | 0.49(0.09,0.90) | 0.02 | 固定 | 0.48(0.24,0.73) | <0.01 |
| 糖化血红蛋白 | [ | 随机 | 0.37(0.02,0.71) | 0.04 | 随机 | 0.44(0.10,0.79) | 0.01 |
| 影响因素 | t值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 1.00 | 0.33 |
| 绝经年限 | 1.25 | 0.24 |
| 糖尿病病程 | -0.21 | 0.84 |
| BMI | -0.63 | 0.54 |
| 血清钙 | -1.15 | 0.30 |
| 血肌酐 | 0.61 | 0.59 |
| 空腹血糖 | 0.27 | 0.79 |
| 糖化血红蛋白 | -0.04 | 0.97 |
表5 我国绝经后2型糖尿病患者骨质疏松影响因素的发表偏倚分析
Table 5 Analysis of publication bias in studies about associated factors for osteoporosis in Chinese postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes
| 影响因素 | t值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 1.00 | 0.33 |
| 绝经年限 | 1.25 | 0.24 |
| 糖尿病病程 | -0.21 | 0.84 |
| BMI | -0.63 | 0.54 |
| 血清钙 | -1.15 | 0.30 |
| 血肌酐 | 0.61 | 0.59 |
| 空腹血糖 | 0.27 | 0.79 |
| 糖化血红蛋白 | -0.04 | 0.97 |
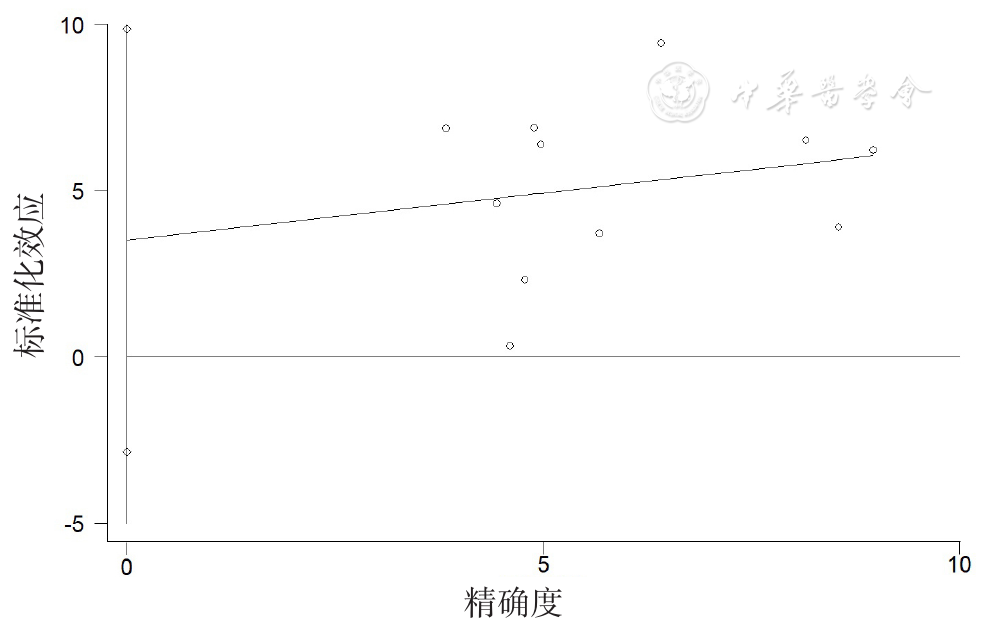
图2 我国绝经后2型糖尿病患者绝经年限对骨质疏松影响的Egger's发表偏倚
Figure 2 Egger's test detecting the publication bias in studies about the effect of years of postmenopause on osteoporosis in Chinese postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes
| [1] |
中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2021,13(4):315-409. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn115791-20210221-00095.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
王小华,王宇强,陈长香,等. 老年人群骨质疏松的影响因素分析[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(9):1107-1111. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2015.09.018.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
中华医学会糖尿病分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2013版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2014,6(7):447-498. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-5809.2014.07.004.
