中国全科医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (20): 2435-2442.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0190
所属专题: 指南/共识最新文章合辑
• 指南解读 • 下一篇
谭惠文1,2, 唐宇1, 余叶蓉1,2,*( ), 李建薇1,2, 李佳琦1,2, 安振梅1,2, 王椿1,2, 魏懿2
), 李建薇1,2, 李佳琦1,2, 安振梅1,2, 王椿1,2, 魏懿2
收稿日期:2022-02-15
修回日期:2022-03-20
出版日期:2022-07-15
发布日期:2022-05-19
通讯作者:
余叶蓉
基金资助:
Huiwen TAN1,2, Yu TANG1, Yerong YU1,2,*( ), Jianwei LI1,2, Jiaqi LI1,2, Zhenmei AN1,2, Chun WANG1,2, Yi WEI2
), Jianwei LI1,2, Jiaqi LI1,2, Zhenmei AN1,2, Chun WANG1,2, Yi WEI2
Received:2022-02-15
Revised:2022-03-20
Published:2022-07-15
Online:2022-05-19
Contact:
Yerong YU
About author:摘要: 库欣病是以高皮质醇血症为特征的内源性库欣综合征最常见的病因,是由分泌促肾上腺皮质激素(ACTH)的垂体腺瘤引起的临床综合征。库欣病过度分泌的ACTH刺激双侧肾上腺皮质增生并引起高皮质醇血症,可导致电解质紊乱,糖、脂代谢紊乱等一系列严重的临床症候群,累及全身多个脏器及系统。库欣病临床症状复杂多样,其诊断和治疗极具挑战性。国际垂体协会在2021年12月发布了《库欣病的诊断和管理共识(更新版)》,该指南更新关注库欣病的并发症和合并症,诸如高凝状态、心血管疾病、骨代谢疾病、生长激素缺乏及感染等;讨论了最新证据在临床实践中的应用,尤其侧重于新的治疗选择、筛查、诊断算法以及防治疾病复发的最佳实践。本文立足于最新的循证医学证据,对《库欣病的诊断和管理共识(更新版)》讨论的库欣病相关的实验室检查、影像学检查、诊断和治疗管理流程及复发监测等多方面进行重点解读,以期提高广大全科及专科医师对库欣病的理解,更好地指导规范化的诊疗,改善库欣病患者预后。
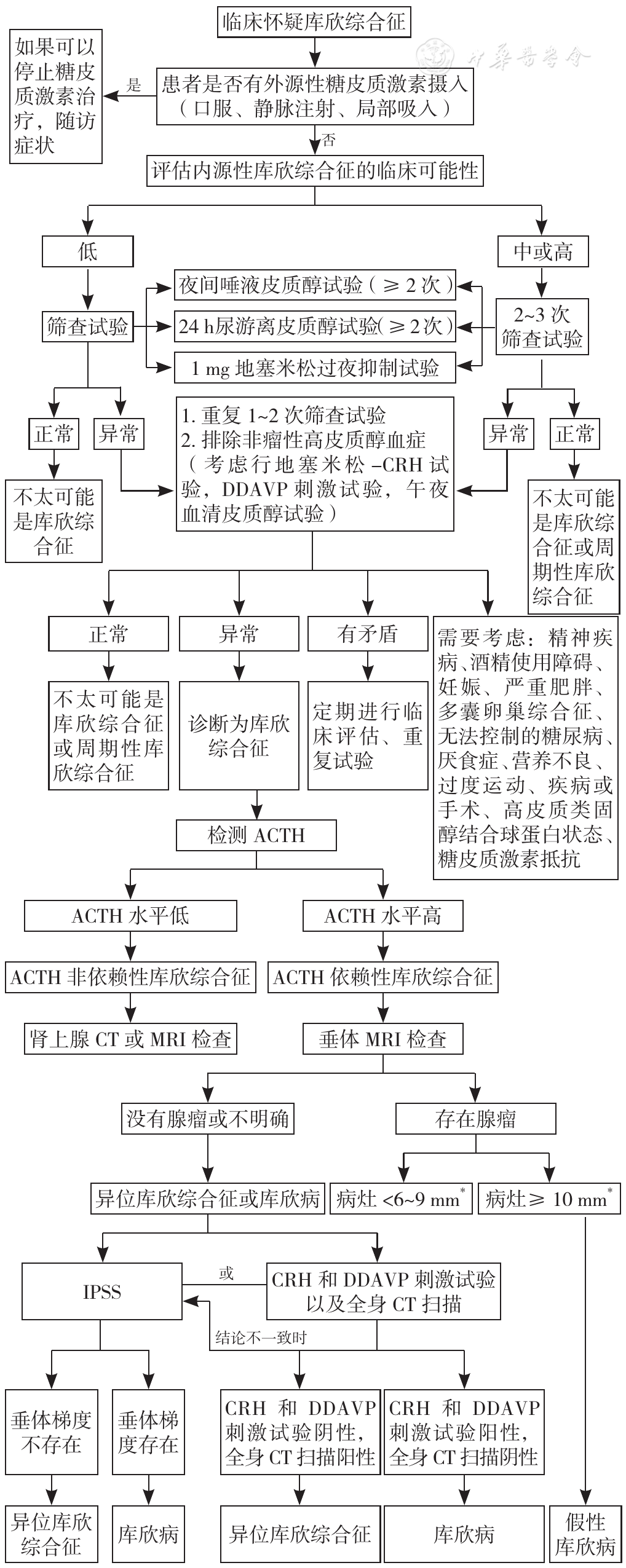
图1 库欣综合征诊断流程图注:ACTH=促肾上腺皮质激素,CRH=促肾上腺皮质激素释放激素,DDAVP=去氨加压素,IPSS=岩下窦静脉采血;*共识认为所有病灶直径<6 mm的患者均应行IPSS,病灶≥10 mm的患者不需要IPSS,但专家对于病灶直径为6~9 mm的病灶意见尚未统一
Figure 1 Diagnostic flow chart of Cushing's syndrome
| 检查项目 | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) | 优、缺点 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS诊断指标 | ||||
| 1 mg-DST | 98 | 81 | 优点:阴性预测值高;易于医疗人员管理 缺点:假阳性率高;地塞米松代谢可影响测定结果;其他药物干扰 | |
