中国全科医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (31): 3933-3943.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0101
• ◆一切为了人民健康——我们这十年·论著·主动健康专题研究 • 上一篇 下一篇
付强强1,2,3,4, 金花1,2,3,4, 李丽5, 马瑜1,2,3,4, 于德华1,2,3,4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-02
修回日期:2022-04-28
出版日期:2022-11-05
发布日期:2022-09-20
通讯作者:
于德华
基金资助:
FU Qiangqiang1,2,3,4, JIN Hua1,2,3,4, LI Li5, MA Yu1,2,3,4, YU Dehua1,2,3,4,*( )
)
Received:2022-03-02
Revised:2022-04-28
Published:2022-11-05
Online:2022-09-20
Contact:
YU Dehua
About author:摘要: 背景 《"健康中国2030"规划纲要》提出:健全覆盖全国的健康素养和生活方式监测体系,强化个人健康责任,提高居民自我健康管理能力和健康水平,提高全民健康素养水平。科学的健康素养测评工具可以系统地了解居民健康素养水平并提供针对性的干预措施。我国的健康素养测评研究起步较晚,现有健康素养测评工具《中国公民健康素养-基本知识与技能(试行)》的评估内容尚存在较大完善空间,因此研发有效、可靠的健康素养评价工具至关重要。 目的 基于主动健康视角,对国内外健康素养评价工具相关文献进行综述。 方法 于2021年7月,以"Health Literacy" "Tool" "Evaluation" "Assessment" "Questionnaire" "Scale" "健康素养" "工具" "测评" "评价" "问卷" "量表"等为中/英文关键词,系统检索PubMed、Web of Science、中国知网、万方数据知识服务平台、维普数据库,以获取健康素养测评工具相关文献,检索时限为1990-01-01至2021-06-30,对健康素养测评工具的现状及内容进行综述。 结果 共筛选出47种健康素养测评工具,包含27个客观测评工具和20个主观测评工具。研发和应用最多的是美国(22个),其次是欧洲地区(13个)。语言方面,英语最多(25个),其次是葡萄牙语(5个)、意大利语(3个)、西班牙语(2个)。测评所需时间方面,成人医学语言阅读能力简化快速测试量表(REALM-SF)、单问题健康素养筛查量表(SILS)用时最短(1 min),汉语健康素养测试量表(MHLS)用时最长(25 min)。测评条目最少的是SILS(1条),最多的是完整版成人医学语言阅读能力测试量表(REALM)(125条)。客观测评工具中被广泛应用的是成人医学语言阅读能力测试量表系列量表(REALM Family)与成人功能性健康素养测试量表系列量表(TOFHLA Family),主观测评工具中被广泛应用的是欧洲健康素养调查问卷(HLS-EU-Q)。测评内容主要涉及阅读理解、计算能力、信息获取、信息应用、信息交流、词汇识别等方面。 结论 在健康素养测评工具的研发和应用中,欧美国家占据主导地位,客观健康素养测评工具数量居多,随着健康素养的内涵从单一的个人评价转变为个人与外部环境的综合评价,我国健康素养测评工具的研发提倡以健康素养内涵深化和主动健康理念为前提,全国建立统一标准,指标以定量或半定量指标为主,开发出涵盖整个生命周期的适合我国国情的健康素养评价工具,从而为提升居民健康素养提供科学、有效的支持。
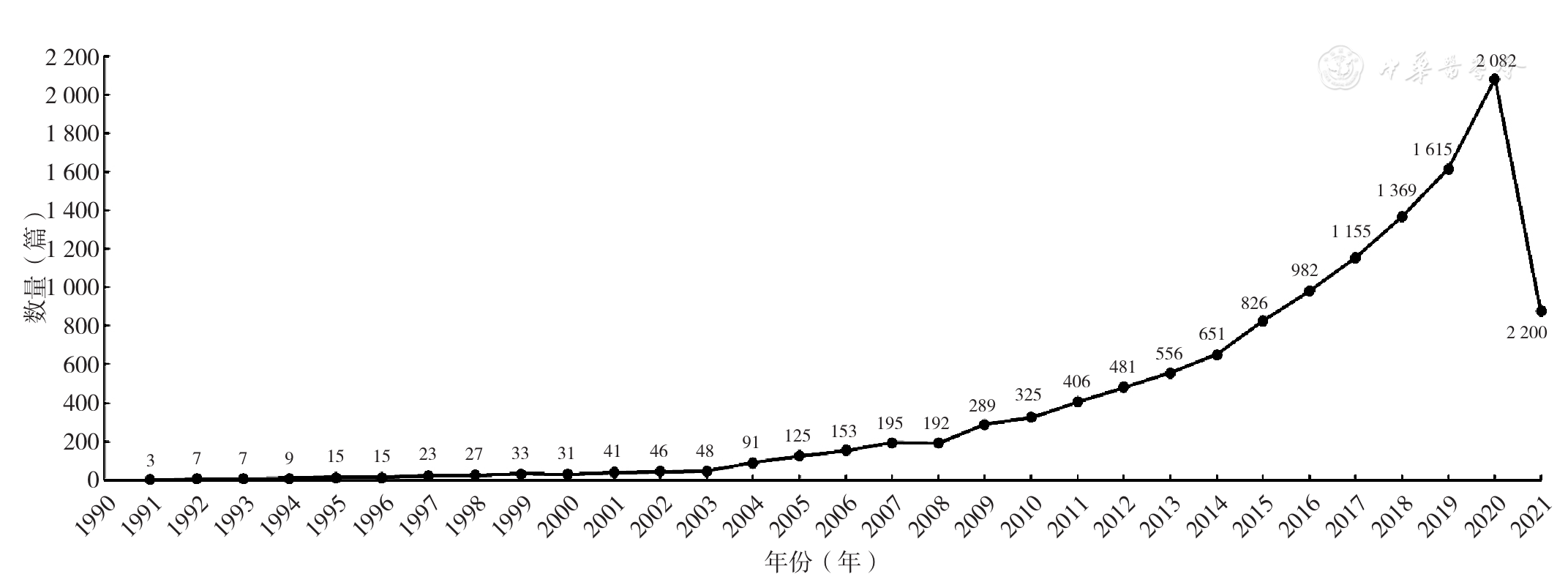
图1 1990—2021年国内外健康素养评价工具相关研究的发文情况注:本文文献检索时限截至2021-06-30,故2021年文献数量不完全
Figure 1 Research on health literacy assessment tools in China and abroad from 1990 to 2021
| 序号 | 评估工具名称 | 作者 | 发表年份(年) | 评估内容 | 评估对象年龄(岁) | 评估形式 | 条目数量(条) | 样本量(例) | 评估时间(min) | 语言 | 受试者国家/地区 | 评定类型 | 量表家族 | 信度(Cronbach's α系数) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | REALM | DAVIS等[ | 1991 | 词汇识别、阅读理解 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 125 | 207 | 2.5 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | REALM Family | 0.99 |
| 2 | REALM-S | DAVIS等[ | 1993 | 词汇识别 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 66 | 230 | 1.5 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | REALM Family | 0.99 |
