中国全科医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (35): 4443-4452.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0413
所属专题: 呼吸疾病文章合辑
收稿日期:2022-04-12
修回日期:2022-08-15
出版日期:2022-12-15
发布日期:2022-09-08
通讯作者:
袁媛
Received:2022-04-12
Revised:2022-08-15
Published:2022-12-15
Online:2022-09-08
Contact:
YUAN Yuan
About author:摘要: 背景 开展经济、便捷的早期筛查对慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)高危人群的识别具有重要意义,但目前筛查工具种类繁多且诊断准确性不一,临床实践中的最佳筛查工具仍缺乏相应的循证医学证据。 目的 应用网状Meta分析方法评价常用COPD筛查工具的诊断价值。 方法 计算机检索PubMed、Cochrane Library、Embase、Web of Science、中国知网、万方数据知识服务平台、维普网,搜索有关COPD筛查及早期诊断工具有效性的诊断性研究,检索时间限定为建库至2021-12-31。由2名研究者独立进行文献筛选和资料提取,并对文献进行质量评价。应用Meta-disc 1.4和Stata 15.0软件进行网状Meta分析。 结果 共纳入46篇文献,涉及7种筛查工具:肺功能问卷(LFQ)、慢阻肺诊断问卷(CDQ)、慢阻肺自我筛查问卷(COPD-SQ)、慢阻肺人群筛查问卷(COPD-PS)、肺量计、呼气流量峰值(PEF)峰流速仪、问卷+PEF峰流速仪。Meta分析结果显示,7种筛查工具筛查COPD的合并灵敏度依次为:0.79〔95%CI(0.75,0.83)〕、0.85〔95%CI(0.83,0.86)〕、0.68〔95%CI(0.65,0.70)〕、0.60〔95%CI(0.56,0.63)〕、0.58〔95%CI(0.54,0.61)〕、0.86〔95%CI(0.84,0.88)〕、0.68〔95%CI(0.65,0.71)〕,合并特异度依次为:0.67〔95%CI(0.65,0.68)〕、0.59〔95%CI(0.58,0.59)〕、0.81〔95%CI(0.80,0.82)〕、0.84〔95%CI(0.83,0.85)〕、0.88〔95%CI(0.87,0.89)〕、0.86〔95%CI(0.84,0.88)〕、0.85〔95%CI(0.84,0.86)〕。网状Meta分析结果显示,7种筛查工具按照灵敏度累积排序概率曲线下面积(SUCRA)从高到低依次为PEF峰流速仪(72.7%)>CDQ(70.1%)>LFQ(61.8%)>问卷+PEF峰流速仪(45.3%)>COPD-SQ(28.5%)>COPD-PS(13.2%)>肺量计(9.1%);特异度SUCRA值从高到低依次为:肺量计(76.8%)>问卷+PEF峰流速仪(66.7%)>COPD-SQ(46.7%)>PEF峰流速仪(45.8%)>COPD-PS(39.2%)>LFQ(11.9%)>CDQ(8.2%)。 结论 在常用的COPD筛查工具中,PEF峰流速仪的灵敏度较高,肺量计的特异度较高,该结论仍需纳入更多大样本、多中心的研究进一步证实。
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 国家 | 人群(岁) | 样本量 | 平均年龄(岁) | 待评价工具 | 阈值 | TP | FP | FN | TN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLORDÉS[ | 2017 | 西班牙 | >40 | 407 | 57.4±8.9 | EGARPOC | Z≥13分 | 87 | 88 | 20 | 212 |
| QUEZADA[ | 2017 | 美国 | ≥40 | 30 | 62.6±11.49 | CAPTURE | Z≥2分 | 17 | 5 | 0 | 8 |
| CAPTURE+PEF峰流速仪 | Z≥2分;男性PEF<350 L/min,女性PEF<250 L/min | 15 | 1 | 2 | 12 | ||||||
| PEF峰流速仪 | 男性PEF<350 L/min,女性PEF<250 L/min | 15 | 2 | 2 | 11 | ||||||
| MARTINEZ[ | 2017 | 美国 | ≥40 | 346 | 62.7±10.1 | CAPTURE | Z≥2分 | 178 | 89 | 8 | 71 |
| CAPTURE+PEF峰流速仪 | Z≥2分;男性PEF<350 L/min,女性PEF<250 L/min | 167 | 35 | 19 | 125 | ||||||
| PEF峰流速仪 | 男性PEF<350 L/min,女性PEF<250 L/min | 164 | 36 | 22 | 124 | ||||||
| DEMIRCI[ | 2017 | 土耳其 | 40~65 | 357 | 55.5±8.8 | CAT | Z>10分 | 10 | 85 | 5 | 257 |
| KART[ | 2014 | 土耳其 | >40 | 694 | 48.3±9.0 | CAT | Z>10分 | 81 | 346 | 29 | 238 |
| 韩丁[ | 2020 | 中国 | ≥40 | 93 | 59.5±11.4 | LFQ | Z≤18分 | 23 | 35 | 3 | 32 |
| COPD-SQ | Z≥16分 | 17 | 24 | 9 | 43 | ||||||
| COPD-PS | Z≥5分 | 20 | 26 | 6 | 41 | ||||||
| SPYRATOS[ | 2017 | 希腊 | ≥40 | 3 234 | 62.4±12.5 | LFQ | Z≤18分 | 277 | 923 | 74 | 1 960 |
| CDQ | Z≥17分 | 260 | 807 | 91 | 2 076 | ||||||
| COPD-PS | Z≥5分 | 197 | 288 | 154 | 2 595 | ||||||
| JARHYAN[ | 2021 | 印度 | ≥40 | 235 | 56.7±10.4 | LFQ | Z≤18分 | 42 | 80 | 14 | 99 |
| COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 39 | 34 | 17 | 145 | ||||||
| LFQ+COPD-6肺量计 | Z≤18分;FEV1/FEV6 <0.7 | 44 | 38 | 12 | 141 | ||||||
| FRITH[ | 2011 | 美国 | ≥50 | 204 | 61±8 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 52 | 93 | 5 | 54 |
| PiKo-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 29 | 10 | 28 | 137 | ||||||
| RONALDSON[ | 2018 | 英国 | ≥35 | 216 | 53 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 37 | 82 | 8 | 89 |
