中国全科医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (28): 3579-3586.DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2022.0084
所属专题: 全民健康最新文章合辑; 全科质控专项研究
• 医学循证 • 上一篇
史钊1,2,3, 李顺平1,2,3,*( ), 吴小燕1,2,3, 刘嘉琪1,2,3, 杜慧敏1,2,3
), 吴小燕1,2,3, 刘嘉琪1,2,3, 杜慧敏1,2,3
收稿日期:2022-02-14
修回日期:2022-06-12
出版日期:2022-10-05
发布日期:2022-07-14
通讯作者:
李顺平
基金资助:
Zhao SHI1,2,3, Shunping LI1,2,3,*( ), Xiaoyan WU1,2,3, Jiaqi LIU1,2,3, Huimin DU1,2,3
), Xiaoyan WU1,2,3, Jiaqi LIU1,2,3, Huimin DU1,2,3
Received:2022-02-14
Revised:2022-06-12
Published:2022-10-05
Online:2022-07-14
Contact:
Shunping LI
About author:摘要: 背景 健康相关生命质量(HRQoL)是用于评价临床疗效的重要指标。目前,不孕不育患者HRQoL量表得到了广泛应用,但尚不确定这些量表应用于临床时是否具有良好的测量性能,缺乏对量表的质量评价。 目的 系统综述与评价不孕不育患者HRQoL量表,为合理选择健康结果测量工具提供参考。 方法 于2020年10月,计算机检索PubMed、Web of Science、the Cochrane Library、EmBase、中国知网、万方数据知识服务平台、维普中文科技期刊全文数据库和中国生物医学文献数据库,获取国内外公开发表的有关不孕不育患者HRQoL的研究,检索时限均为建库至2020-10-05。由两名研究者独立筛选文献和提取资料后,采用健康测量工具遴选标准(COSMIN)对不孕不育患者HRQoL特异性量表开发研究的方法学质量,以及量表的测量性能进行评价,采用描述分析法对评价结果进行汇总、分析。 结果 共纳入229篇文献,涉及19个不孕不育患者HRQoL量表,其中4个为不孕不育患者HRQoL特异性量表〔TLMK、生育生活质量量表(FertiQoL)、QOLICQ及中医肝郁型不孕症生命质量量表〕,4个为用于测评癌症及其他疾病患者HRQoL的特异性量表,11个为普适性HRQoL量表,FertiQoL量表在现有不孕不育患者HRQoL相关研究中被使用的频次最高〔39.1%(91/233)〕。PROMs开发方面,除FertiQoL量表开发的总体质量为"有问题的"外,其余3个量表开发的总体质量均为"不合格"。内容效度方面,FertiQoL、QOLICQ量表开发研究的方法学质量分别为"非常好""有问题的",TLMK、中医肝郁型不孕症生命质量量表开发研究的方法学质量均为"合格"。结构效度方面,除QOLICQ量表开发研究方法学质量为"有问题的"外,其余3个量表开发研究的方法学质量为"合格";4个量表的结构效度均为"不确定"。内部一致性方面,4个量表开发研究的方法学质量均为"非常好",4个量表的内部一致性均为"足够"。重测信度方面,QOLICQ量表开发研究的方法学质量为"有问题的",量表的重测信度为"不确定"。效标效度方面,中医肝郁型不孕症生命质量量表开发研究的方法学质量为"非常好",量表的效标效度为"足够"。建构效度方面,TLMK量表开发研究的方法学质量为"非常好",量表的建构效度为"足够"。反应度/灵敏度方面,FertiQoL量表开发研究的方法学质量为"非常好",量表的反应度/灵敏度为"足够"。 结论 现存的不孕不育患者HRQoL特异性量表中,FertiQoL量表开发研究的方法学质量及量表的测量性能相对较高。中国不孕不育患者HRQoL特异性量表研究数量相对不足,未来应开展更多的研究。
| 研制者(第一作者) | 量表(全)简称 | 研制时间(年) | 适用对象 | 研制国家/地区(组织) | 量表维度 | 量表条目数(条) | 有无中文版 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不孕不育患者HRQoL特异性量表 | ||||||||
| SCHANZ等[ | TLMK | 2005 | 男性不育患者 | 德国 | 4个维度a:对孩子的渴望(desire for a child)、两性关系(sexual relationship)、性别认同(gender identity)、心理幸福感(psychological well-being) | 35 | 无 | |
| BOIVIN等[ | FertiQoL | 2011 | 不孕不育夫妇 | 欧洲人类生殖和胚胎学会/美国生殖医学协会 | 6个维度:情感、认知/躯体、伴侣关系、社会关系、环境、耐受性 | 36 | 有 | |