|
| [7] |
夏维波,章振林,林华,等. 原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2017)[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(3):281-309. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2019.03.001.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
曾宪涛,刘慧,陈曦,等. Meta分析系列之四:观察性研究的质量评价工具[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志,2012,4(4):297-299. DOI:10.3969/j.1674-4055.2012.04.004.
|
| [10] |
周友俊,全兴胜,何美琼,等. 绝经后骨质疏松合并2型糖尿病患者的多因素分析[J]. 昆明医学院学报,2010,31(12):72-75. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-4706.2010.12.019.
|
| [11] |
征海华,雷涛,张秀珍,等. 绝经后2型糖尿病妇女血脂水平和骨密度的关系[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2010,16(1):39-42. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2010.01.010.
|
| [12] |
征海华,雷涛,江东梅,等. 绝经后2型糖尿病患者血脂与骨代谢的关系[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2011,17(8):705-708. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2011.08.013.
|
| [13] | |
| [14] |
应蓉,龚仪雯,顾涛,等. 老年女性2型糖尿病患者合并骨质疏松的临床因素分析[J]. 中国医刊,2017,52(12):51-54.
|
| [15] |
王瑜,陈飞,孙颖. 绝经后2型糖尿病患者合并骨质疏松症相关危险因素分析[J]. 中国妇幼保健,2021,36(12):2827-2829. DOI:10.19829/j.zgfybj.issn.1001-4411.2021.12.046.
|
| [16] |
王燕,刘岩,张伟,等. 绝经后2型糖尿病患者骨质疏松影响因素及骨转换特点[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2011,31(9):1506-1508. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2011.09.004.
|
| [17] |
王小华,殷士良,王彩云,等. 老年糖尿病妇女骨质疏松的相关危险因素分析[J]. 中国医药导刊,2014,16(8):1206-1207,1209. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-0959.2014.08.009.
|
| [18] |
马剑侠,薛鹏,王燕,等. 绝经后女性2型糖尿病患者血脂、血压与骨质疏松的关系[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2016,36(5):1074-1076. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2016.05.023.
|
| [19] |
吕晓双,黄雌友,姚伟峰,等. T2DM女性患者绝经后骨密度和血清25(OH)D水平分析[J]. 江苏医药,2021,47(1):69-72. DOI:10.19460/j.cnki.0253-3685.2021.01.018.
|
| [20] |
林珊珊,杨雪梅,郭丽敏. 2型糖尿病患者绝经后骨质疏松危险因素的Logistic回归分析[J]. 河北医药,2019,41(19):3016-3018. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2019.19.037.
|
| [21] |
李琪,陈先丹,牟芝群,等. 绝经后2型糖尿病患者血清25(OH)D、Leptin与骨代谢的相关性[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(12):1612-1616. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2018.12.011.
|
| [22] |
黄银琼,林夏鸿,陈晓毓,等. 2型糖尿病绝经后患者82例骨强度影响因素的分析[J]. 福建医药杂志,2019,41(5):40-43. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-2600.2019.05.013.
|
| [23] |
何丽,李皓雲,秦贵军,等. 2型糖尿病绝经后女性患者血尿酸水平与骨密度和骨折的相关性研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(6):799-803,836. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2019.06.014.
|
| [24] |
巩伟伟,雷涛. 绝经后2型糖尿病患者骨代谢变化及其影响因素分析[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版),2018,39(3):104-109. DOI:10.16118/j.1008-0392.2018.03.020.
|
| [25] |
陈雪,石晓聪,安辉,等. 女性绝经后2型糖尿病与骨质疏松症的相关性分析[J]. 浙江临床医学,2018,20(4):699-701.
|
| [26] |
赖春红. 合并2型糖尿病的绝经后女性骨质疏松症的相关因素分析[D]. 南昌:南昌大学,2020.