| COPD-PS | Z>5分 | 24 | 37 | 21 | 134 | ||||||
| SICHLETIDIS[ | 2011 | 希腊 | >40 | 1 078 | 65.3±11.4 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 101 | 493 | 10 | 474 |
| PiKo-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 89 | 48 | 22 | 919 | ||||||
| CDQ+PiKo-6肺量计 | Z≥17分;FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 80 | 39 | 31 | 938 | ||||||
| FUJITA[ | 2019 | 日本 | ≥40 | 2 008 | 64.1±10 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 74 | 769 | 30 | 1 135 |
| COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 89 | 484 | 15 | 1 420 | ||||||
| CDQ+COPD-6肺量计 | Z≥17分;FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 91 | 512 | 13 | 1 392 | ||||||
| 王石林[ | 2014 | 中国 | >40 | 400 | 51.12 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 169 | 66 | 31 | 134 |
| 王娟[ | 2012 | 中国 | >40 | 349 | 60.9+13.4 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 124 | 69 | 17 | 139 |
| 李云海[ | 2019 | 中国 | >40 | 49 | 61.2±10.7 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 13 | 10 | 5 | 21 |
| 陶学芳[ | 2019 | 中国 | >40 | 218 | 67.9±7.9 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 128 | 68 | 2 | 20 |
| TSUKUYA[ | 2016 | 日本 | ≥40 | 2 336 | 63.9±9.6 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 129 | 1 176 | 21 | 1 010 |
| 徐宪韬[ | 2018 | 中国 | >40 | 151 | 59.4±6.2 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 61 | 6 | 20 | 64 |
| COPD风险量表 | Z≥5分 | 50 | 4 | 31 | 66 | ||||||
| 陈淑云[ | 2014 | 中国 | ≥40 | 4 241 | 56.6±11.6 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 471 | 1 324 | 144 | 2 302 |
| COPD-SQ | Z≥16分 | 366 | 611 | 249 | 3 015 | ||||||
| 2 901 | 58.1 | PEF峰流速仪 | PEF%pred<80% | 434 | 1 013 | 72 | 1 382 | ||||
| COPD-SQ+PEF峰流速仪 | Z≥16分;PEF%pred<80% | 283 | 290 | 223 | 2 105 | ||||||
| 吉珉[ | 2019 | 中国 | ≥60 | 1 200 | 64.8±2.6 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 88 | 319 | 3 | 790 |
| 刘妍[ | 2015 | 中国 | ≥40 | 483 | 49.8±10.7 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 36 | 128 | 1 | 318 |
| 周为[ | 2021 | 中国 | ≥40 | 557 | 65.9±9.5 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 131 | 266 | 8 | 152 |
| COPD-SQ | Z≥16分 | 94 | 124 | 45 | 294 | ||||||
| COPD-PS | Z≥5分 | 105 | 87 | 34 | 331 | ||||||
| 简易筛查问卷 | Z≥6分 | 105 | 109 | 34 | 309 | ||||||
| KOTZ[ | 2008 | 荷兰 | 40~70 | 676 | 52.3±7.3 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 248 | 301 | 30 | 97 |
| PRICE[ | 2006 | 英、美 | ≥40 | 818 | 58.2±11.2 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 91 | 152 | 64 | 511 |
| STANLEY[ | 2014 | 澳大利亚 | 40~85 | 1 054 | 61±11.3 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 110 | 487 | 28 | 429 |
| 石喆[ | 2014 | 中国 | ≥40 | 629 | 61±10.5 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 227 | 106 | 27 | 269 |
| KAWAYAMA[ | 2008 | 日本 | ≥40 | 169 | 61.57 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 31 | 81 | 2 | 55 |
| 葛妍麟[ | 2014 | 中国 | ≥40 | 347 | 56.1±9.6 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 58 | 160 | 7 | 122 |
| 金沿欣[ | 2021 | 中国 | ≥60 | 712 | 70.7 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 56 | 63 | 13 | 580 |
| 杜明明[ | 2021 | 中国 | ≥60 | 744 | 68.4±6.1 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 60 | 67 | 21 | 596 |