| FARIDEH等[ | QOLICQ | 2013 | 不孕不育夫妇 | 伊朗 | 7个维度a:身体(physical)、心理(psychological)、精神和宗教信仰(spiritual and religious beliefs)、经济(economic)、性生活(sexual)、情感(emotional)和社会(social) | 72 | 无 | |
| 王英[ | 中医肝郁型不孕症生命质量量表 | 2017 | 女性不孕患者 | 中国 | 4个维度:症状体征、情志状态、社会功能状态、满意度 | 29 | 有 | |
| 其他疾病患者HRQoL特异性量表 | ||||||||
| AARONSON等[ | EORTC QLQ-C30 | 1993 | 癌症患者 | 欧洲癌症研究治疗组织 | 5个维度:躯体功能、认知功能、情绪功能、角色功能、社会功能 | 30 | 有 | |
| CRONIN等[ | PCOSQ | 1998 | 多囊卵巢综合征患者 | 美国 | 5个维度:情绪障碍、多毛症、肥胖、不孕、月经失调 | 26 | 有 | |
| JONES等[ | EHP-30 | 2001 | 子宫内膜异位症患者 | 英国 | 第1部分包括5个维度:疼痛、控制和无力感、情绪健康、社会支持和自我形象。第2部分包括6个维度:雇佣工作、与孩子之间的关系、性生活、对医疗职业的感受、治疗情况和不孕 | 53(30+23) | 有 | |
| BARNARD等[ | MPCOSQ | 2007 | 多囊卵巢综合征患者 | 加拿大 | 6个维度:情绪障碍、多毛症、肥胖、痤疮、不孕、月经失调(也可分为月经症状及月经的可预见性) | 30 | 有 | |
| 普适性HRQoL量表 | ||||||||
| HUNT等[ | NHP | 1981 | 一般人群 | 英国 | 第1部分健康问卷包括6个维度:躯体活动、精力、疼痛、睡眠、社会关系、情感反应。第2部分个人生活包括7个方面:工作、照料家庭、社会生活、家庭生活、性生活、爱好与兴趣、度假 | 45 | 有 | |
| FERRANS等[ | QLI | 1985 | 一般人群或特定疾病人群 | 美国 | 4个维度a:健康和身体功能(health and functioning)、社会经济(socio-economic)、心理/精神(psychological/spiritual)、家庭(family)[ | 32 | 无 | |
| WARE等[ | SF-36 | 1992 | 一般人群 | 美国 | 8个维度:生理机能、生理职能、躯体疼痛、一般健康状况、精力、社会功能、情感职能、精神健康 | 36 | 有 | |
| The WHOQOL Group[ | WHOQOL-100 | 1994 | 一般人群 | WHO | 6个领域:生理、心理、独立性、社会关系、环境、精神/宗教信仰 | 100 | 有 | |
| MICHAEL[ | QOLI | 1994 | 一般人群 | 美国 | 16个维度a:健康(health)、自尊(self-esteem)、目标和价值观(goals and values)、经济(money)、工作(work)、娱乐(play)、学习(learning)、创造力(creativity)、帮助(helping)、爱(love)、朋友(friends)、孩子(children)、亲戚(relatives)、家庭(home)、邻里(neighbourhood)、社区(community) | 32 | 无 | |
| WARE等[ | SF-12 | 1996 | 一般人群 | 美国 | 8个维度:生理功能、身体角色限制、情感角色限制、心理健康、身体疼痛、总体健康、活力、社会功能 | 12 | 有 | |
| HICKEY等[ | SEIQoL-DW | 1996 | 一般人群 | 爱尔兰 | NR | NR | 无 | |
| KAPLAN等[ | QWB-SA | 1997 | 一般人群 | 美国 | 4个部分:移动、生理活动、社会活动和58个症状/复合健康问题 | 61 | 有 | |
| The WHOQOL Group[ | WHOQOL-BREF | 1998 | 一般人群 | WHO | 4个领域:生理、心理、社会关系、环境 | 26 | 有 | |
| 李凌江等[ | GQOLI-74 | 1999 | 一般人群 | 中国 | 4个维度:躯体功能、心理功能、社会功能、物质生活状态 | 74 | 有 | |
| 刘凤斌等[ | ChQOL | 2007 | 一般人群 | 中国 | 3个领域:形(身体机能)、神(意识思维)、情志(七情) | 50 | 有 | |
表1 纳入的不孕不育患者HRQoL量表的基本信息
Table 1 Basic characteristics of the included HRQoL instruments for infertility patients