|
| [27] |
姜璐. 绝经后女性2型糖尿病患者并发骨质疏松的预测研究[D]. 济南:山东大学,2017.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
叶紫梦玮,戴璇,刘亚鸽,等. 糖尿病性骨质疏松症的临床诊断方法探讨[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(7):1005-1010. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2021.07.013.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
张丽媛,纳青青,周丽敏,等. 虾青素对去卵巢糖尿病大鼠骨质流失的防治作用[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(4):508-513,525. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2021.04.009.
|
| [36] |
蒋兰兰,朱剑,吴锦丹,等. 绝经后2型糖尿病患者不同部位骨密度的变化情况及影响因素[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2012,18(3):229-233. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2012.03.009.
|
| [37] |
伍海艳,吴荣艳,钟凤元,等. 雌激素代谢紊乱对老年女性骨质疏松患者的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2021,41(12):2567-2569. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2021.12.033.
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
李硕,倪向敏,王建. 2型糖尿病性骨质疏松症发病机制研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(11):1661-1665. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2021.11.020.
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
王志全,戴芳芳. 2型糖尿病合并骨质疏松相关因素的分析[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(11):1455-1458,1476. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2016.11.019.
|
| [1] | 许佳兰, 阎红, 文君, 周紫彤, 王思宇. 老年癌症患者潜在不适当用药发生率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3815-3822. |
| [2] | 张天宇, 于海搏, 陈飞, 李新, 张佳佳, 詹晓凯, 申曼, 汤然, 范斯斌, 赵凤仪, 黄仲夏. POEMS综合征全身系统性治疗疗效和安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3447-3455. |
| [3] | 全家霖, 朱琳, 苏煜, 陈泽恺, 陈梓淇, 张卓凡. 运动方式对超重或肥胖儿童青少年执行功能改善效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3422-3431. |
| [4] | 张睿敏, 董哲毅, 李爽, 王倩, 陈香美. 基于肾活检病理诊断的糖尿病肾病中医相关因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3307-3313. |
| [5] | 胡洁蔓, 谭斐翔, 袁安新, 陈世宇, 唐楚蕾, 殷月姮, 巴磊, 许勤. 结直肠癌患者术后衰弱变化轨迹及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3276-3282. |
| [6] | 丑欣彤, 彭瀚瑜, 马慧, 张珍, 苏先, 邱红燕. 产妇对避孕决策的偏好及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3294-3299. |
| [7] | 魏姣花, 彭慧如, 彭建业, 谭文婷, 黄金娥, 方立. MOTS-c在心房颤动患者血清中的表达及其与心房重构的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3271-3276. |
| [8] | 褚艺婧, 严雨格, 顾杰, 席彪, 祝墡珠, 黄蛟灵. 中国基层医务人员留用意愿影响因素分析:基于城乡差异比较[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3161-3168. |
| [9] | 余孜孜, 刘杜丽, 李熙敏, 阮春怡, 尹向阳, 蔡乐. 农村高血压患病和自我管理现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3137-3143. |
| [10] | 范博阳, 张玉, 孙雯宁, 张慧芳, 王英杰, 张奥, 赵洋, 王海鹏. 基层医生慢性病医防融合服务行为意向及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(25): 3144-3150. |
| [11] | 王汝朋, 南京, 胡奕然, 杨升华, 金泽宁. 三酰甘油-葡萄糖体质量指数对2型糖尿病合并急性心肌梗死行急诊经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后患者慢血流/无复流的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2985-2992. |
| [12] | 蒋世华, 朱政, 任盈盈, 朱垚磊, 王越, 高希彬. 中国儿童青少年近视患病率及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3043-3052. |
| [13] | 李浩, 李江涛, 刘丹, 王建军. 贝利尤单抗和阿尼鲁单抗及泰它西普治疗系统性红斑狼疮疗效和安全性的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2924-2933. |
| [14] | 吴越, 王雪彤, 柯碧莲. 近视性黄斑病变低视力患者视觉相关生活质量评估及影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2908-2914. |
| [15] | 王笑林, 李秋月, 周彦君, 张金辉, 梁涛. 转移性结直肠癌患者呋喹替尼治疗相关心血管毒性发生率和风险的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2934-2940. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