| 张小娥[ | 2017 | 中国 | ≥40 | 378 | 61.00±10.96 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 55 | 76 | 10 | 237 |
| PEF峰流速仪 | PEF%pred<80% | 50 | 48 | 15 | 265 | ||||||
| CDQ+PEF峰流速仪 | Z≥17分;PEF%pred<80% | 63 | 103 | 2 | 210 | ||||||
| 任涟萍[ | 2018 | 中国 | ≥40 | 150 | 62.5±12.9 | 改良CDQ | Z≥17.5分 | 56 | 14 | 14 | 56 |
| ZHOU[ | 2013 | 中国 | ≥40 | 3 231 | 56.1±10.0 | COPD-SQ | Z≥16分 | 198 | 430 | 129 | 2 474 |
| 姚艳颜[ | 2021 | 中国 | ≥40 | 3 811 | 56.9±9.6 | COPD-SQ | Z≥16分 | 618 | 731 | 187 | 2 275 |
| SAMUKAWA[ | 2017 | 日本 | 40~79 | 2 066 | 67.9±8.7 | COPD-Q | Z≥4分 | 71 | 588 | 29 | 1 378 |
| MARTINEZ[ | 2009 | 美国 | >35 | 295 | 62.1±13.0 | COPD-PS | Z≥5分 | 95 | 72 | 18 | 110 |
| TSUKUYA[ | 2015 | 日本 | 40~79 | 2 357 | 65.0±10.4 | COPD-PS | Z≥5分 | 53 | 456 | 100 | 1 748 |
| LÓPEZ VARELA[ | 2016 | 拉丁美洲 | ≥40 | 1 540 | 57.9 | COPD风险量表 | Z≥5分 | 229 | 433 | 80 | 798 |
| LÓPEZ VARELA[ | 2019 | 拉丁美洲 | ≥40 | 2 512 | 54.1 | COPD风险量表 | Z≥5分 | 384 | 1 287 | 66 | 775 |
| LABOR[ | 2016 | 克罗地亚 | ≥40 | 227 | 52.5±6.8 | COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 14 | 0 | 29 | 184 |
| THORN[ | 2012 | 瑞典 | 45~85 | 305 | 61.2 | COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 41 | 24 | 36 | 204 |
| REPRESAS-REPRESAS[ | 2016 | 西班牙 | >40 | 362 | 55 | COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 44 | 17 | 70 | 231 |
| SAMI[ | 2020 | 伊朗 | >40 | 122 | 53.2±9.0 | COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 16 | 2 | 3 | 101 |
| 王小燕[ | 2018 | 中国 | 40~75 | 475 | 57.78±9.18 | COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 30 | 44 | 3 | 398 |
| CHEN[ | 2021 | 中国 | ≥40 | 1 487 | 59 | COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6≤0.7 | 96 | 26 | 133 | 1 232 |
| JACKSON[ | 2003 | 英国 | 50~90 | 3 874 | 65 | PEF峰流速仪 | PEF%pred<80% | 235 | 679 | 30 | 2 930 |
表1 纳入文献的基本特征
Table 1 Basic characteristics of the included studies
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 国家 | 人群(岁) | 样本量 | 平均年龄(岁) | 待评价工具 | 阈值 | TP | FP | FN | TN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLORDÉS[ | 2017 | 西班牙 | >40 | 407 | 57.4±8.9 | EGARPOC | Z≥13分 | 87 | 88 | 20 | 212 |
| QUEZADA[ | 2017 | 美国 | ≥40 | 30 | 62.6±11.49 | CAPTURE | Z≥2分 | 17 | 5 | 0 | 8 |
| CAPTURE+PEF峰流速仪 | Z≥2分;男性PEF<350 L/min,女性PEF<250 L/min | 15 | 1 | 2 | 12 | ||||||
| PEF峰流速仪 | 男性PEF<350 L/min,女性PEF<250 L/min | 15 | 2 | 2 | 11 | ||||||
| MARTINEZ[ | 2017 | 美国 | ≥40 | 346 | 62.7±10.1 | CAPTURE | Z≥2分 | 178 | 89 | 8 | 71 |
| CAPTURE+PEF峰流速仪 | Z≥2分;男性PEF<350 L/min,女性PEF<250 L/min | 167 | 35 | 19 | 125 | ||||||
| PEF峰流速仪 | 男性PEF<350 L/min,女性PEF<250 L/min | 164 | 36 | 22 | 124 | ||||||
| DEMIRCI[ | 2017 | 土耳其 | 40~65 | 357 | 55.5±8.8 | CAT | Z>10分 | 10 | 85 | 5 | 257 |
| KART[ | 2014 | 土耳其 | >40 | 694 | 48.3±9.0 | CAT | Z>10分 | 81 | 346 | 29 | 238 |
| 韩丁[ | 2020 | 中国 | ≥40 | 93 | 59.5±11.4 | LFQ | Z≤18分 | 23 | 35 | 3 | 32 |
| COPD-SQ | Z≥16分 | 17 | 24 | 9 | 43 | ||||||
| COPD-PS | Z≥5分 | 20 | 26 | 6 | 41 | ||||||
| SPYRATOS[ | 2017 | 希腊 | ≥40 | 3 234 | 62.4±12.5 | LFQ | Z≤18分 | 277 | 923 | 74 | 1 960 |
| CDQ | Z≥17分 | 260 | 807 | 91 | 2 076 | ||||||
| COPD-PS | Z≥5分 | 197 | 288 | 154 | 2 595 | ||||||
| JARHYAN[ | 2021 | 印度 | ≥40 | 235 | 56.7±10.4 | LFQ | Z≤18分 | 42 | 80 | 14 | 99 |
| COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 39 | 34 | 17 | 145 | ||||||
| LFQ+COPD-6肺量计 | Z≤18分;FEV1/FEV6 <0.7 | 44 | 38 | 12 | 141 | ||||||
| FRITH[ | 2011 | 美国 | ≥50 | 204 | 61±8 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 52 | 93 | 5 | 54 |
| PiKo-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 29 | 10 | 28 | 137 | ||||||
| RONALDSON[ | 2018 | 英国 | ≥35 | 216 | 53 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 37 | 82 | 8 | 89 |
| COPD-PS | Z>5分 | 24 | 37 | 21 | 134 | ||||||
| SICHLETIDIS[ | 2011 | 希腊 | >40 | 1 078 | 65.3±11.4 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 101 | 493 | 10 | 474 |
| PiKo-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 89 | 48 | 22 | 919 | ||||||
| CDQ+PiKo-6肺量计 | Z≥17分;FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 80 | 39 | 31 | 938 | ||||||
| FUJITA[ | 2019 | 日本 | ≥40 | 2 008 | 64.1±10 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 74 | 769 | 30 | 1 135 |
| COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 89 | 484 | 15 | 1 420 | ||||||
| CDQ+COPD-6肺量计 | Z≥17分;FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 91 | 512 | 13 | 1 392 | ||||||
| 王石林[ | 2014 | 中国 | >40 | 400 | 51.12 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 169 | 66 | 31 | 134 |
| 王娟[ | 2012 | 中国 | >40 | 349 | 60.9+13.4 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 124 | 69 | 17 | 139 |
| 李云海[ | 2019 | 中国 | >40 | 49 | 61.2±10.7 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 13 | 10 | 5 | 21 |
| 陶学芳[ | 2019 | 中国 | >40 | 218 | 67.9±7.9 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 128 | 68 | 2 | 20 |
| TSUKUYA[ | 2016 | 日本 | ≥40 | 2 336 | 63.9±9.6 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 129 | 1 176 | 21 | 1 010 |
| 徐宪韬[ | 2018 | 中国 | >40 | 151 | 59.4±6.2 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 61 | 6 | 20 | 64 |
| COPD风险量表 | Z≥5分 | 50 | 4 | 31 | 66 | ||||||
| 陈淑云[ | 2014 | 中国 | ≥40 | 4 241 | 56.6±11.6 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 471 | 1 324 | 144 | 2 302 |
| COPD-SQ | Z≥16分 | 366 | 611 | 249 | 3 015 | ||||||
| 2 901 | 58.1 | PEF峰流速仪 | PEF%pred<80% | 434 | 1 013 | 72 | 1 382 | ||||
| COPD-SQ+PEF峰流速仪 | Z≥16分;PEF%pred<80% | 283 | 290 | 223 | 2 105 | ||||||
| 吉珉[ | 2019 | 中国 | ≥60 | 1 200 | 64.8±2.6 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 88 | 319 | 3 | 790 |
| 刘妍[ | 2015 | 中国 | ≥40 | 483 | 49.8±10.7 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 36 | 128 | 1 | 318 |
| 周为[ | 2021 | 中国 | ≥40 | 557 | 65.9±9.5 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 131 | 266 | 8 | 152 |
| COPD-SQ | Z≥16分 | 94 | 124 | 45 | 294 | ||||||
| COPD-PS | Z≥5分 | 105 | 87 | 34 | 331 | ||||||
| 简易筛查问卷 | Z≥6分 | 105 | 109 | 34 | 309 | ||||||
| KOTZ[ | 2008 | 荷兰 | 40~70 | 676 | 52.3±7.3 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 248 | 301 | 30 | 97 |
| PRICE[ | 2006 | 英、美 | ≥40 | 818 | 58.2±11.2 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 91 | 152 | 64 | 511 |
| STANLEY[ | 2014 | 澳大利亚 | 40~85 | 1 054 | 61±11.3 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 110 | 487 | 28 | 429 |
| 石喆[ | 2014 | 中国 | ≥40 | 629 | 61±10.5 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 227 | 106 | 27 | 269 |
| KAWAYAMA[ | 2008 | 日本 | ≥40 | 169 | 61.57 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 31 | 81 | 2 | 55 |
