中国全科医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (05): 621-628.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0303
杨玲1, 侯黎莉2,*( ), 陈卫宏1, 翁夕媚1, 罗莎莎3, 夏佳琳1
), 陈卫宏1, 翁夕媚1, 罗莎莎3, 夏佳琳1
收稿日期:2022-02-24
修回日期:2022-06-25
出版日期:2023-02-15
发布日期:2022-11-17
通讯作者:
侯黎莉
基金资助:
YANG Ling1, HOU Lili2,*( ), CHEN Weihong1, WENG Ximei1, LUO Shasha3, XIA Jialin1
), CHEN Weihong1, WENG Ximei1, LUO Shasha3, XIA Jialin1
Received:2022-02-24
Revised:2022-06-25
Published:2023-02-15
Online:2022-11-17
Contact:
HOU Lili
摘要: 背景 口腔癌具有较高的发病率,大多数口腔癌是由口腔潜在恶性疾患造成,口腔白斑是常见的口腔潜在恶性病变。口腔白斑恶变不仅会影响患者的身心健康,而且会给患者家庭和社会带来沉重的经济负担。由于受到样本量、地区差异等因素的限制,我国口腔白斑患者恶变的流行病学特征结果不一。 目的 系统评价中国人群口腔白斑的恶变率。 方法 计算机检索中国知网、中国生物医学文献数据库、维普中文科技期刊全文数据库、万方数据知识服务平台、PubMed、Web of Science、Embase、Cochrane Library,获取有关中国人群口腔白斑恶变率的队列研究,检索时限均为建库至2022年2月,由2名研究员独立筛选文献,对纳入的研究进行质量评价与数据提取,采用Stata 15.0软件进行统计学分析。 结果 最终纳入30篇队列研究,包括109 047例患者。Meta分析结果显示,我国口腔白斑患者恶变率为9.0%〔95%CI(7.0%,11.3%)〕。亚组分析结果显示,男性患者口腔白斑恶变率为7.6%〔95%CI(5.1%,10.6%)〕,女性患者口腔白斑恶变率为13.2%〔95%CI(9.5%,17.4%)〕;<60岁患者口腔白斑恶变率为12.3%〔95%CI(9.2%,15.7%)〕,≥60岁患者口腔白斑恶变率为17.9%〔95%CI(13.8%,22.5%)〕;舌部口腔白斑患者的恶变率为16.2%〔95%CI(11.0%,22.2%)〕,其他部位口腔白斑患者的恶变率为6.1%〔95%CI(3.2%,9.6%)〕。 结论 当前证据表明,中国人群口腔白斑的恶变率较高,女性、年龄≥60岁、舌部口腔白斑恶变率较高。
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 调查地区 | 研究时间 | 年龄 | 恶变例数/样本量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 陈蔚华[ | 2015 | 南昌 | 2006年3月—2014年10月 | 10~87岁,平均52岁 | 8/170 |
| 王宇峰[ | 2011 | 上海 | 1978年1月—2009年9月 | 15~91岁,平均51.2岁 | 66/576 |
| 褚青松[ | 2009 | 沧州 | 1988年12月—2004年8月 | 14~80岁,平均52.2岁 | 14/150 |
| 葛化冰[ | 1999 | 北京 | 1981年12月—1998年8月 | 14~83岁,平均52.4岁 | 14/211 |
| 武文妍[ | 2018 | 上海 | 2000年1月—2015年12月 | - | 41/2 628 |
| 高岩[ | 2012 | 北京 | 1984年1月—2010年12月 | 29~83岁,平均51.2岁 | 85/1 832 |
| 蓝爱仙[ | 2009 | 北京 | 1980年11月—2007年12月 | 14~84岁,平均(53.3±13.9)岁 | 52/409 |
| 刘宏伟[ | 2007 | 北京 | 1976年12月—2006年10月 | - | 30/436 |
| 关晓兵[ | 2001 | 北京 | — | 23~83岁 | 13/110 |
| 史慧宝[ | 1992 | 上海 | 1976年—1991年6月 | 32~84岁,平均53.4岁 | 32/235 |
| 庞玲娟[ | 2007 | 广州 | 2002—2004年 | - | 3/61 |
| 汪说之[ | 1985 | 湖北 | 1962年1月—1981年12月 | - | 8/313 |
| 胡碧琼[ | 1985 | 北京 | 平均2.8年 | - | 9/261 |
| 冯淑梅[ | 2008 | 吉林 | 2004年9月—2007年9月 | 45~86岁 | 18/156 |
| 符攀峰[ | 2017 | 河南 | 2013年3月—2015年10月 | 19~81岁,平均(50.3±21.9)岁 | 14/85 |
| YANG[ | 2021 | 台湾 | 2002年9月—2020年9月,男:平均(5.4±3.8)年,女:平均(5.91 ± 4.7)年 | 23~83岁,平均(53.0±11.9)岁 | 32/485 |