| 3 | TOFHLA | PAPKER等[ | 1995 | 阅读理解、计算能力、信息获取 | 18~64 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 67 | 200 | 22 | 西班牙语 | 美国 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | 0.98 |
| 4 | S-TOFHLA | BAKER等[ | 1999 | 计算能力、阅读理解 | 18~65 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 40 | 211 | 12 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | 计算能力维度为0.68,阅读理解维度为0.97 |
| 5 | BHLS | CHEW等[ | 2004 | 信息获取 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 3 | 332 | 1.5 | 英语 | 美国 | 主观 | — | — |
| 6 | NVS | WEISS等[ | 2005 | 计算能力、阅读理解、信息获取 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 6 | 148 | 3 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | — |
| 7 | MDIT | SCHWARTZ等[ | 2005 | 阅读理解 | 18~64 | 邮件调查 | 18 | 178 | — | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | — | — |
| 8 | REALM-Teen | DAVIS等[ | 2006 | 阅读理解 | 10~17 | 面谈 | 66 | 1 533 | 2.5 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | REALM Family | 0.94 |
| 9 | SILS | MORRIS等[ | 2006 | 阅读理解、信息应用 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 1 | 999 | 1 | 英语 | 美国 | 主观 | — | — |
| 10 | REALM-SF | AROZULLAH等[ | 2007 | 词汇识别 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 7 | 1 500 | 1 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | REALM Family | — |
| 11 | HHLT | BARON-EPEL等[ | 2007 | 阅读理解、计算能力 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 12 | 119 | — | 希伯来语 | 以色列 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | 0.98 |
| 12 | SNS | FAGERLIN等[ | 2007 | 计算能力 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 8 | 287 | — | 英语 | 美国 | 主观 | — | — |
| 13 | DAHL | HANCHATE等[ | 2008 | 阅读理解、计算能力、信息获取 | >65 | 面谈 | 40 | 9 643 | — | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | — |
| 14 | CCHL | ISHIKAWA等[ | 2008 | 阅读理解、信息获取、信息传播 | 18~64 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 5 | 190 | — | 日语 | 日本 | 主观 | — | — |
| 15 | SAHLE | LEE等[ | 2010 | 词汇识别、计算能力、信息获取 | 18~64 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 18 | 403 | 2.5 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | — | 0.89 |
| 16 | HLSI | MCCORMACK等[ | 2010 | 阅读理解、计算能力、信息获取、信息交流、信息应用 | 18~64 | 电子问卷 | 25 | 889 | 12 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | — | 0.86 |
| 17 | METER | RAWSON等[ | 2010 | 词汇识别、阅读理解 | 18~64 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 40 | 148 | 2 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | REALM Family | — |