| 葛妍麟[ | 2014 | 中国 | ≥40 | 347 | 56.1±9.6 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 58 | 160 | 7 | 122 |
| 金沿欣[ | 2021 | 中国 | ≥60 | 712 | 70.7 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 56 | 63 | 13 | 580 |
| 杜明明[ | 2021 | 中国 | ≥60 | 744 | 68.4±6.1 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 60 | 67 | 21 | 596 |
| 张小娥[ | 2017 | 中国 | ≥40 | 378 | 61.00±10.96 | CDQ | Z≥17分 | 55 | 76 | 10 | 237 |
| PEF峰流速仪 | PEF%pred<80% | 50 | 48 | 15 | 265 | ||||||
| CDQ+PEF峰流速仪 | Z≥17分;PEF%pred<80% | 63 | 103 | 2 | 210 | ||||||
| 任涟萍[ | 2018 | 中国 | ≥40 | 150 | 62.5±12.9 | 改良CDQ | Z≥17.5分 | 56 | 14 | 14 | 56 |
| ZHOU[ | 2013 | 中国 | ≥40 | 3 231 | 56.1±10.0 | COPD-SQ | Z≥16分 | 198 | 430 | 129 | 2 474 |
| 姚艳颜[ | 2021 | 中国 | ≥40 | 3 811 | 56.9±9.6 | COPD-SQ | Z≥16分 | 618 | 731 | 187 | 2 275 |
| SAMUKAWA[ | 2017 | 日本 | 40~79 | 2 066 | 67.9±8.7 | COPD-Q | Z≥4分 | 71 | 588 | 29 | 1 378 |
| MARTINEZ[ | 2009 | 美国 | >35 | 295 | 62.1±13.0 | COPD-PS | Z≥5分 | 95 | 72 | 18 | 110 |
| TSUKUYA[ | 2015 | 日本 | 40~79 | 2 357 | 65.0±10.4 | COPD-PS | Z≥5分 | 53 | 456 | 100 | 1 748 |
| LÓPEZ VARELA[ | 2016 | 拉丁美洲 | ≥40 | 1 540 | 57.9 | COPD风险量表 | Z≥5分 | 229 | 433 | 80 | 798 |
| LÓPEZ VARELA[ | 2019 | 拉丁美洲 | ≥40 | 2 512 | 54.1 | COPD风险量表 | Z≥5分 | 384 | 1 287 | 66 | 775 |
| LABOR[ | 2016 | 克罗地亚 | ≥40 | 227 | 52.5±6.8 | COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 14 | 0 | 29 | 184 |
| THORN[ | 2012 | 瑞典 | 45~85 | 305 | 61.2 | COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 41 | 24 | 36 | 204 |
| REPRESAS-REPRESAS[ | 2016 | 西班牙 | >40 | 362 | 55 | COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 44 | 17 | 70 | 231 |
| SAMI[ | 2020 | 伊朗 | >40 | 122 | 53.2±9.0 | COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 16 | 2 | 3 | 101 |
| 王小燕[ | 2018 | 中国 | 40~75 | 475 | 57.78±9.18 | COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6<0.7 | 30 | 44 | 3 | 398 |
| CHEN[ | 2021 | 中国 | ≥40 | 1 487 | 59 | COPD-6肺量计 | FEV1/FEV6≤0.7 | 96 | 26 | 133 | 1 232 |
| JACKSON[ | 2003 | 英国 | 50~90 | 3 874 | 65 | PEF峰流速仪 | PEF%pred<80% | 235 | 679 | 30 | 2 930 |
| 工具 | 合并灵敏度(95%CI) | 合并特异度(95%CI) | 合并诊断比值比(95%CI) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFQ | 0.79(0.75,0.83) | 0.67(0.65,0.68) | 7.16(5.68,9.04) | 0.79 |
| CDQ | 0.85(0.83,0.86) | 0.59(0.58,0.59) | 8.28(6.14,11.17) | 0.79 |
| COPD-SQ | 0.68(0.65,0.70) | 0.81(0.80,0.82) | 7.46(5.75,9.67) | 0.78 |
| COPD-PS | 0.60(0.56,0.63) | 0.84(0.83,0.85) | 6.09(2.99,12.41) | 0.78 |
| 肺量计 | 0.58(0.54,0.61) | 0.88(0.87,0.89) | 26.28(14.17,48.73) | 0.91 |
| PEF峰流速仪 | 0.86(0.84,0.88) | 0.86(0.84,0.88) | 20.10(9.45,42.79) | 0.79 |
| 问卷+PEF峰流速仪 | 0.68(0.65,0.71) | 0.85(0.84,0.86) | 27.45(9.15,82.39) | 0.91 |
表2 LFQ、CDQ、COPD-SQ、COPD-PS、肺量计、PEF峰流速仪、问卷+PEF峰流速仪诊断COPD价值的Meta分析结果
Table 2 Meta-analysis of combined sensitivity,specificity,DOR and AUC of included studies
| 工具 | 合并灵敏度(95%CI) | 合并特异度(95%CI) | 合并诊断比值比(95%CI) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFQ | 0.79(0.75,0.83) | 0.67(0.65,0.68) | 7.16(5.68,9.04) | 0.79 |
| CDQ | 0.85(0.83,0.86) | 0.59(0.58,0.59) | 8.28(6.14,11.17) | 0.79 |
| COPD-SQ | 0.68(0.65,0.70) | 0.81(0.80,0.82) | 7.46(5.75,9.67) | 0.78 |