| 研制者(第一作者) | 量表(全)简称 | 研制时间(年) | 适用对象 | 研制国家/地区(组织) | 量表维度 | 量表条目数(条) | 有无中文版 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不孕不育患者HRQoL特异性量表 | ||||||||
| SCHANZ等[ | TLMK | 2005 | 男性不育患者 | 德国 | 4个维度a:对孩子的渴望(desire for a child)、两性关系(sexual relationship)、性别认同(gender identity)、心理幸福感(psychological well-being) | 35 | 无 | |
| BOIVIN等[ | FertiQoL | 2011 | 不孕不育夫妇 | 欧洲人类生殖和胚胎学会/美国生殖医学协会 | 6个维度:情感、认知/躯体、伴侣关系、社会关系、环境、耐受性 | 36 | 有 | |
| FARIDEH等[ | QOLICQ | 2013 | 不孕不育夫妇 | 伊朗 | 7个维度a:身体(physical)、心理(psychological)、精神和宗教信仰(spiritual and religious beliefs)、经济(economic)、性生活(sexual)、情感(emotional)和社会(social) | 72 | 无 | |
| 王英[ | 中医肝郁型不孕症生命质量量表 | 2017 | 女性不孕患者 | 中国 | 4个维度:症状体征、情志状态、社会功能状态、满意度 | 29 | 有 | |
| 其他疾病患者HRQoL特异性量表 | ||||||||
| AARONSON等[ | EORTC QLQ-C30 | 1993 | 癌症患者 | 欧洲癌症研究治疗组织 | 5个维度:躯体功能、认知功能、情绪功能、角色功能、社会功能 | 30 | 有 | |
| CRONIN等[ | PCOSQ | 1998 | 多囊卵巢综合征患者 | 美国 | 5个维度:情绪障碍、多毛症、肥胖、不孕、月经失调 | 26 | 有 | |
| JONES等[ | EHP-30 | 2001 | 子宫内膜异位症患者 | 英国 | 第1部分包括5个维度:疼痛、控制和无力感、情绪健康、社会支持和自我形象。第2部分包括6个维度:雇佣工作、与孩子之间的关系、性生活、对医疗职业的感受、治疗情况和不孕 | 53(30+23) | 有 | |
| BARNARD等[ | MPCOSQ | 2007 | 多囊卵巢综合征患者 | 加拿大 | 6个维度:情绪障碍、多毛症、肥胖、痤疮、不孕、月经失调(也可分为月经症状及月经的可预见性) | 30 | 有 | |
| 普适性HRQoL量表 | ||||||||
| HUNT等[ | NHP | 1981 | 一般人群 | 英国 | 第1部分健康问卷包括6个维度:躯体活动、精力、疼痛、睡眠、社会关系、情感反应。第2部分个人生活包括7个方面:工作、照料家庭、社会生活、家庭生活、性生活、爱好与兴趣、度假 | 45 | 有 | |
| FERRANS等[ | QLI | 1985 | 一般人群或特定疾病人群 | 美国 | 4个维度a:健康和身体功能(health and functioning)、社会经济(socio-economic)、心理/精神(psychological/spiritual)、家庭(family)[ | 32 | 无 | |
| WARE等[ | SF-36 | 1992 | 一般人群 | 美国 | 8个维度:生理机能、生理职能、躯体疼痛、一般健康状况、精力、社会功能、情感职能、精神健康 | 36 | 有 | |
| The WHOQOL Group[ | WHOQOL-100 | 1994 | 一般人群 | WHO | 6个领域:生理、心理、独立性、社会关系、环境、精神/宗教信仰 | 100 | 有 | |
| MICHAEL[ | QOLI | 1994 | 一般人群 | 美国 | 16个维度a:健康(health)、自尊(self-esteem)、目标和价值观(goals and values)、经济(money)、工作(work)、娱乐(play)、学习(learning)、创造力(creativity)、帮助(helping)、爱(love)、朋友(friends)、孩子(children)、亲戚(relatives)、家庭(home)、邻里(neighbourhood)、社区(community) | 32 | 无 | |
| WARE等[ | SF-12 | 1996 | 一般人群 | 美国 | 8个维度:生理功能、身体角色限制、情感角色限制、心理健康、身体疼痛、总体健康、活力、社会功能 | 12 | 有 | |
| HICKEY等[ | SEIQoL-DW | 1996 | 一般人群 | 爱尔兰 | NR | NR | 无 | |
| KAPLAN等[ | QWB-SA | 1997 | 一般人群 | 美国 | 4个部分:移动、生理活动、社会活动和58个症状/复合健康问题 | 61 | 有 | |