| 18 | SEHL | SARKAR等[ | 2011 | 阅读理解 | 10~17或18~64 | 面谈或电话访谈 | 3 | 296 | — | 西班牙语 | 美国 | 主观 | — | — |
| 19 | GLS | GALESIC等[ | 2011 | 计算能力、信息获取、阅读理解、信息应用 | 18~64 | 电子问卷 | 13 | 987 | 9.5 | 英语 | 西班牙、美国、德国 | 客观 | — | — |
| 20 | MHLS | TSAI等[ | 2011 | 阅读理解、计算能力、信息获取 | 18~64 | 纸质问卷 | 63 | 323 | 25 | 汉语 | 中国台湾 | 客观 | — | — |
| 21 | eHEALS | VAART等[ | 2011 | 信息获取、信息交流 | 18~64 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 8 | 277 | 5 | 荷兰语 | 荷兰 | 主观 | — | — |
| 22 | TAIMI | TAKAHASHI等[ | 2011 | 阅读理解、计算能力 | 18~64 | 电子问卷 | 7 | 6 047 | — | 日语 | 日本 | 主观 | — | — |
| 23 | BNT-S | COKELY等[ | 2012 | 计算能力 | 18~64 | 电子问卷、纸质问卷 | 4 | — | 3 | 英语 | 美国、德国 | 客观 | — | — |
| 24 | SAHLPA-18 | APOLINARIO等[ | 2012 | 词汇识别、阅读理解 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 18 | 226 | 1.5 | 葡萄牙语 | 巴西 | 客观 | REALM Family | 0.90 |
| 25 | HLSI-10 | BANN等[ | 2012 | 阅读理解、计算能力、信息获取、信息交流、信息应用 | 18~64 | 纸质问卷、面谈 | 10 | 889 | 5 | 英语 | 美国、德国 | 客观 | — | — |
| 26 | NUMi | SCHAPIRA等[ | 2012 | 计算能力 | 18~64 | 纸质问卷、面谈 | 20 | 1 000 | — | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | — | 0.86 |
| 27 | SAHLPA-50 | APOLINARIO等[ | 2012 | 词汇识别、阅读理解 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 50 | 226 | 4.5 | 葡萄牙语 | 巴西 | 客观 | REALM Family | 0.93 |
| 28 | BRIEF | HAUN等[ | 2012 | 信息获取 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 4 | 378 | 2 | 英语 | 美国 | 主观 | — | — |
| 29 | C-eHEALS | KOO等[ | 2012 | 信息获取、信息交流 | 10~17 | 纸质问卷、面谈 | 8 | 216 | — | 汉语 | 中国台湾 | 主观 | — | 0.92 |
| 30 | STOFHLA | CONNOR等[ | 2013 | 阅读理解、计算能力 | 18~64 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 40 | 659 | 12 | 法语、德语、意大利语 | 瑞士 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | — |
| 31 | CHLCC | LEUNG等[ | 2013 | 阅读理解、信息应用 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 20 | 262 | 7 | 汉语 | 中国 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | — |
| 32 | AAHLS | CHINN等[ | 2013 | 信息应用 | 18~64 | 纸质问卷 | 14 | 146 | 7 | 英语 | 英国 | 主观 | — | 0.74 |
| 33 | HeLMS | JORDAN等[ | 2013 | 阅读理解、信息获取、信息应用 | 18~64 | 纸质问卷 | 29 | 683 | — | 英语 | 澳大利亚 | 主观 | — | — |
| 34 | METER-PT | PAIVA等[ | 2014 | 词汇识别、阅读理解 | 18~64或≥65 | 纸质问卷 | 70 | 249 | 3 | 葡萄牙语 | 葡萄牙 | 客观 | REALM Family | 0.89 |
| 35 | HLS-EU-Q47 | NAKAYAMA等[ | 2015 | 阅读理解、信息获取、信息应用 | 18~64 | 电子问卷 | 47 | 1 054 | — | 日语 | 日本 | 主观 | — | 0.97 |