| YANG[ | 2021 | 台湾 | 2002年9月—2019年10月,平均(54.9±54.4)个月 | 25~83岁,平均(52.2±11.7)岁 | 12/144 |
| YANG[ | 2020 | 台湾 | 2002年7月—2017年9月,平均(42.5±35.2)个月 | 65~83岁,平均(71.2±4.9)岁 | 8/69 |
| CHIANG[ | 2020 | 台湾 | 2012—2018年 | - | 22/350 |
| WU[ | 2019 | 上海 | 2000—2015年,平均5.5年 | - | 41/2 628 |
| CHUANG[ | 2018 | 台湾 | 2004—2009年 | 18~94岁 | 161/5 142 |
| WANG[ | 2018 | 台湾 | 平均(4.6±3.3)年 | 18~65岁,平均(45.8±10.7)岁 | 102/1 898 |
| YANG[ | 2017 | 台湾 | 13年 | - | 30/191 |
| LIU[ | 2012 | 上海 | 1990—2010年,平均5.1年 | 21~83岁,平均(54.1±11.6)岁 | 57/320 |
| LIU[ | 2011 | 上海 | 1996—2009年 | 平均(59.8±13.3)岁 | 11/53 |
| LIU[ | 2010 | 上海 | 1978—2008年,平均5.3年 | 21~84岁,平均(52.7±11.2)岁 | 39/218 |
| SHIU[ | 2000 | 台湾 | 1988—1998年 | - | 60/435 |
| LIU[ | 2011 | 上海 | 1978—2008年,平均5.1年 | 15~83岁,平均(52.8±12.2)岁 | 36/115 |
| LEE[ | 2006 | 台湾 | 1997年1月—2004年6月 | 19~93岁,平均(50.0±12.1)岁 | 135/1 046 |
| YANG[ | 2011 | 台湾 | 2002—2008年,平均(3.4±1.3)年 | 23~82岁,平均(49.7±12.2)岁 | 13/114 |
表1 纳入文献的基本特征
Table 1 Basic information of the included studies
| 第一作者 | 发表时间(年) | 调查地区 | 研究时间 | 年龄 | 恶变例数/样本量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 陈蔚华[ | 2015 | 南昌 | 2006年3月—2014年10月 | 10~87岁,平均52岁 | 8/170 |
| 王宇峰[ | 2011 | 上海 | 1978年1月—2009年9月 | 15~91岁,平均51.2岁 | 66/576 |
| 褚青松[ | 2009 | 沧州 | 1988年12月—2004年8月 | 14~80岁,平均52.2岁 | 14/150 |
| 葛化冰[ | 1999 | 北京 | 1981年12月—1998年8月 | 14~83岁,平均52.4岁 | 14/211 |
| 武文妍[ | 2018 | 上海 | 2000年1月—2015年12月 | - | 41/2 628 |
| 高岩[ | 2012 | 北京 | 1984年1月—2010年12月 | 29~83岁,平均51.2岁 | 85/1 832 |
| 蓝爱仙[ | 2009 | 北京 | 1980年11月—2007年12月 | 14~84岁,平均(53.3±13.9)岁 | 52/409 |
| 刘宏伟[ | 2007 | 北京 | 1976年12月—2006年10月 | - | 30/436 |
| 关晓兵[ | 2001 | 北京 | — | 23~83岁 | 13/110 |
| 史慧宝[ | 1992 | 上海 | 1976年—1991年6月 | 32~84岁,平均53.4岁 | 32/235 |
| 庞玲娟[ | 2007 | 广州 | 2002—2004年 | - | 3/61 |
| 汪说之[ | 1985 | 湖北 | 1962年1月—1981年12月 | - | 8/313 |
| 胡碧琼[ | 1985 | 北京 | 平均2.8年 | - | 9/261 |
| 冯淑梅[ | 2008 | 吉林 | 2004年9月—2007年9月 | 45~86岁 | 18/156 |
| 符攀峰[ | 2017 | 河南 | 2013年3月—2015年10月 | 19~81岁,平均(50.3±21.9)岁 | 14/85 |
| YANG[ | 2021 | 台湾 | 2002年9月—2020年9月,男:平均(5.4±3.8)年,女:平均(5.91 ± 4.7)年 | 23~83岁,平均(53.0±11.9)岁 | 32/485 |
| YANG[ | 2021 | 台湾 | 2002年9月—2019年10月,平均(54.9±54.4)个月 | 25~83岁,平均(52.2±11.7)岁 | 12/144 |
| YANG[ | 2020 | 台湾 | 2002年7月—2017年9月,平均(42.5±35.2)个月 | 65~83岁,平均(71.2±4.9)岁 | 8/69 |
| CHIANG[ | 2020 | 台湾 | 2012—2018年 | - | 22/350 |
| WU[ | 2019 | 上海 | 2000—2015年,平均5.5年 | - | 41/2 628 |