| The WHOQOL Group[ | WHOQOL-BREF | 1998 | 一般人群 | WHO | 4个领域:生理、心理、社会关系、环境 | 26 | 有 | |
| 李凌江等[ | GQOLI-74 | 1999 | 一般人群 | 中国 | 4个维度:躯体功能、心理功能、社会功能、物质生活状态 | 74 | 有 | |
| 刘凤斌等[ | ChQOL | 2007 | 一般人群 | 中国 | 3个领域:形(身体机能)、神(意识思维)、情志(七情) | 50 | 有 | |
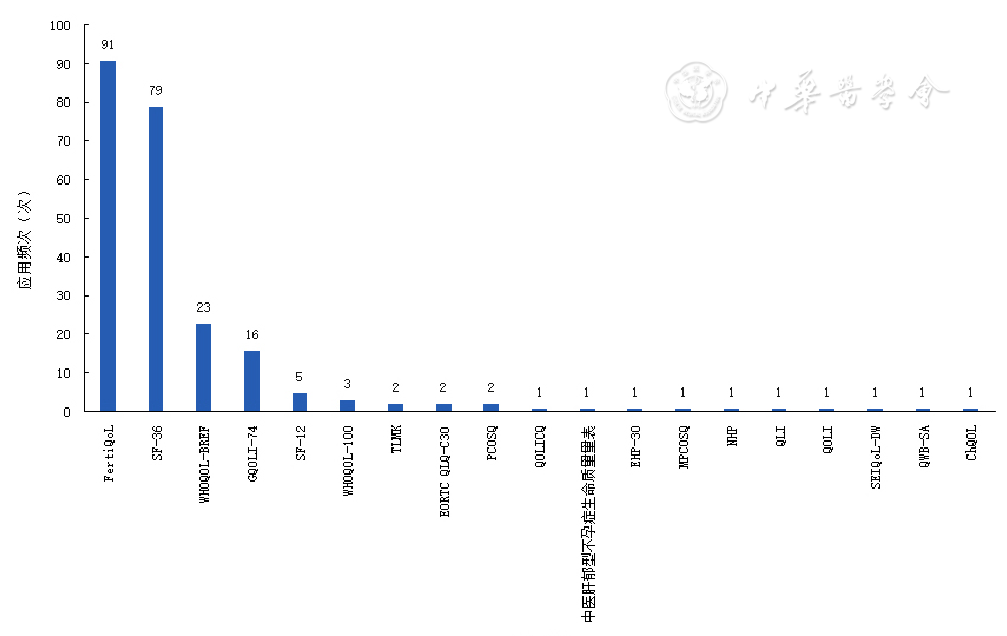
图2 不孕不育患者HRQoL量表的应用频次(截至2020-10-05)注:FertiQoL=生育生活质量量表,SF-36=健康调查简表,WHOQOL-BREF=世界卫生组织生存质量测定量表简表,GQOLI-74=生活质量综合评定问卷,SF-12=健康调查12条简表,WHOQOL-100=世界卫生组织生存质量测定量表,TLMK=Tübinger Lebensqualit?tsfragebogen für M?nner mit Kinderwunsch,EORTC QLQ-C30=癌症患者生命质量测定量表,PCOSQ=多囊卵巢综合征患者生活质量问卷,QOLICQ=Quality of Life in Infertile Couple Questionnaire,EHP-30=子宫内膜异位症健康相关生命质量量表,MPCOSQ=多囊卵巢综合征患者生活质量问卷修订版,NHP=诺丁汉健康量表,QLI=Quality of Life Index,QOLI=Quality of Life Inventory,SEIQoL-DW=Schedule for the Evaluation of Individual Quality of Life-Direct Weighting,QWB-SA=良好适应状态质量评估量表,ChQOL=中华生存质量量表
Figure 2 The application frequency of HRQoL instruments in infertility patients as of October 5,2020
| 量表(全)简称 | HRQoL量表设计 | 认知访谈研究 | HRQoL量表开发质量总体评价 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 清晰的测量结构a | 结构的来源清晰a | 清晰地描述所开发量表的目标人群a | 清晰地描述使用背景a | 量表开发在能够代表目标人群的样本中实施a | 概念引出 | 量表设计总体评价 | 总体设计要求:对能够代表目标人群的样本进行认知访谈 | 可理解性 | 全面性 | 认知访谈研究总体评价 | ||
| TLMK[ | 不合格 | - | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 有问题的 | 不合格 | 非常好 | 不合格 | 有问题的 | 不合格 | 不合格 |
| FertiQoL[ | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 非常好 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 |
| QOLICQ[ | 非常好 | 有问题的 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 合格 | 不合格 | 有问题的 | 不合格 | 不合格 |
| 中医肝郁型不孕症生命质量量表[ | 非常好 | 有问题的 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | - | - | - | - | 不合格 |
表2 不孕不育患者HRQoL特异性量表开发质量评价
Table 2 Evaluation of the development quality of infertility-specific HRQoL instruments
| 量表(全)简称 | HRQoL量表设计 | 认知访谈研究 | HRQoL量表开发质量总体评价 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 清晰的测量结构a | 结构的来源清晰a | 清晰地描述所开发量表的目标人群a | 清晰地描述使用背景a | 量表开发在能够代表目标人群的样本中实施a | 概念引出 | 量表设计总体评价 | 总体设计要求:对能够代表目标人群的样本进行认知访谈 | 可理解性 | 全面性 | 认知访谈研究总体评价 | ||
| TLMK[ | 不合格 | - | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 有问题的 | 不合格 | 非常好 | 不合格 | 有问题的 | 不合格 | 不合格 |