| 24 hUFC | 91.0 | 81.5 | 优点:参考范围广 缺点:操作繁琐;样本之间的多变性可能为50%,需要留取2~3个样本 | |
| LNSC | 97.0 | 97.5 | 优点:患者易于操作;应提醒患者在收集唾液样本15 min前不要进食、饮水、吸烟或刷牙 缺点:多变性;根据参考实验室的不同,临界值会有很大的不同;可能被局部氢化可的松污染;并非所有中心均能检测 | |
| CD复发监测 | ||||
| LNSC | 75~90 | 93~95 | 优点:多数患者LNSC的异常早于DST和24 hUFC的异常 缺点:多变性;易出现正常或阴性结果 | |
| 24 hUFC | 68 | 100 | 优点:相对便捷 缺点:大约50%存在变异;容易受体积计量影响而导致异常结果 | |
| DDAVP刺激试验 | 68 | 95 | 优点:可预测存在促肾上腺皮质激素腺瘤;临床腺瘤复发前可以变阳性 缺点:多次采血,动态密集检测 | |
| 1 mg-DST | NA | NA | 优点:可能会在24 hUFC之前出现异常 缺点:评估复发效用方面的证据有限 | |
表1 CS诊断与CD复发监测的实验室检查指标
Table 1 Laboratory tests for Cushing's syndrome diagnosis and monitoring for Cushing's disease recurrence
| 检查项目 | 灵敏度(%) | 特异度(%) | 优、缺点 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS诊断指标 | ||||
| 1 mg-DST | 98 | 81 | 优点:阴性预测值高;易于医疗人员管理 缺点:假阳性率高;地塞米松代谢可影响测定结果;其他药物干扰 | |
| 24 hUFC | 91.0 | 81.5 | 优点:参考范围广 缺点:操作繁琐;样本之间的多变性可能为50%,需要留取2~3个样本 | |
| LNSC | 97.0 | 97.5 | 优点:患者易于操作;应提醒患者在收集唾液样本15 min前不要进食、饮水、吸烟或刷牙 缺点:多变性;根据参考实验室的不同,临界值会有很大的不同;可能被局部氢化可的松污染;并非所有中心均能检测 | |
| CD复发监测 | ||||
| LNSC | 75~90 | 93~95 | 优点:多数患者LNSC的异常早于DST和24 hUFC的异常 缺点:多变性;易出现正常或阴性结果 | |
| 24 hUFC | 68 | 100 | 优点:相对便捷 缺点:大约50%存在变异;容易受体积计量影响而导致异常结果 | |
| DDAVP刺激试验 | 68 | 95 | 优点:可预测存在促肾上腺皮质激素腺瘤;临床腺瘤复发前可以变阳性 缺点:多次采血,动态密集检测 | |
| 1 mg-DST | NA | NA | 优点:可能会在24 hUFC之前出现异常 缺点:评估复发效用方面的证据有限 | |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
李佳琦,孙丽思,余叶蓉. 库欣综合征筛查试验的选择和临床应用[J]. 国际内分泌代谢杂志,2021,41(6):573-577. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn121383-20210831-08083.