| 36 | eHEALS | CHUNG等[ | 2015 | 信息获取、信息交流、信息应用 | 18~64 | 电子问卷 | 8 | 866 | — | 英语 | 美国 | 主观 | — | 0.94 |
| 37 | HELMA | GHANBARI等[ | 2016 | 计算能力、阅读理解、信息应用 | 10~17 | 纸质问卷 | 44 | 582 | — | 英语 | 伊朗 | 主观 | — | — |
| 38 | NVS-PT | PAIVA等[ | 2017 | 计算能力、阅读理解、信息应用 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 6 | 249 | 5 | 葡萄牙语 | 葡萄牙 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | 0.85 |
| 39 | NVS-BR | RODRIGUES等[ | 2017 | 计算能力、阅读理解、信息交流 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 6 | 490 | 7 | 葡萄牙语 | 巴西 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | 0.75 |
| 40 | HLS-EU-Q16 | EFTHYMIOU等[ | 2017 | 信息获取、信息应用、信息交流 | 18~64或≥65 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 16 | 107 | 15 | 希腊语 | 希腊、塞浦路斯 | 主观 | — | 0.77 |
| 41 | HL-SDHQ | MATSUMOTO等[ | 2017 | 阅读理解、信息应用 | 18~64或≥65 | 电子问卷 | 33 | 831 | 15 | 日语 | 日本 | 主观 | — | 0.92 |
| 42 | SILS-IT | BONACCIRSI等[ | 2017 | 阅读理解、信息应用 | 18~64或≥65 | 面谈 | 1 | 174 | 1 | 意大利语 | 意大利 | 主观 | — | — |
| 43 | NVS-HR | BRANGAN等[ | 2018 | 计算能力、阅读理解 | 18~64或≥65 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 6 | 100 | 4 | 克罗地亚语 | 克罗地亚 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | — |
| 44 | CCHLS | PLEASANT等[ | 2018 | 阅读理解,信息获取、信息交流、信息应用 | 18~64或≥65 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 5 | 633 | — | 英语 | 美国 | 主观 | — | 0.80 |
| 45 | PPSI | AYRE等[ | 2020 | 阅读理解、计算能力、信息获取、信息交流、信息应用 | 18~64 | 电子问卷 | 13 | 1 000 | 8 | 英语 | 澳大利亚 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | 0.70 |
| 46 | HLS-Child-Q15 | BOLLWEG等[ | 2020 | 阅读理解、信息交流、信息应用 | 0~9或10~17 | 纸质问卷 | 15 | 907 | 10 | 德语 | 德国 | 主观 | — | 0.79 |
| 47 | HLVa-IT | BIASIO等[ | 2020 | 阅读理解、信息获取、信息交流 | 18~64或≥65 | 纸质问卷 | 14 | 200 | 5 | 意大利语 | 意大利 | 主观 | — | 0.82 |
表1 47个健康素养评价工具的基本特征
Table 1 Study characteristics of 47 health literacy assessment tools
| 序号 | 评估工具名称 | 作者 | 发表年份(年) | 评估内容 | 评估对象年龄(岁) | 评估形式 | 条目数量(条) | 样本量(例) | 评估时间(min) | 语言 | 受试者国家/地区 | 评定类型 | 量表家族 | 信度(Cronbach's α系数) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | REALM | DAVIS等[ | 1991 | 词汇识别、阅读理解 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 125 | 207 | 2.5 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | REALM Family | 0.99 |
| 2 | REALM-S | DAVIS等[ | 1993 | 词汇识别 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 66 | 230 | 1.5 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | REALM Family | 0.99 |