| CHUANG[ | 2018 | 台湾 | 2004—2009年 | 18~94岁 | 161/5 142 |
| WANG[ | 2018 | 台湾 | 平均(4.6±3.3)年 | 18~65岁,平均(45.8±10.7)岁 | 102/1 898 |
| YANG[ | 2017 | 台湾 | 13年 | - | 30/191 |
| LIU[ | 2012 | 上海 | 1990—2010年,平均5.1年 | 21~83岁,平均(54.1±11.6)岁 | 57/320 |
| LIU[ | 2011 | 上海 | 1996—2009年 | 平均(59.8±13.3)岁 | 11/53 |
| LIU[ | 2010 | 上海 | 1978—2008年,平均5.3年 | 21~84岁,平均(52.7±11.2)岁 | 39/218 |
| SHIU[ | 2000 | 台湾 | 1988—1998年 | - | 60/435 |
| LIU[ | 2011 | 上海 | 1978—2008年,平均5.1年 | 15~83岁,平均(52.8±12.2)岁 | 36/115 |
| LEE[ | 2006 | 台湾 | 1997年1月—2004年6月 | 19~93岁,平均(50.0±12.1)岁 | 135/1 046 |
| YANG[ | 2011 | 台湾 | 2002—2008年,平均(3.4±1.3)年 | 23~82岁,平均(49.7±12.2)岁 | 13/114 |
| 第一作者 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 陈蔚华[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 王宇峰[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 褚青松[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 葛化冰[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 武文妍[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 高岩[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 蓝爱仙[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 刘宏伟[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 关晓兵[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 史慧宝[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 庞玲娟[ | 是 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 汪说之[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 胡碧琼[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 冯淑梅[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 符攀峰[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| YANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| YANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| YANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| CHIANG[ | 是 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| WU[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| CHUANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| WANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| YANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| LIU[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| LIU[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| LIU[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| SHIU[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| LIU[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| LEE[ | 是 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| YANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