| COPD-PS | 0.60(0.56,0.63) | 0.84(0.83,0.85) | 6.09(2.99,12.41) | 0.78 |
| 肺量计 | 0.58(0.54,0.61) | 0.88(0.87,0.89) | 26.28(14.17,48.73) | 0.91 |
| PEF峰流速仪 | 0.86(0.84,0.88) | 0.86(0.84,0.88) | 20.10(9.45,42.79) | 0.79 |
| 问卷+PEF峰流速仪 | 0.68(0.65,0.71) | 0.85(0.84,0.86) | 27.45(9.15,82.39) | 0.91 |
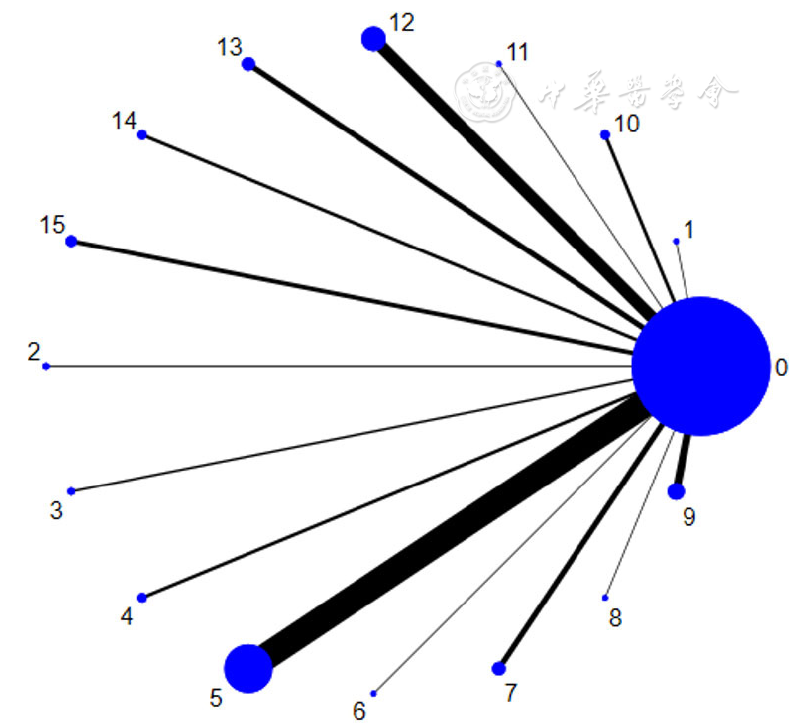
图2 筛查工具比较的证据网络图注:0=肺功能检查(PFTS),1=EGARPOC,2=CAPTURE,3=CAT,4=LFQ,5=CDQ,6=改良CDQ,7=COPD-SQ,8=COPD-Q,9=COPD-PS,10=COPD风险量表,11=简易筛查问卷,12=肺量计,13=PEF峰流速仪,14=问卷+肺量计,15=问卷+PEF峰流速仪
Figure 2 Network evidence of frequencies of use of seven COPD screening tools
| 评估工具 | LFQ | CDQ | COPD-SQ | COPD-PS | 肺量计 | PEF峰流速仪 | 问卷+PEF峰流速仪 | PFTS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFQ | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| CDQ | 0.95(0.71,1.28) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| COPD-SQ | 1.24(0.89,1.72) | 1.30(1.06,1.59) | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| COPD-PS | 1.37(0.98,1.93) | 1.44(1.16,1.78) | 1.11(0.85,1.45) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 肺量计 | 1.41(1.02,1.97) | 1.48(1.22,1.78) | 1.14(0.89,1.45) | 1.02(0.79,1.32) | — | — | — | — |
| PEF峰流速仪 | 0.93(0.66,1.31) | 0.97(0.79,1.22) | 0.75(0.58,0.98) | 0.68(0.51,0.89) | 0.66(0.51,0.86) | — | — | — |
| 问卷+PEF峰流速仪 | 1.11(0.77,1.60) | 1.16(0.90,1.50) | 0.90(0.67,1.21) | 0.81(0.60,1.10) | 0.79(0.59,1.05) | 1.19(0.87,1.62) | — | — |
| PFTS | 0.76(0.58,1.00) | 0.80(0.73,0.88) | 0.61(0.51,0.73) | 0.55(0.46,0.67) | 0.54(0.46,0.64) | 0.82(0.67,0.99) | 0.68(0.54,0.87) | — |
表3 COPD筛查工具灵敏度的网状Meta分析结果〔OR(95%CI)〕
Table 3 Results of network meta-analysis of sensitivity of seven COPD screening tools
| 评估工具 | LFQ | CDQ | COPD-SQ | COPD-PS | 肺量计 | PEF峰流速仪 | 问卷+PEF峰流速仪 | PFTS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFQ | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| CDQ | 0.95(0.71,1.28) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| COPD-SQ | 1.24(0.89,1.72) | 1.30(1.06,1.59) | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| COPD-PS | 1.37(0.98,1.93) | 1.44(1.16,1.78) | 1.11(0.85,1.45) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 肺量计 | 1.41(1.02,1.97) | 1.48(1.22,1.78) | 1.14(0.89,1.45) | 1.02(0.79,1.32) | — | — | — | — |
| PEF峰流速仪 | 0.93(0.66,1.31) | 0.97(0.79,1.22) | 0.75(0.58,0.98) | 0.68(0.51,0.89) | 0.66(0.51,0.86) | — | — | — |
| 问卷+PEF峰流速仪 | 1.11(0.77,1.60) | 1.16(0.90,1.50) | 0.90(0.67,1.21) | 0.81(0.60,1.10) | 0.79(0.59,1.05) | 1.19(0.87,1.62) | — | — |
| PFTS | 0.76(0.58,1.00) | 0.80(0.73,0.88) | 0.61(0.51,0.73) | 0.55(0.46,0.67) | 0.54(0.46,0.64) | 0.82(0.67,0.99) | 0.68(0.54,0.87) | — |
| 评估工具 | LFQ | CDQ | COPD-SQ | COPD-PS | 肺量计 | PEF峰流速仪 | 问卷+PEF峰流速仪 | PFTS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFQ | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| CDQ | 1.00(0.47,2.13) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| COPD-SQ | 0.54(0.22,1.32) | 0.54(0.30,0.98) | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| COPD-PS | 0.56(0.24,1.34) | 0.56(0.32,0.98) | 1.04(0.50,2.15) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 肺量计 | 0.35(0.15,0.78) | 0.35(0.22,0.55) | 0.64(0.33,1.25) | 0.62(0.33,1.16) | — | — | — | — |
| PEF峰流速仪 | 0.55(0.22,1.35) | 0.55(0.30,1.01) | 1.01(0.47,2.19) | 0.97(0.46,2.06) | 1.57(0.80,3.10) | — | — | — |