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] | |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
茅江峰,柴晓峰,刘丽萍,等. 外周DDAVP兴奋试验在促肾上腺皮质激素依赖性库欣综合征鉴别诊断中的价值[J]. 中国实用内科杂志,2014,34(10):1000-1003.
|
| [33] |
张微微,余叶蓉,谭惠文,等. 精氨酸血管加压素刺激试验与大剂量地塞米松抑制试验在库欣病与异位促肾上腺皮质激素综合征诊断中的价值[J]. 中华医学杂志,2016,96(11):845-849. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2016.11.004.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
朱蕾蕾,余叶蓉,肖珍,等. 清晨血皮质醇及促肾上腺皮质激素水平用作库欣病经蝶术后缓解标准的临床价值[J]. 四川大学学报:医学版,2019,50(2):260-263. DOI:10.13464/j.scuxbyxb.2019.02.024.
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [1] | 郑博月, 付积艺, 吴佳霏, 王珺, 李慧. 卡非佐米治疗多发性骨髓瘤的疗效及安全性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3806-3814. |
| [2] | 贾高鹏, 陈秋雨. 老年急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后心绞痛复发风险预测模型构建和验证:基于CYP2C19相关基因检测[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3779-3786. |
| [3] | 张鹏, 刘力滴, 张颖, 杨梓钰, 刘长明, 唐以俊, 廖晓阳, 贾禹. 2024意大利《成人超重、肥胖和代谢合并症行为治疗抵抗的管理指南》解读与启示[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3747-3752. |
| [4] | 张天宇, 于海搏, 陈飞, 李新, 张佳佳, 詹晓凯, 申曼, 汤然, 范斯斌, 赵凤仪, 黄仲夏. POEMS综合征全身系统性治疗疗效和安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3447-3455. |
| [5] | 崔译元, 闫逸婧, 王颖, 孟祥聚, 张庆林, 刘丽星, 李思聪, 冯利, 癌因性疲乏中西医结合诊疗指南工作组. 癌因性疲乏中西医结合诊疗指南[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(27): 3345-3358. |
| [6] | 王亚静, 段晓阳, 侯冉, 黄娅婕, 史健. 表皮生长因子受体阳性非小细胞肺癌脑转移患者靶向联合治疗研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3328-3337. |
| [7] | 智从从, 李雪, 程一乘, 王孝龙, 郑丽华. 痔中西医结合诊疗指南(2025版)[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3217-3228. |
| [8] | 王汝朋, 南京, 胡奕然, 杨升华, 金泽宁. 三酰甘油-葡萄糖体质量指数对2型糖尿病合并急性心肌梗死行急诊经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后患者慢血流/无复流的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2985-2992. |
| [9] | 李苗秀, 朱博文, 孔令军, 房敏. 青少年脊柱侧弯保守治疗临床评估工具研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3079-3088. |
| [10] | 国家感染性疾病临床医学研究中心江西分中心, 江西省结核病重点实验室. 肺结核合并慢性乙型肝炎病毒感染者治疗专家共识[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 2961-2967. |
| [11] | 阮万百, 李俊峰, 尹艳梅, 彭磊, 朱克祥. 胰腺癌靶向治疗及免疫治疗的研究新进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2950-2960. |
| [12] | 王久格, 湛武逸, 何安霞. 急性心肌梗死经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后早期微循环灌注对左心室功能的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(23): 2878-2884. |
| [13] | 马盼盼, 王思静, 游娜, 丁大法, 鲁一兵. Danuglipron与Orforglipron治疗2型糖尿病疗效及安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2679-2685. |
| [14] | 中国老年医学学会, 浙江省医学会全科医学分会, 全科未分化疾病专家协作组. 消瘦诊治与管理专家共识(2025)[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2577-2594. |
| [15] | 杨江, 李建生, 陈耀龙, 刘辉国, 王建新, 喻佳洁, 李慧茹, 肖琼华, 谢洋, 李素云, 王明航. 中成药治疗成人社区获得性肺炎临床应用指南(2025版)[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(20): 2464-2480. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