表2 纳入研究的偏倚风险评价结果
Table 2 Bias risk assessment results of the included studies
| 第一作者 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 陈蔚华[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 王宇峰[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 褚青松[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 葛化冰[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 武文妍[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 高岩[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 蓝爱仙[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 刘宏伟[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 关晓兵[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 史慧宝[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 庞玲娟[ | 是 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 汪说之[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 胡碧琼[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 冯淑梅[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 符攀峰[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| YANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| YANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| YANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| CHIANG[ | 是 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| WU[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| CHUANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| WANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| YANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| LIU[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| LIU[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| LIU[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| SHIU[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| LIU[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| LEE[ | 是 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| YANG[ | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 不清楚 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 亚组 | 纳入文献数量(篇) | 异质性检验 | 效应模型 | Meta分析结果 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2(%) | P值 | 恶变率(%) | 95%CI(%) | Z值 | P值 | ||||
| 性别 | |||||||||
| 男 | 14[ | 88.22 | <0.001 | 随机效应模型 | 7.6 | (5.1,10.6) | 9.20 | <0.001 | |
| 女 | 14[ | 81.06 | <0.001 | 随机效应模型 | 13.2 | (9.5,17.4) | 11.00 | <0.001 | |
| 年龄 | |||||||||
| <60岁 | 5[ | 58.31 | <0.001 | 随机效应模型 | 12.3 | (9.2,15.7) | 12.18 | <0.001 | |
| ≥60岁 | 4[ | 48.63 | 0.120 | 固定效应模型 | 17.9 | (13.8,22.5) | 13.26 | <0.001 | |
| 恶变部位 | |||||||||
| 舌部 | 9[ | 81.57 | <0.001 | 随机效应模型 | 16.2 | (11.0,22.2) | 9.56 | <0.001 | |
| 其他部位 | 8[ | 76.05 | <0.001 | 随机效应模型 | 6.1 | (3.2,9.6) | 5.98 | <0.001 | |
表3 不同亚组OLK恶变率的Meta分析结果
Table 3 Meta-analysis results of malignant transformation rate in Chinese patients with oral leukoplakia by sex,age and affected site in the oral cavity
| 亚组 | 纳入文献数量(篇) | 异质性检验 | 效应模型 | Meta分析结果 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2(%) | P值 | 恶变率(%) | 95%CI(%) | Z值 | P值 | ||||
| 性别 | |||||||||
| 男 | 14[ | 88.22 | <0.001 | 随机效应模型 | 7.6 | (5.1,10.6) | 9.20 | <0.001 | |
| 女 | 14[ | 81.06 | <0.001 | 随机效应模型 | 13.2 | (9.5,17.4) | 11.00 | <0.001 | |
| 年龄 | |||||||||
| <60岁 | 5[ | 58.31 | <0.001 | 随机效应模型 | 12.3 | (9.2,15.7) | 12.18 | <0.001 | |
| ≥60岁 | 4[ | 48.63 | 0.120 | 固定效应模型 | 17.9 | (13.8,22.5) | 13.26 | <0.001 | |
| 恶变部位 | |||||||||
| 舌部 | 9[ | 81.57 | <0.001 | 随机效应模型 | 16.2 | (11.0,22.2) | 9.56 | <0.001 | |
| 其他部位 | 8[ | 76.05 | <0.001 | 随机效应模型 | 6.1 | (3.2,9.6) | 5.98 | <0.001 | |
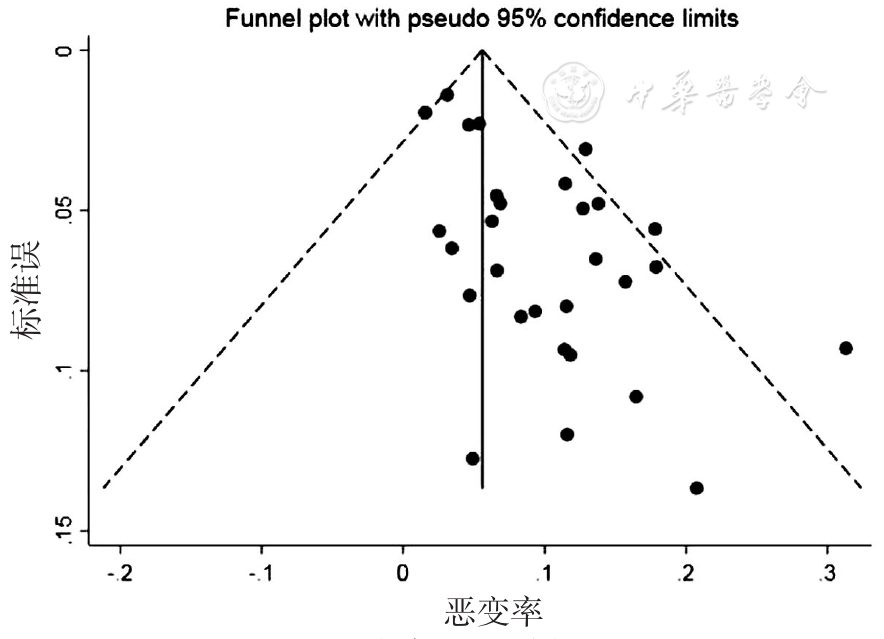
图4 OLK恶变率Meta分析的漏斗图
Figure 4 Funnel plot assessing potential publication bias instudies included in the meta-analysis of malignant transformation rate in Chinese patients with oral leukoplakia
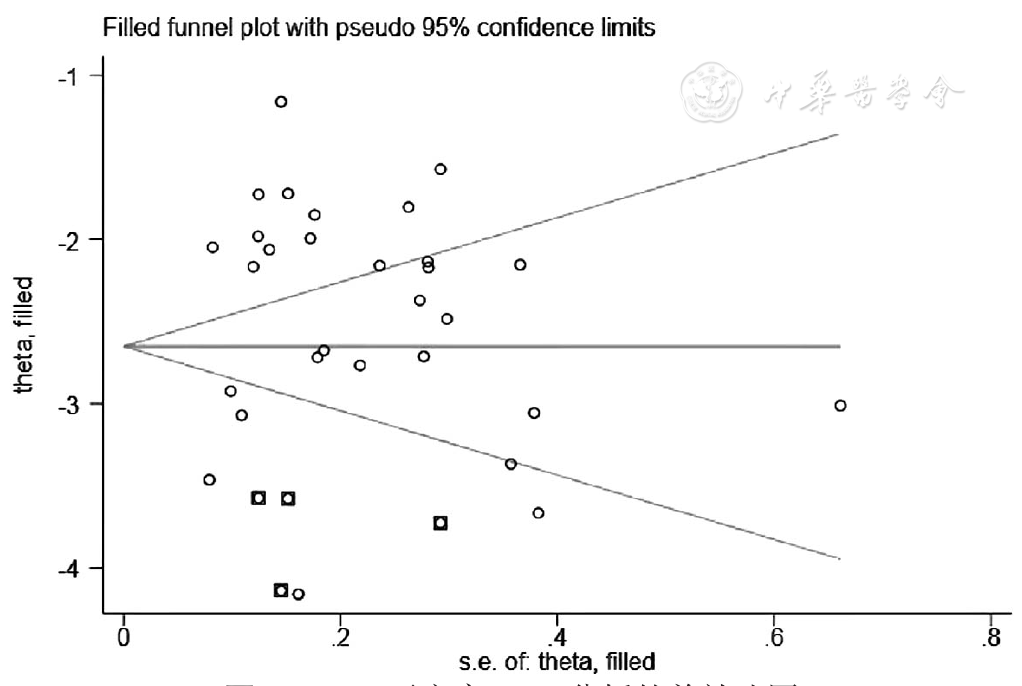
图5 OLK恶变率Meta分析的剪补法图
Figure 5 Trim-and-fill analysis of potential publication bias instudies included in the meta-analysis of malignant transformation rate in Chinese patients with oral leukoplakia
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] | |
| [14] |
王宇峰,尚书,周曾同,等. 口腔白斑癌变率与癌变时间及其影响因素的回顾分析[J]. 上海口腔医学,2011,20(1):55-61.
|
| [15] |
褚青松,苗群爱,郅克谦,等. 150例口腔黏膜白斑的回顾分析[J]. 临床口腔医学志,2009,25(5):311-312. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-1634.2009.05.025.
|
| [16] |
葛化冰,孙正,沈胜利. 211例口腔白斑的临床分析[J]. 北京口腔医学,1999,7(3):117-118.
|
| [17] |
武文妍.口腔白斑临床特征、HPV感染及服用Gp效果研究[D]. 上海:上海交通大学,2018.
|
| [18] |
高岩,郭竹玲,罗海燕,等. 口腔黏膜白斑癌变85例临床病理分析[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志,2012,47(7):410-413. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2012.07.008.