| FertiQoL[ | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 非常好 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 |
| QOLICQ[ | 非常好 | 有问题的 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 合格 | 不合格 | 有问题的 | 不合格 | 不合格 |
| 中医肝郁型不孕症生命质量量表[ | 非常好 | 有问题的 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | - | - | - | - | 不合格 |
| 项目 | TLMK[ | FertiQoL[ | QOLICQ[ | 中医肝郁型不孕症生命质量量表[ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 条目生成 | |||||
| 患者访谈/调查 | √ | √ | √ | - | |
| 专家意见 | √ | √ | - | √ | |
| 系统综述 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 基于其他量表 | √ | √ | - | √ | |
| 研究者经验 | - | - | - | - | |
| 条目筛选 | |||||
| 出现频率 | - | - | √ | √ | |
| 条目冗余 | √ | √ | - | - | |
| 专家意见 | - | √ | √ | √ | |
| 缺失数据 | - | - | - | - | |
| 因子分析 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
表3 不孕不育患者HRQoL特异性量表条目的形成与筛选
Table 3 Item generation and screening toward developing infertility-specific HRQoL instruments
| 项目 | TLMK[ | FertiQoL[ | QOLICQ[ | 中医肝郁型不孕症生命质量量表[ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 条目生成 | |||||
| 患者访谈/调查 | √ | √ | √ | - | |
| 专家意见 | √ | √ | - | √ | |
| 系统综述 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 基于其他量表 | √ | √ | - | √ | |
| 研究者经验 | - | - | - | - | |
| 条目筛选 | |||||
| 出现频率 | - | - | √ | √ | |
| 条目冗余 | √ | √ | - | - | |
| 专家意见 | - | √ | √ | √ | |
| 缺失数据 | - | - | - | - | |
| 因子分析 | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 量表(全)简称 | 内容效度 | 结构效度 | 内部一致性 | 重测信度 | 效标效度 | 建构效度 | 反应度/灵敏度 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相关性(询问患者) | 全面性(询问患者) | 可理解性(询问患者) | 相关性(询问专家) | 全面性(询问专家) | 聚合效度 | 区分效度 | ||||||
| TLMK[ | 合格 | 合格 | 合格 | - | - | 合格 | 非常好 | - | - | 非常好 | 非常好 | - |
| FertiQoL[ | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 合格 | 非常好 | - | - | - | - | 非常好 |
| QOLICQ[ | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 非常好 | 有问题的 | - | - | - | - |
| 中医肝郁型不孕症生命质量量表[ | - | - | - | 合格 | 合格 | 合格 | 非常好 | - | 非常好 | - | - | - |
表4 不孕不育患者HRQoL特异性量表开发研究的方法学质量评价
Table 4 Methodological quality of research on the development of infertility-specific HRQoL instruments
| 量表(全)简称 | 内容效度 | 结构效度 | 内部一致性 | 重测信度 | 效标效度 | 建构效度 | 反应度/灵敏度 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 相关性(询问患者) | 全面性(询问患者) | 可理解性(询问患者) | 相关性(询问专家) | 全面性(询问专家) | 聚合效度 | 区分效度 | ||||||