| 3 | TOFHLA | PAPKER等[ | 1995 | 阅读理解、计算能力、信息获取 | 18~64 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 67 | 200 | 22 | 西班牙语 | 美国 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | 0.98 |
| 4 | S-TOFHLA | BAKER等[ | 1999 | 计算能力、阅读理解 | 18~65 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 40 | 211 | 12 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | 计算能力维度为0.68,阅读理解维度为0.97 |
| 5 | BHLS | CHEW等[ | 2004 | 信息获取 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 3 | 332 | 1.5 | 英语 | 美国 | 主观 | — | — |
| 6 | NVS | WEISS等[ | 2005 | 计算能力、阅读理解、信息获取 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 6 | 148 | 3 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | — |
| 7 | MDIT | SCHWARTZ等[ | 2005 | 阅读理解 | 18~64 | 邮件调查 | 18 | 178 | — | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | — | — |
| 8 | REALM-Teen | DAVIS等[ | 2006 | 阅读理解 | 10~17 | 面谈 | 66 | 1 533 | 2.5 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | REALM Family | 0.94 |
| 9 | SILS | MORRIS等[ | 2006 | 阅读理解、信息应用 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 1 | 999 | 1 | 英语 | 美国 | 主观 | — | — |
| 10 | REALM-SF | AROZULLAH等[ | 2007 | 词汇识别 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 7 | 1 500 | 1 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | REALM Family | — |
| 11 | HHLT | BARON-EPEL等[ | 2007 | 阅读理解、计算能力 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 12 | 119 | — | 希伯来语 | 以色列 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | 0.98 |
| 12 | SNS | FAGERLIN等[ | 2007 | 计算能力 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 8 | 287 | — | 英语 | 美国 | 主观 | — | — |
| 13 | DAHL | HANCHATE等[ | 2008 | 阅读理解、计算能力、信息获取 | >65 | 面谈 | 40 | 9 643 | — | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | — |
| 14 | CCHL | ISHIKAWA等[ | 2008 | 阅读理解、信息获取、信息传播 | 18~64 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 5 | 190 | — | 日语 | 日本 | 主观 | — | — |
| 15 | SAHLE | LEE等[ | 2010 | 词汇识别、计算能力、信息获取 | 18~64 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 18 | 403 | 2.5 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | — | 0.89 |
| 16 | HLSI | MCCORMACK等[ | 2010 | 阅读理解、计算能力、信息获取、信息交流、信息应用 | 18~64 | 电子问卷 | 25 | 889 | 12 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | — | 0.86 |
| 17 | METER | RAWSON等[ | 2010 | 词汇识别、阅读理解 | 18~64 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 40 | 148 | 2 | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | REALM Family | — |