|
| [19] |
蓝爱仙,关晓兵,孙正. 口腔黏膜白斑癌变的相关危险因素分析[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志,2009,44(6):327-331. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2009.06.003.
|
| [20] |
刘宏伟,胡碧琼,曹采方.436例口腔白斑的临床病理资料的分析及随访观察[C]//中国抗癌协会.全国肿瘤流行病学和肿瘤病因学学术会议论文集. 辽宁:中国抗癌协会,2007:87.
|
| [21] | |
| [22] |
史慧宝.口腔粘膜白斑癌变的分析[J]. 上海口腔医学,1992,1(2):63-65.
|
| [23] | |
| [24] |
汪说之,苏倩倩. 口腔白斑313例的组织病理研究[J]. 口腔医学纵横,1985,1(3):128-131.
|
| [25] |
胡碧琼,马慧敏,沙月琴,等. 261例口腔白斑的临床分析[J]. 中华口腔科杂志,1985,20(2):115-117.
|
| [26] |
冯淑梅,陈英新,柳淑杰,等. 吸烟对中老年口腔白斑癌变的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2008,28(9):293-294. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2008.09.044.
|
| [27] |
符攀峰.口腔粘膜白斑临床病理分析[J]. 西藏医药,2017,38(2):11-13.
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [1] | 张爱丽, 侯旗旗, 韩全乐, 张伯亨, 张佳伟, 曹宏霞, 张超, 陈朔华, 吴寿岭, 李康博. 中国北方人群心房颤动与新发慢性肾脏病发病风险的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(36): 4521-4526. |
| [2] | 谢雪梅, 高静, 柏丁兮, 卢贤英, 何佳丽, 李月. 老年人多重用药依从性现状及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(35): 4394-4403. |
| [3] | 王越, 陈晴, 刘鲁蓉. 中国老年人抑郁检出率及影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4329-4335. |
| [4] | 王喆, 董志浩, 郑好, 孔文程, 张玉宽, 张秋月, 韩晶. 针刺干预偏头痛优势方案构建研究:基于熵权TOPSIS法[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(34): 4336-4342. |
| [5] | 蹇秋枫, 徐荣华, 姚倩, 周媛媛. 中国老年脑卒中患者认知障碍患病率和影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4070-4079. |
| [6] | 贾钰, 周紫彤, 曹学华, 胡婉琴, 向凤, 熊浪宇, 王晓霞. 中国40~65岁女性围绝经期综合征发生率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4080-4088. |
| [7] | 张帅, 李琴, 李东锋, 肖金平, 李云鹏. 使用固体燃料与中国老年人高血压发病风险的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4001-4006. |
| [8] | 李纪新, 邱林杰, 任燕, 王文茹, 李美洁, 张晋. 膳食炎症指数与超重和肥胖及腹型肥胖关系的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(32): 4089-4097. |
| [9] | 陈希, 章娟, 李霖, 张佳琪, 吴耀丽, 郭慧, 王超群. 中国中老年人体力活动与全因死亡风险的关系:前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(31): 3890-3895. |
| [10] | 张鹏, 高鹰, 杨洪喜, 万春晓. 中国长寿地区老年人血尿酸水平与慢性肾脏病发病风险研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(31): 3884-3889. |
| [11] | 何静漪, 王芳, 税晓玲, 李玲, 梁倩. 非药物干预改善围绝经期失眠症状疗效的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(31): 3963-3974. |
| [12] | 张懂理, 沈冲, 张卫川, 陈海滨, 赵建军. 程序性死亡因子1/程序性死亡因子1配体抑制剂治疗肾细胞癌有效性及安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(30): 3815-3822. |
| [13] | 温雯, 张凯楠, 陈玉岚, 李瑜, 张向阳. 代谢指数作为预测因子与阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停的相关性分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(30): 3740-3747. |
| [14] | 朱琳, 郭闫葵, 高琛, 陈学志, 王法帅. 单纯西药、中成药及其联合治疗卒中后失眠疗效的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(30): 3823-3832. |
| [15] | 何应梅, 贾雪, 朱国军, 刘冰. 血清尿酸纵向轨迹对新发高三酰甘油血症的影响:前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(29): 3636-3639. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