| TLMK[ | 合格 | 合格 | 合格 | - | - | 合格 | 非常好 | - | - | 非常好 | 非常好 | - |
| FertiQoL[ | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 非常好 | 合格 | 非常好 | - | - | - | - | 非常好 |
| QOLICQ[ | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 有问题的 | 非常好 | 有问题的 | - | - | - | - |
| 中医肝郁型不孕症生命质量量表[ | - | - | - | 合格 | 合格 | 合格 | 非常好 | - | 非常好 | - | - | - |
| 量表 | 结构效度 | 内部一致性 | 重测信度 | 效标效度 | 聚合效度/区分效度 | 反应度/灵敏度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLMK[ | ?a | + | 0 | 0 | + | 0 |
| FertiQoL[ | ?a | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | + |
| QOLICQ[ | ?a | + | ?b | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 中医肝郁型不孕症生命质量量表[ | ?a | + | 0 | + | 0 | 0 |
表5 不孕不育患者HRQoL特异性量表测量性能评价
Table 5 Quality of measurement properties of infertility-specific HRQoL instruments
| 量表 | 结构效度 | 内部一致性 | 重测信度 | 效标效度 | 聚合效度/区分效度 | 反应度/灵敏度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLMK[ | ?a | + | 0 | 0 | + | 0 |
| FertiQoL[ | ?a | + | 0 | 0 | 0 | + |
| QOLICQ[ | ?a | + | ?b | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 中医肝郁型不孕症生命质量量表[ | ?a | + | 0 | + | 0 | 0 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
新京报. 我国不孕不育率达12%~15%[N]. 新京报,2018-10-30(D03).
|
| [6] |
U.S. Food and Drug Administration(FDA). Guidance for industry patient-reported outcome measures:use in medical product development to support labeling claims[EB/OL]. [2022-05-30].
|
| [7] |
周星宇,冯淑娴,李雪兰,等. 40岁以上妇女行体外受精-胚胎移植治疗的结局分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2016,36(12):1632-1637. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2016.12.08.
|
| [8] |
季静娟,刘雨生,骆丽华,等. 两种促卵泡生长激素三种使用方法在体外受精-胚胎移植中疗效比较和经济学分析[J]. 生殖医学杂志,2012,21(4):329-333.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
单伟超,杨娜,单伟颖. 不孕症相关量表的研究现状[J]. 中国计划生育学杂志,2015,23(8):573-576.
|
| [12] |
杨娜,李青,单伟颖. 不孕症专用量表的研究现状[J]. 中国实用护理杂志,2015,31(2):150-153.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
COSMIN. Guideline for systematic reviews of outcome measurement instruments[EB/OL]. [2022-05-30].
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
王英. 中医肝郁型不孕症生命质量量表的研制[D]. 北京:北京中医药大学,2017.