| 18 | SEHL | SARKAR等[ | 2011 | 阅读理解 | 10~17或18~64 | 面谈或电话访谈 | 3 | 296 | — | 西班牙语 | 美国 | 主观 | — | — |
| 19 | GLS | GALESIC等[ | 2011 | 计算能力、信息获取、阅读理解、信息应用 | 18~64 | 电子问卷 | 13 | 987 | 9.5 | 英语 | 西班牙、美国、德国 | 客观 | — | — |
| 20 | MHLS | TSAI等[ | 2011 | 阅读理解、计算能力、信息获取 | 18~64 | 纸质问卷 | 63 | 323 | 25 | 汉语 | 中国台湾 | 客观 | — | — |
| 21 | eHEALS | VAART等[ | 2011 | 信息获取、信息交流 | 18~64 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 8 | 277 | 5 | 荷兰语 | 荷兰 | 主观 | — | — |
| 22 | TAIMI | TAKAHASHI等[ | 2011 | 阅读理解、计算能力 | 18~64 | 电子问卷 | 7 | 6 047 | — | 日语 | 日本 | 主观 | — | — |
| 23 | BNT-S | COKELY等[ | 2012 | 计算能力 | 18~64 | 电子问卷、纸质问卷 | 4 | — | 3 | 英语 | 美国、德国 | 客观 | — | — |
| 24 | SAHLPA-18 | APOLINARIO等[ | 2012 | 词汇识别、阅读理解 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 18 | 226 | 1.5 | 葡萄牙语 | 巴西 | 客观 | REALM Family | 0.90 |
| 25 | HLSI-10 | BANN等[ | 2012 | 阅读理解、计算能力、信息获取、信息交流、信息应用 | 18~64 | 纸质问卷、面谈 | 10 | 889 | 5 | 英语 | 美国、德国 | 客观 | — | — |
| 26 | NUMi | SCHAPIRA等[ | 2012 | 计算能力 | 18~64 | 纸质问卷、面谈 | 20 | 1 000 | — | 英语 | 美国 | 客观 | — | 0.86 |
| 27 | SAHLPA-50 | APOLINARIO等[ | 2012 | 词汇识别、阅读理解 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 50 | 226 | 4.5 | 葡萄牙语 | 巴西 | 客观 | REALM Family | 0.93 |
| 28 | BRIEF | HAUN等[ | 2012 | 信息获取 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 4 | 378 | 2 | 英语 | 美国 | 主观 | — | — |
| 29 | C-eHEALS | KOO等[ | 2012 | 信息获取、信息交流 | 10~17 | 纸质问卷、面谈 | 8 | 216 | — | 汉语 | 中国台湾 | 主观 | — | 0.92 |
| 30 | STOFHLA | CONNOR等[ | 2013 | 阅读理解、计算能力 | 18~64 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 40 | 659 | 12 | 法语、德语、意大利语 | 瑞士 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | — |
| 31 | CHLCC | LEUNG等[ | 2013 | 阅读理解、信息应用 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 20 | 262 | 7 | 汉语 | 中国 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | — |
| 32 | AAHLS | CHINN等[ | 2013 | 信息应用 | 18~64 | 纸质问卷 | 14 | 146 | 7 | 英语 | 英国 | 主观 | — | 0.74 |
| 33 | HeLMS | JORDAN等[ | 2013 | 阅读理解、信息获取、信息应用 | 18~64 | 纸质问卷 | 29 | 683 | — | 英语 | 澳大利亚 | 主观 | — | — |
| 34 | METER-PT | PAIVA等[ | 2014 | 词汇识别、阅读理解 | 18~64或≥65 | 纸质问卷 | 70 | 249 | 3 | 葡萄牙语 | 葡萄牙 | 客观 | REALM Family | 0.89 |
| 35 | HLS-EU-Q47 | NAKAYAMA等[ | 2015 | 阅读理解、信息获取、信息应用 | 18~64 | 电子问卷 | 47 | 1 054 | — | 日语 | 日本 | 主观 | — | 0.97 |