| 问卷+PEF峰流速仪 | 0.40(0.15,1.04) | 0.40(0.20,0.79) | 0.74(0.32,1.70) | 0.71(0.32,1.60) | 1.15(0.55,2.42) | 0.73(0.32,1.70) | — | — |
| PFTS | 0.21(0.10,0.42) | 0.21(0.16,0.26) | 0.38(0.22,0.65) | 0.37(0.22,0.60) | 0.59(0.40,0.87) | 0.37(0.21,0.65) | 0.51(0.27,0.96) | — |
表4 COPD筛查工具特异度的网状Meta分析结果〔OR(95%CI)〕
Table 4 Results of network meta-analysis of specificity of seven COPD screening tools
| 评估工具 | LFQ | CDQ | COPD-SQ | COPD-PS | 肺量计 | PEF峰流速仪 | 问卷+PEF峰流速仪 | PFTS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFQ | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| CDQ | 1.00(0.47,2.13) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| COPD-SQ | 0.54(0.22,1.32) | 0.54(0.30,0.98) | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| COPD-PS | 0.56(0.24,1.34) | 0.56(0.32,0.98) | 1.04(0.50,2.15) | — | — | — | — | — |
| 肺量计 | 0.35(0.15,0.78) | 0.35(0.22,0.55) | 0.64(0.33,1.25) | 0.62(0.33,1.16) | — | — | — | — |
| PEF峰流速仪 | 0.55(0.22,1.35) | 0.55(0.30,1.01) | 1.01(0.47,2.19) | 0.97(0.46,2.06) | 1.57(0.80,3.10) | — | — | — |
| 问卷+PEF峰流速仪 | 0.40(0.15,1.04) | 0.40(0.20,0.79) | 0.74(0.32,1.70) | 0.71(0.32,1.60) | 1.15(0.55,2.42) | 0.73(0.32,1.70) | — | — |
| PFTS | 0.21(0.10,0.42) | 0.21(0.16,0.26) | 0.38(0.22,0.65) | 0.37(0.22,0.60) | 0.59(0.40,0.87) | 0.37(0.21,0.65) | 0.51(0.27,0.96) | — |
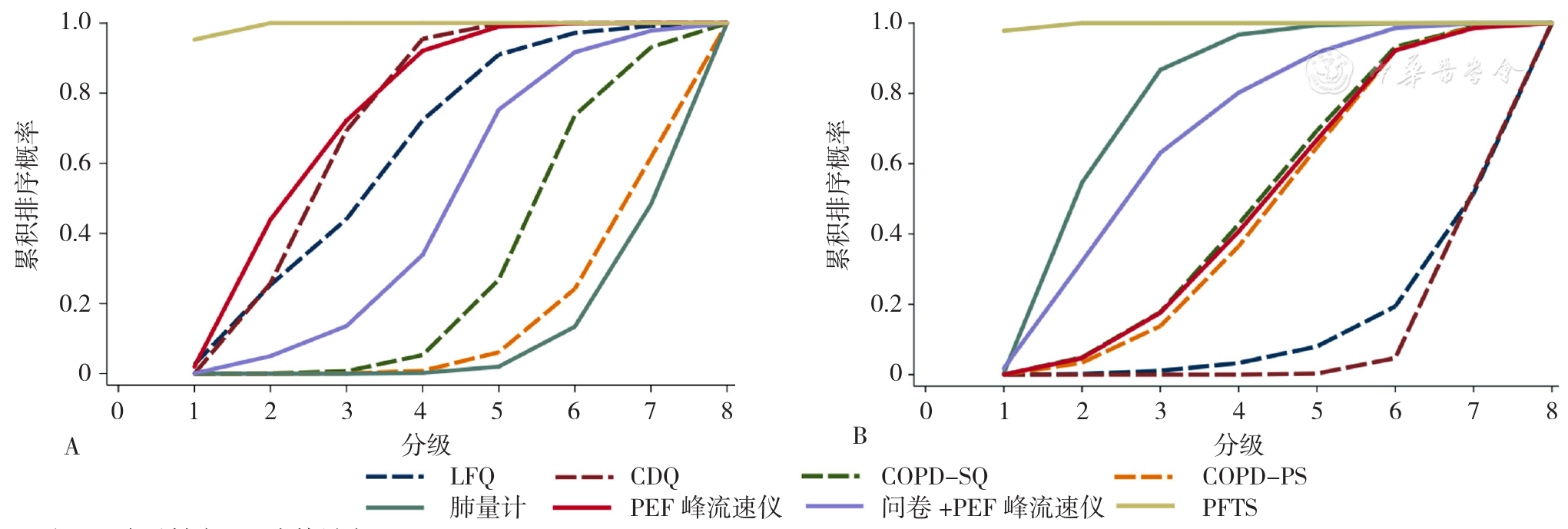
图3 各筛查工具灵敏度和特异度的累积排序概率曲线图注:A为灵敏度,B为特异度
Figure 3 The surface under the cumulative ranking curve for sensitivity and specificity of seven COPD screening tools
| [1] |
迟春花. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重的风险识别和管理新进展[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志,2021,44(1):66-70. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20200803-00872.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
黄可,杨汀. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病的筛查与早期诊断[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志,2021,44(3):279-282. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20200727-00850.
|
| [5] |
卢敏贞,高兴林. 2020年慢性阻塞性肺疾病全球倡议更新解读[J]. 临床药物治疗杂志,2021,19(1):17-21. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-3384.2021.01.004.
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
韩丁. 三种问卷在慢性阻塞性肺疾病中的筛查价值[D]. 昆明:昆明医科大学,2020.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
王石林,陈树丹,卢健聪,等. 基于症状的COPD筛查问卷对COPD高危人员的相关性研究[J]. 中外医疗,2014,33(13):155-156. DOI:10.16662/j.cnki.1674-0742.2014.13.034.
|
| [20] |
王娟,许文兵,曾学军,等. 中文版慢性阻塞性肺疾病筛查问卷在吸烟者中的初步检验与评价[J]. 中华内科杂志,2012(4):311-312.
|
| [21] |
李云海,李俊,张楠,等. 慢阻肺筛查问卷加肺功能检查对慢阻肺的早期诊断作用研究[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(61):246-247. DOI:10.19613/j.cnki.1671-3141.2019.61.149.
|
| [22] |
陶学芳,邵银燕,孙金军,等. 基于症状的慢性阻塞性肺疾病筛查问卷诊断效果评价[J]. 预防医学,2019,31(7):693-695. DOI:10.19485/j.cnki.issn2096-5087.2019.07.011.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
徐宪韬,吴丰芹,徐琴. COPD风险七项评分量表在COPD早期筛查中的应用价值[J]. 现代医药卫生,2018,34(20):3152-3155. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-5519.2018.20.015.
|
| [25] |
陈淑云. 慢性阻塞性肺病社区综合防治适宜技术的初步研究[D]. 广州:广州医科大学,2014.
|
| [26] |
吉珉. 筛查问卷与肺功能检查在宁海山区老年人慢阻肺诊断中的应用价值分析[J]. 医药前沿,2019,9(20):254.
|
| [27] |
刘妍,邓笑伟. 筛查问卷与肺功能检查在慢性阻塞性肺疾病早期诊断中的研究[J]. 临床肺科杂志,2015,20(3):500-503. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6663.2015.03.038.