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
The WHOQOL Group. The development of the WHO Quality of Life (the WHOQOL)assessment instrument[M]. Berlin:Springer-Verlag,1994:1-57.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
The WHOQOL Group. Development of the World Health Organization WHOQOL-BREF quality of life assessment[J]. Psychol Med,1998,28(3):551-558. DOI:10.1017/S0033291798006667.
|
| [38] |
李凌江,杨德森. 生活质量综合评定问卷(GQOLL-74)心理卫生评定量表手册(增订版)[M]. 北京:中国心理卫生杂志社,1999.
|
| [39] |
刘凤斌,赵利,郎建英,等. 中华生存质量量表的研制[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(52):10492-10495,10515. DOI:10.3321/j.issn/1673-8225.2007.52.027.
|
| [40] |
杨晓萍. 生育生活质量特异性量表的应用及信效度分析[D]. 广州:南方医科大学,2016.
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
高明,王永博,高转,等. 中文版FertiQoL量表信效度检验及其适用性研究[J]. 中国继续医学教育,2019,11(10):102-104. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-9308.2019.10.044.
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
林岳卿,张伟涛,方积乾. 项目反应理论在医学量表条目筛选中的应用[J]. 中国医药导报,2014,11(5):155-158.
|
| [53] |
|
| [1] | 田晨, 刘佳宁, 田金徽, 葛龙. 动态系统评价制作方法与流程[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(30): 3853-3860. |
| [2] | 韩笑, 李奇遇, 葛蒲, 范思园, 刘迪玥, 吴一波, 张清霜. 高血压患者行为生活方式对生命质量的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(26): 3248-3258. |
| [3] | 于文华, 李建国, 段文燕, 高旭妍, 李夏夏, 张子龙, 张丽, 马丽娜. 老年人功能受损评估量表在社区老年人中的信效度检验[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(24): 3000-3004. |
| [4] | 唐笑睿, 徐晶晶, 顾子君, 王清玉, 林征, 朱秋瑞, 雷阳. 糖尿病自我护理指数量表的汉化及信效度检验[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(21): 2643-2651. |
| [5] | 文永霞, 孙海, 陈小菊, 蔡婉静, 李淑妮, 郭洪花. 孕产妇分娩心理创伤评估工具的系统评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(20): 2555-2561. |
| [6] | 邓洁, 陶立元, 刘楠, 李俊, 闫温馨, 秦宸媛, 刘巧, 杜敏, 汪亚萍, 刘珏. 约克郡新冠康复量表改良版(C19-YRSm)的汉化及信效度检验研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(13): 1642-1648. |
| [7] | 王晓雨, 冯贞贞, 王军, 郭小川, 李建生. 急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者并发急性肾损伤危险因素的系统评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(12): 1527-1537. |
| [8] | 孙清, 吴玉霄, 崔立敏. 中国2型糖尿病患者肌少-骨质疏松症患病率的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(12): 1520-1526. |
| [9] | 黎芮彤, 岳玉川, 谷续洁, 熊玲玲. 儿童难治性肺炎支原体肺炎风险预测模型的系统评价[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(09): 1105-1114. |
| [10] | 范佳宁, 陈洁婷, 王梓琪, 范津赫, 井明霞. 中老年心血管代谢性疾病患者健康相关生命质量发展轨迹及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(08): 923-932. |
| [11] | 牛国辉, 谢加阳, 朱登纳, 崔博, 赵会玲, 王明梅, 冯欢欢, 张萌萌, 李停停. 维生素D治疗全面性发育迟缓患儿的临床疗效研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(03): 346-351. |
| [12] | 齐鸣瑞, 王文娟, 田利民. 中国西北地区老年高血压人群的健康相关生命质量研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(02): 199-207. |
| [13] | 张连芳, 郑雅斌, 林雪烽, 谢榕城, 马杰飞. 未成熟血小板比率联合其他指标对脓毒症严重程度及其预后的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(35): 4417-4425. |
| [14] | 郭佳, 曹春梅, 刘国纯, 郑满, 朱芮含, 龙伟. 不同运动方式对失眠患者睡眠影响效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(35): 4376-4387. |
| [15] | 冯天笑, 王旭, 卜寒梅, 秦晓宽, 肖想玉, 魏戌, 朱立国. 手法治疗中医骨伤科领域临床优势病种的证据图谱研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2024, 27(32): 4021-4028. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||