| 36 | eHEALS | CHUNG等[ | 2015 | 信息获取、信息交流、信息应用 | 18~64 | 电子问卷 | 8 | 866 | — | 英语 | 美国 | 主观 | — | 0.94 |
| 37 | HELMA | GHANBARI等[ | 2016 | 计算能力、阅读理解、信息应用 | 10~17 | 纸质问卷 | 44 | 582 | — | 英语 | 伊朗 | 主观 | — | — |
| 38 | NVS-PT | PAIVA等[ | 2017 | 计算能力、阅读理解、信息应用 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 6 | 249 | 5 | 葡萄牙语 | 葡萄牙 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | 0.85 |
| 39 | NVS-BR | RODRIGUES等[ | 2017 | 计算能力、阅读理解、信息交流 | 18~64 | 面谈 | 6 | 490 | 7 | 葡萄牙语 | 巴西 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | 0.75 |
| 40 | HLS-EU-Q16 | EFTHYMIOU等[ | 2017 | 信息获取、信息应用、信息交流 | 18~64或≥65 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 16 | 107 | 15 | 希腊语 | 希腊、塞浦路斯 | 主观 | — | 0.77 |
| 41 | HL-SDHQ | MATSUMOTO等[ | 2017 | 阅读理解、信息应用 | 18~64或≥65 | 电子问卷 | 33 | 831 | 15 | 日语 | 日本 | 主观 | — | 0.92 |
| 42 | SILS-IT | BONACCIRSI等[ | 2017 | 阅读理解、信息应用 | 18~64或≥65 | 面谈 | 1 | 174 | 1 | 意大利语 | 意大利 | 主观 | — | — |
| 43 | NVS-HR | BRANGAN等[ | 2018 | 计算能力、阅读理解 | 18~64或≥65 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 6 | 100 | 4 | 克罗地亚语 | 克罗地亚 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | — |
| 44 | CCHLS | PLEASANT等[ | 2018 | 阅读理解,信息获取、信息交流、信息应用 | 18~64或≥65 | 面谈、纸质问卷 | 5 | 633 | — | 英语 | 美国 | 主观 | — | 0.80 |
| 45 | PPSI | AYRE等[ | 2020 | 阅读理解、计算能力、信息获取、信息交流、信息应用 | 18~64 | 电子问卷 | 13 | 1 000 | 8 | 英语 | 澳大利亚 | 客观 | TOFHLA Family | 0.70 |
| 46 | HLS-Child-Q15 | BOLLWEG等[ | 2020 | 阅读理解、信息交流、信息应用 | 0~9或10~17 | 纸质问卷 | 15 | 907 | 10 | 德语 | 德国 | 主观 | — | 0.79 |
| 47 | HLVa-IT | BIASIO等[ | 2020 | 阅读理解、信息获取、信息交流 | 18~64或≥65 | 纸质问卷 | 14 | 200 | 5 | 意大利语 | 意大利 | 主观 | — | 0.82 |
| 序号 | 测评内容 | 测评工具数量(个) | 百分比(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 阅读理解 | 34 | 72.3 |
| 2 | 计算能力 | 20 | 42.6 |
| 3 | 信息获取 | 20 | 42.6 |
| 4 | 信息应用 | 17 | 36.2 |
| 5 | 信息交流 | 11 | 23.4 |
| 6 | 词汇识别 | 8 | 17.0 |
表2 健康素养评价工具的测评内容
Table 2 Analysis of the evaluation content of the health literacy assessment tools
| 序号 | 测评内容 | 测评工具数量(个) | 百分比(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 阅读理解 | 34 | 72.3 |
| 2 | 计算能力 | 20 | 42.6 |
| 3 | 信息获取 | 20 | 42.6 |
| 4 | 信息应用 | 17 | 36.2 |
| 5 | 信息交流 | 11 | 23.4 |
| 6 | 词汇识别 | 8 | 17.0 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] | |
| [3] | |
| [4] | |
| [5] | |
| [6] |
刘小娜,常春,孙昕霙. 健康素养全球研究概况及其在中国的发展展望[J]. 中国健康教育,2012,28(2):150-153. DOI:10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2012.02.022.