|
| [28] |
周为. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病基层简易筛查问卷的建立及验证研究[D]. 北京:北京协和医学院,2021.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
石喆,王石林,汪海燕,等. 适宜国人BMI分级的慢性阻塞性肺疾病筛查问卷的检验与评价[J]. 中华全科医师杂志,2014(3):184-187.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
葛妍麟,陈红,杨嫦娟. 基于症状的慢性阻塞性肺疾病筛查问卷在社区人群中的应用[J]. 当代护士:下旬刊,2014(11):124-125.
|
| [35] |
金沿欣,高艳玲,何艳,等. 基于症状的COPD筛查问卷在社区老年人群COPD筛查中的应用[J]. 国际呼吸杂志,2021,41(10):756-760. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn131368-20200314-00160.
|
| [36] |
杜明明,董礼,吕俊. 两种方法筛查宜宾市60岁以上居民慢性阻塞性肺疾病的一致性研究[J]. 实用老年医学,2021,35(2):141-144.
|
| [37] |
张小娥. 问卷调查联合呼气峰流速(PEF)测定筛查慢性阻塞性肺疾病的效力[D]. 延安:延安大学,2017.
|
| [38] |
任涟萍,张悦,施萍,等. 针对中国患者的基于症状的慢性阻塞性肺疾病筛查问卷建立的初步研究[J]. 国际呼吸杂志,2018(23):1766-1770. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-436X.2018.23.002.
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
姚艳颜,田禾燊,吴繁,等. 慢性阻塞性肺病筛查问卷(COPD-SQ)在社区中的应用评价[J]. 广州医科大学学报,2021,49(3):41-46.
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
王小燕,夏国光,戴丽,等. 使用便携式肺功能仪对烟草暴露人群筛查COPD的应用价值[J]. 国际呼吸杂志,2018,38(18):1381-1385. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-436X.2018.18.005.
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
王洪刚,于兵,韩丽,等. 肺功能测定在ACOS、COPD急性发作期鉴别中的应用价值[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘,2018,18(16):160-162. DOI:10.19613/j.cnki.1671-3141.2018.16.071.
|
| [54] |
田佳. 成人呼气峰流速预计值公式建立及其在COPD患者气流受限初筛中的作用研究[D]. 广州:广州医学院,2010.
|
| [55] |
刘亚男. 峰流速仪与IPAG问卷在COPD诊断和评估中的作用[D]. 北京:北京协和医学院,2015.
|
| [56] |
吴仲平,黄锐波,郑劲平,等. 肺功能仪容量定标筒的质量检测方法的建立及其应用价值对比研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2022,25(2):149-152. DOI:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.01.037.
|
| [57] |
周玉民,陈淑云,田佳,等. 中国慢性阻塞性肺疾病筛查问卷的制定与验证[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志,2014(12):892.
|
| [58] |
李东,董越,杨双,等. 筛查问卷在慢性阻塞性肺疾病早期诊断中的应用进展[J]. 中国临床医学,2022,29(3):486-492.
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [1] | 徐百川, 王艳, 张彭, 李艺婷, 刘飞来, 谢洋. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病共病肺癌筛查工具分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3847-3852. |
| [2] | 李玲, 李雅萍, 钱时兴, 聂婧, 陆春华, 李霞. 社区中老年人认知功能影响因素及风险预测研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3773-3778. |
| [3] | 全家霖, 朱琳, 苏煜, 陈泽恺, 陈梓淇, 张卓凡. 运动方式对超重或肥胖儿童青少年执行功能改善效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3422-3431. |
| [4] | 李浩, 李江涛, 刘丹, 王建军. 贝利尤单抗和阿尼鲁单抗及泰它西普治疗系统性红斑狼疮疗效和安全性的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2924-2933. |
| [5] | 石佳瑞, 王梓力, 张薛晴, 宋玉磊, 徐桂华, 柏亚妹. 南京市社区认知症服务中心认知初步筛查服务开展现况研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2784-2790. |
| [6] | 李佳, 谭文彬. 继发性骨质疏松症防治困境与对策探究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(17): 2075-2081. |
| [7] | 金锋, 黎旺玲, 谢飞. 基于"慢阻肺防治平台"的闭环管理案例研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(16): 2059-2064. |
| [8] | 陈典, 隆寰宇, 张丛溪, 褚岚和, 李姝润, 陈亚红. 2025年GOLD慢性阻塞性肺疾病诊断、治疗、管理及预防全球策略更新要点解读[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(16): 1937-1949. |
| [9] | 章琪, 和申, 李华. 2022年美国预防临床服务指南工作组《儿童和青少年抑郁症和自杀风险筛查推荐声明》解读[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(15): 1823-1830. |
| [10] | 曾泳添, 陈日玲, 农雪艳, 刘洲, 梁力中, 朱子健. 数字疗法在自闭症筛查到干预的临床研究进展与挑战[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1702-1708. |
| [11] | 何芸, 范焕芳, 马盼, 许绍青, 杨柳, 金明哲, 张明蕊, 陈佳琪. 不同针灸治疗方式干预乳腺癌术后上肢淋巴水肿效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1788-1794. |
| [12] | 吴大东, 刘慧敏, 张嘉怡, 刘思源, 赵光临, 靳淑雁, 姜蕾. 围产期抑郁筛查与干预移动平台的应用与效果评价研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1773-1780. |
| [13] | 朱胜杰, 刁华琼, 杭晓屹, 孙文军. 不同中成药注射液治疗后循环缺血性眩晕效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(14): 1795-1808. |
| [14] | 郦奇锋, 隆寰宇, 王泽茂, 封敏, 陈亚红, 胡征. 物联网技术在基层医疗卫生机构肺功能检查与管理中的应用[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(13): 1674-1675. |
| [15] | 迟洵, 刘思思, 陈巧, 胡玥, 王伟仙. 不同营养筛查工具对肝硬化患者营养筛查适用性的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(11): 1395-1402. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||