|
| [7] | |
| [8] |
张士靖,李信,刘海通. 国际健康素养测评工具概述[J]. 中国健康教育,2014,30(10):920-924. DOI:10.16168/j.cnki.issn.1002-9982.2014.10.016.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [1] | 卫梦雨, 王佳佳, 张莹莹, 李春阳, 李建生. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停患者报告结局测评工具研究现状分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(30): 3725-3733. |
| [2] | 段玉霞, 李珍, 张斯齐, 房志学, 秦月兰. 结直肠癌诊疗中患者决策辅助工具应用效果的系统评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(25): 3194-3201. |
| [3] | 韩知浩, 马小琴. 癌症晚期患者代理决策者预立医疗照护计划参与度影响因素的混合方法系统评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(22): 2785-2792. |
| [4] | 刘晶涛, 苏荷, 秦小金, 兰云霞, 张金枝. 冠心病患者心脏康复相关指南的系统评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(19): 2323-2331. |
| [5] | 张露露, 陈欢, 罗欢, 陈婷婷, 陈昕羽, 高静. 基于健康测量工具的共识标准对癌症复发恐惧评估工具的系统评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(17): 2138-2146. |
| [6] | 袁程, 魏晓敏, 武晓宇, 刘惠琳, 姜综敏. 中老年居民网络健康信息使用习惯与其电子健康素养的关系研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(16): 1989-1994. |
| [7] | 章雨桐, 王秋琴, 徐语晨, 翁恒, 梁咏琪, 汪露露, 王庆, 徐桂华. 帕金森病患者疼痛影响因素的系统评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(14): 1766-1774. |
| [8] | 郑卿勇, 赵亮, 隗伟, 任雪君, 王超, 孙瑞, 丛明华, 于雷, 杨敏. 正念减压疗法可改善乳腺癌患者心理状况:基于系统评价再评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(12): 1503-1512. |
| [9] | 李玲玲, 黄海量, 于莹, 贾雨琦, 刘志遥, 石鑫, 王方琪, 刘鑫玥. 非侵入性脑刺激对孤独症谱系障碍治疗效果的系统评价及网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(11): 1389-1397. |
| [10] | 王茜茜, 沈睿, 王俊杰, 徐霓影. 绝经后骨质疏松症患者运动干预的最佳证据总结[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(09): 1151-1158. |
| [11] | 李家青, 杨晴, 袁敦禄, 黄晶晶, 常青, 聂静雯, 周竹, 李青. 罗沙司他治疗血液透析患者肾性贫血的有效性和安全性Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(06): 704-710. |
| [12] | 黄梦洁, 曾雷霄, 葛蒲, 闵鹤葳, 黄新城, 王雨佳, 吴一波. 社区居民健康科普需求及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(04): 426-433. |
| [13] | 皇甫晓娟, 李小娟, 陈敏, 刘吉红, 翟蕊, 蔡志鹏, 李俐涛. 新型冠状病毒感染对脑卒中患者病死率影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(03): 348-355. |
| [14] | 王哲, 赵海滨, 汪国梁, 马晓娟, 殷惠军. 完全血运重建治疗急性心肌梗死合并多支血管病变效果的系统评价再评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(02): 142-153. |
| [15] | 沈巧, 唐语蔓, 冷虹瑶, 雷若冰, 郑显兰. 新生儿疼痛评估量表测量学性能的系统评价再评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(35): 4453-4461. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





